Context
Recently, Global Hepatitis Report 2024 was released by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
Global Hepatitis Report 2024: Key Highlights
- As per the Global Hepatitis Report 2024, India has one of the highest viral hepatitis burden (causing liver inflammation damage and may lead to liver cancer).
- Infection rates: There are around 304 million people living with Hepatitis B and C across the world as per the report.
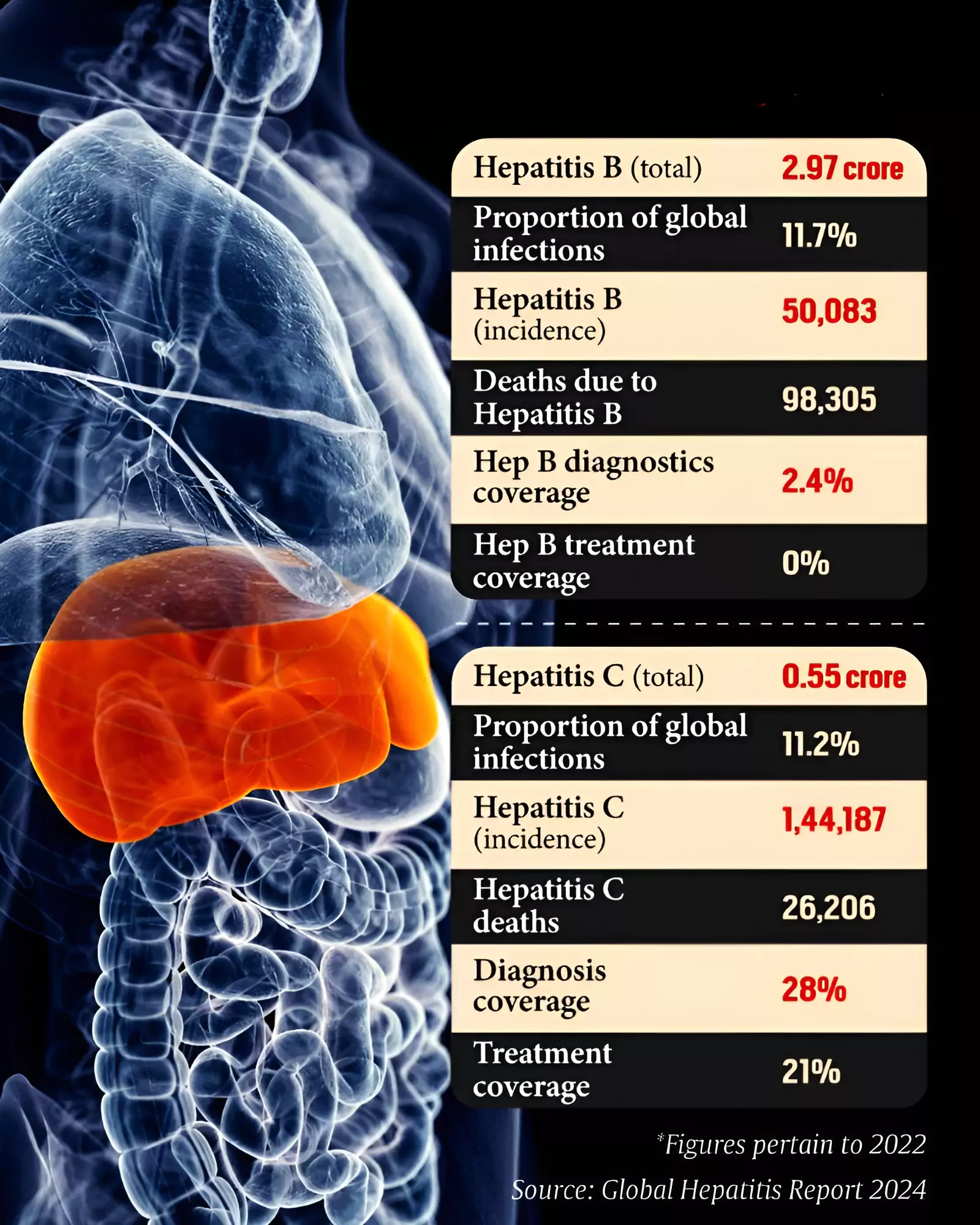 Largest killer: A global death rate of 1.3 million annually, viral hepatitis with tuberculosis were the second biggest infectious killer in 2022, behind only the deaths caused by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Largest killer: A global death rate of 1.3 million annually, viral hepatitis with tuberculosis were the second biggest infectious killer in 2022, behind only the deaths caused by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is Viral Hepatitis?
- Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. It causes liver diseases including acute and chronic infections, liver failure, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
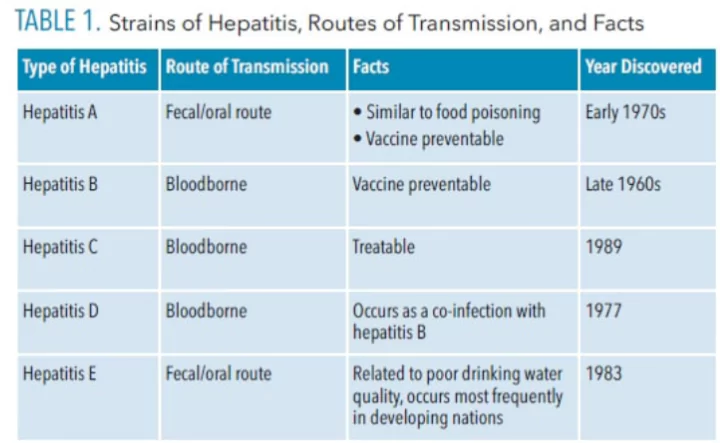
- Mode of transmission: By infectious sources (virus and food and water contamination and sexual transmission) and non – infectious source like (heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions)
- Hepatitis B: The infection is mainly driven by transmission from mother to child with almost 90 per cent of transmission happening from the mother to the child .
- Main strains of Hepatitis: There are 5 main strains of Hepatitis ie. A, B, C, D and E.
- They all cause liver disease, they differ in important ways including modes of transmission, severity of the illness, geographical distribution and prevention methods
- Symptoms:
 Hepatitis B: It is known to cause acute infection with nausea, vomitting and yellowing of the eye and skin for several weeks.
Hepatitis B: It is known to cause acute infection with nausea, vomitting and yellowing of the eye and skin for several weeks.- Chronic Hepatitis: It can cause life-long liver disease especially when children get it and can lead to scarring of the liver called cirrhosis and increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Hepatitis C: Symptoms occur two to 12 weeks after exposure which include, yellow skin or eyes, loss of appetite, nausea, stomach ache, fever, dark urine, light-coloured stool, joint pain and exhaustion.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: The report says that only 2.4 per cent of the Hepatitis B cases were diagnosed and 0 per cent received treatment. For Hepatitis C, 28 per cent were being diagnosed and 21 per cent received treatment.
- Hepatitis B can be prevented through vaccination and there is a need to ensure that all newborns receive complete vaccination and all adults should be offered, who were born before the vaccine was included in the national programme.
- Hepatitis C is curable with medicines.
- Vaccination: Hepatitis B vaccine is offered to children under the Universal Immunisation Programme in India whereas, the government’s National viral hepatitis control programme also offers the vaccine to high-risk adults such as healthcare workers as well.
- Treatment for both Hepatitis B and C is available under the programme.
- But the reach is limited. People have not been utilising the free diagnostics and treatment offered under the programme.
Also Read: Cancer Prevalence In India
![]() 11 Apr 2024
11 Apr 2024
 Largest killer: A global death rate of 1.3 million annually, viral hepatitis with tuberculosis were the second biggest infectious killer in 2022, behind only the deaths caused by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Largest killer: A global death rate of 1.3 million annually, viral hepatitis with tuberculosis were the second biggest infectious killer in 2022, behind only the deaths caused by the Covid-19 pandemic.  Hepatitis B: It is known to cause acute infection with nausea, vomitting and yellowing of the eye and skin for several weeks.
Hepatitis B: It is known to cause acute infection with nausea, vomitting and yellowing of the eye and skin for several weeks.