Heating and cooling of the atmosphere occur through four main processes: conduction, convection, advection, and terrestrial radiation. These processes involve the transfer of heat through molecular movement, fluid motion, horizontal air movement, and radiation from the Earth’s surface to the atmosphere.
Heating and Cooling Processes in the Atmosphere
Source of Heat
- The Sun: The main source of heat for Earth and its atmosphere is predominantly the energy received from the sun.
- Secondary Sources: While there are minor contributions from Earth’s cooling, hot springs, and volcanic eruptions, these sources are limited in their impact due to their localized occurrence.
- Solar energy plays a pivotal role in distributing heat and energy across the globe, despite various factors influencing its distribution.
Methods of Heating and Cooling the Atmosphere
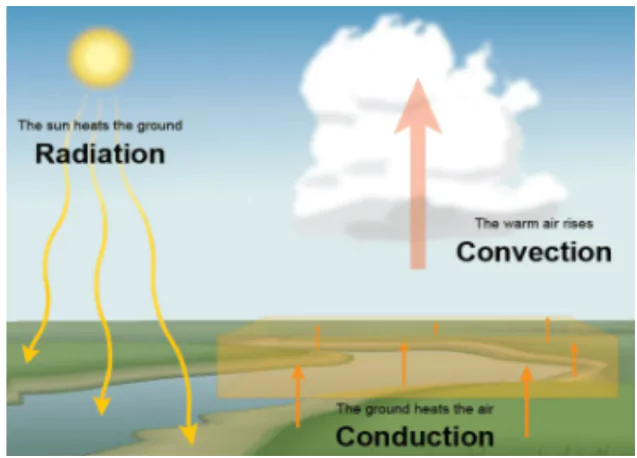
- Conduction: Process in which heat flows from objects with higher temperatures to objects with lower temperatures through molecular movement.
- It primarily heats the atmosphere’s lower layers.
- Air is a poor conductor of heat, resulting in a slow transfer of heat in a mass of air.
- Conduction heats a thin layer close to the Earth’s surface, but its significance is limited.
- As air molecules are not densely packed, conduction has a minor role in heating the atmosphere.
- Once heated, Air becomes lighter and less dense, moving upward.
- Convection: Transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas) between areas of different temperatures.
- Earth’s surface is heated by incoming solar energy.
- Heating of the surface warms the air in contact with it.
- Warmed air becomes less dense and rises upward.
- Rising air creates convection, moving large quantities of air upward.
- Expansion of air at ground level creates low pressure, causing cooler air nearby to move in to fill the gap.
- Heat is transferred upward by vertically moving air.
- Convection occurs locally and on larger regional scales, illustrated by phenomena like Hadley, Ferrel, and Polar cells.
- Convection transfers heat energy from the sun to the surface and from the surface to the atmosphere.
- It is limited to the troposphere.
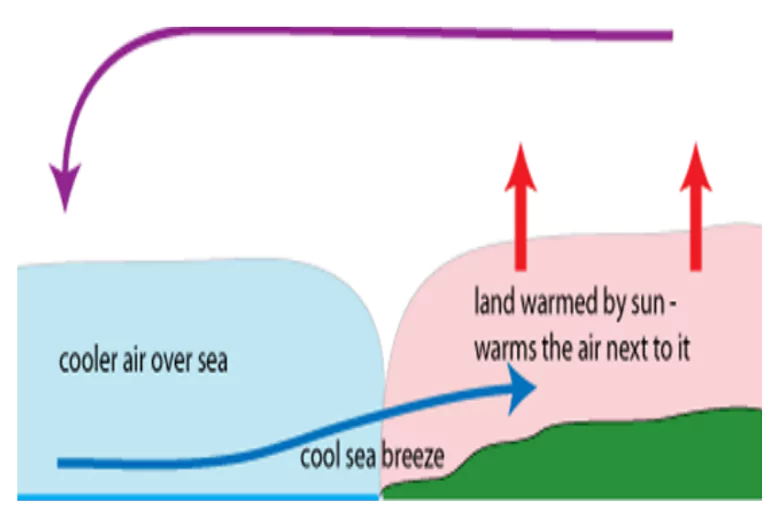 Advection: Advection refers to the horizontal transfer of substances from one place to another.
Advection: Advection refers to the horizontal transfer of substances from one place to another.
- In middle latitudes, most diurnal (day & night) variations in daily weather and in tropical regions effects of loo are the result of the advection process.
- Differences in atmospheric pressure at local, regional, and global levels cause continuous movement of gases.
- Local Advection: can be observed in phenomena like monsoon winds.
- Regional Advection: is exemplified by the planetary permanent wind system.
- Both local and regional advection transfer heat from one area to another.
- Hydrospheric Advection: involves movement of water, such as ocean currents.
- Ocean currents redistribute energy from high to low concentration zones.
- Ocean currents are also influenced by atmospheric advection movements.
- Terrestrial Radiation: Heat transfer from one body to another without actual contact or movement. Terrestrial radiation is a significant method of atmospheric heating.
- Absorption and Emission by Earth: Earth absorbs shortwave radiation (UV and Visible portion of electromagnetic spectrum) warming the surface;
- It emits long wave radiation (Infrared rays) which heats up the atmosphere. [UPSC 2023].
- Terrestrial radiation occurs continuously, maintaining a static temperature on Earth.
- Earth’s Temperature Regulation: Greenhouse gases and water vapor trap outgoing longwave radiation, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
- Cloud Cover: reduces incoming radiation and traps outgoing radiation, behaving similarly to greenhouse gases.
- Without the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average temperature would plummet to minus 170°C.
- Energy Transfer: occurs from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration, leading to heating and cooling processes at different levels.
- Plank’s law states that the hotter body radiates more energy and short wavelength radiation.
Conclusion
- Earth’s atmosphere is heated and cooled by various processes primarily driven by energy from the sun. Solar energy plays a vital role in distributing heat globally, despite factors affecting its distribution.
- Processes like conduction, convection, advection, and terrestrial radiation transfer heat within the atmosphere and between the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
- These processes help maintain Earth’s temperature, with mechanisms such as the greenhouse effect and cloud cover playing essential roles and also governing the temperature and climate patterns observed on Earth.
![]() April 29, 2024
April 29, 2024
![]() 3654
3654
![]() 0
0

 Advection: Advection refers to the horizontal transfer of substances from one place to another.
Advection: Advection refers to the horizontal transfer of substances from one place to another.