Introduction
The grasslands in the westerly wind belt, known as Steppe, Prairies, Pampas, and more, experience seasonal variations with warm summers and cold winters. With low rainfall, they promote grass growth, making them ideal for livestock rearing. These regions, famous for extensive wheat cultivation, are often called the ‘granaries of the world‘, supporting nomadic herding and pastoral farming.
Exploring Steppe: Climate, Vegetation, and Economic Activities
Distribution
- Lies in the westerly wind belt but they are so remote from maritime influence that the grasslands are practically treeless (between 40° and 55° N and S of the equator).
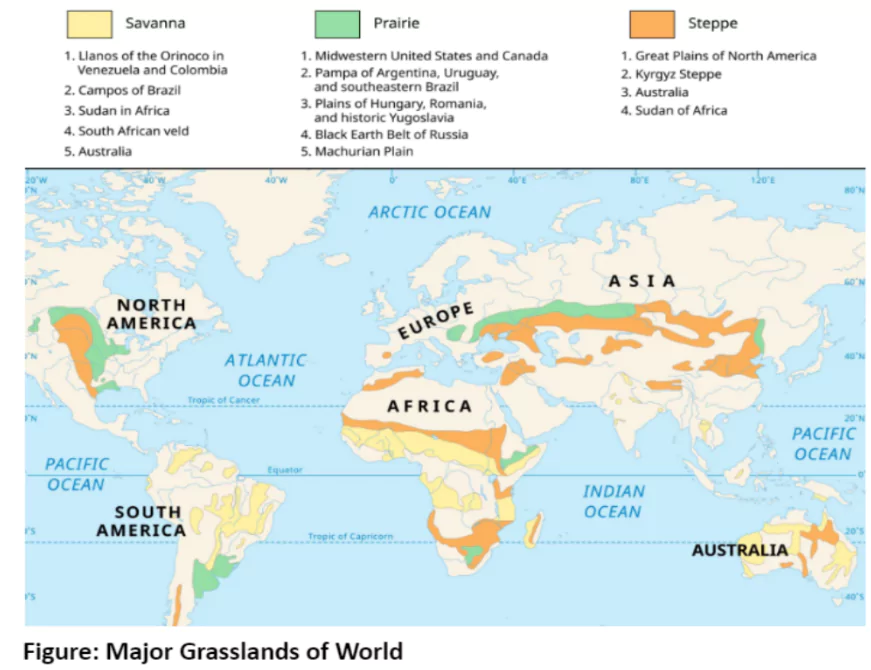
- They are known as
- Steppe: Eurasia, and Pustaz: Hungary,
- Prairies: North America,
- Pampas: Argentina and Uruguay,
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
-
- Bush-Veld: North South Africa and High-Veld: Southern South Africa,
- Downs: Australia and Canterbury: New Zealand.
Climate
- Temperature: Seasonal variations with warm to hot summers (often exceeding 30°C) and cold winters.
- Extremes of temperature in the northern hemisphere, a steppe type of climate than in the southern hemisphere.
- Southern hemisphere: is never severe (maritime influence) and winters are mild.
- Winters are so mild that temperatures range from 1°C to 13°C.
- Freezing temperatures in mid-winter (July) are rare.
- Example: Pretoria has a mid-winter (July) mean temperature of 11°C, Johannesburg, Buenos Aires, and Mildura, also have mild winters.
- Oceans play a moderating role in southern hemisphere climates.
- Annual Temperature Range:
- The annual temperature range is significant due to continentality.
- Eurasian Steppes experience cold winters with snow cover for several months.
- There’s a notable difference in annual temperature range between northern and southern hemispheres due to continentality.
- Example: Winnipeg’s range is °C, three times greater than Pretoria’s range at -3 °C.
- Precipitation: low annual rainfall (25-75 cm); the dry season is particularly pronounced in temperate grasslands adjoining desert;
- Summer rainfall (Maximum) from conventional sources when continental interiors are heated.
- Winter rainfall (lesser) by occasional depressions of the Westerlies.
- Annual precipitation: generally light, averaging around 20 inches.
- Winter months receive minimal precipitation, mostly in the form of snow.
- Most rain falls during summer, influenced by conventional sources.
- Maritime Influence in Southern Hemisphere Steppe Climates
- In the southern hemisphere, greater rainfall because of warm ocean currents Annual precipitation exceeds 50 cm due to warm ocean currents.
- Droughts during the winter months (June to August) impact the sheep-rearing industry.
- Temperate grasslands adjacent to deserts, like in Australia, face pronounced dry seasons.
- In the southern hemisphere, Johannesburg and Buenos Aires, receive moderate rainfall.
- Local Winds and Their Impact
- Chinook wind in the eastern slopes of the Rockies is similar to Fohn wind in Switzerland.
- Chinook winds bring warm, dry air to melting snow-covered pastures.
- Rapid temperature increases, up to 5°C in 20 minutes, accelerate agricultural activities.
- Farmers welcome Chinooks for mild winters and enhanced grazing conditions.
Vegetation
- Steppe Vegetation: It refers to sparse vegetation in sub-arid lands of continental Eurasia. Modern interpretations extend the term to temperate grasslands worldwide.
- Steppe grasslands include regions like the Steppes, Prairies, Pampas, Veld, and Downs.
- Grasslands: are practically treeless, and grass is nutritious, thus promoting livestock rearing in the region.
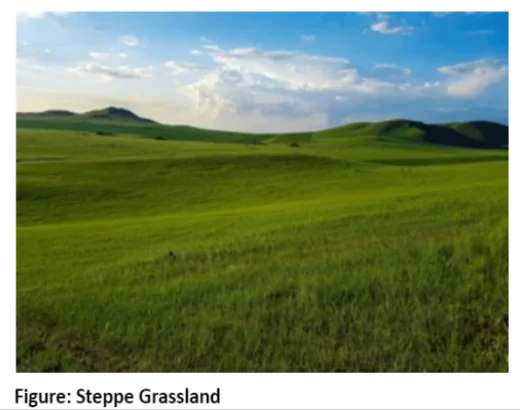 Grasses are not only shorter but also wiry and sparse. In arid areas like Asia’s continental interiors, wiry grasses favour ranching over arable farming.
Grasses are not only shorter but also wiry and sparse. In arid areas like Asia’s continental interiors, wiry grasses favour ranching over arable farming.- Ranching in Short Grasslands: Short grasslands are less suitable for arable farming and often used for ranching, like the High Plains of the USA.
- Seasonal Changes in the Grasses
- Appearance of temperate grasslands changes throughout the seasons.
- Summer heat and evaporation scorch the grass, turning it yellow and brown.
- Autumn sees withering and dormancy as winter approaches, with snow cover but not of great depth.
- With the next spring, the cycle repeats, and the steppe comes back to life.
- Scarcity of Trees
- Limited Growth: Scanty rainfall, long droughts, and severe winters limit tree growth in the steppes.
- Rolling Plains: vast stretches of grass, interrupted only by watercourses where low willows, poplars, or alders grow.
- Wooded Steppes: Poleward regions with increased precipitation may transition into wooded steppes, gradually introducing conifers.
Economic activity
- Nomadic Hunting:
- Tribes: Grazing in major grasslands has nearly vanished, impacting wandering tribes such as the Kirghiz, Kazakhs, and Kalmuk.
- These nomads once roamed vast distances, like Bedouins, seeking grass and water for their livestock,like cattle, sheep, goats, and horses.
- Extensive Mechanized Wheat Cultivation,
- Ideal Condition: With cool springs and light showers during ripening, grains swell for a good yield, Temperate grasslands provide an ideal setting for extensive wheat farming.
- The flat terrain makes ploughing and harvesting easy with mechanical tools
- Example: Combine harvesters.
- Due to extensive, mechanised wheat cultivation, they are known as the ‘granaries of the world’.
- Less Yeild: However, this method often yields less compared to intensive farming.
- Winter Wheat: It dominates in colder regions, while spring wheat suits milder climates, like the Canadian Prairies.
- Advancements in plant breeding allow for cold-resistant varieties, expanding wheat cultivation northward into regions like Canada’s Peace River area.
- Pastoral Farming:
 Ideal Conditions for Animal Farming: Temperate grasslands proved ideal for animal farming. Cattle, sheep, pigs, and horses were introduced, thriving in these conditions.
Ideal Conditions for Animal Farming: Temperate grasslands proved ideal for animal farming. Cattle, sheep, pigs, and horses were introduced, thriving in these conditions. - Export Hubs: Grasslands became major exporters of beef, mutton, wool, and hides.
- Improving Livestock in the Pampas: Tuft grass was replaced by sown alfalfa, and in regions like the Pampas, imported pedigree stock from Europe improved livestock.
- The Pampas: A global beef exporter, establishing large ranches linked to meat-packing factories in coastal ports by extensive road and rail networks.
- Wool Exporter: Similar growth occurred in regions like the Great Plains of the USA and Australia, which became the world’s leading wool exporter.
- Eurasian Steppes: there’s a growing focus on animal ranching for meat production.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
- Temperate grasslands stand as vital contributors to global agriculture, characterised by their unique climatic patterns and rich vegetation.
- From nomadic herding to extensive wheat cultivation and pastoral farming, these regions have adapted to human activity over millennia.
- Advancements in agriculture have enabled these grasslands to remain significant players in the world economy, exporting essential commodities and sustaining livelihoods across continents.
![]() May 1, 2024
May 1, 2024
![]() 3565
3565
![]() 0
0

 Grasses are not only shorter but also wiry and sparse. In arid areas like Asia’s continental interiors, wiry grasses favour ranching over arable farming.
Grasses are not only shorter but also wiry and sparse. In arid areas like Asia’s continental interiors, wiry grasses favour ranching over arable farming. Ideal Conditions for Animal Farming: Temperate grasslands proved ideal for animal farming. Cattle, sheep, pigs, and horses were introduced, thriving in these conditions.
Ideal Conditions for Animal Farming: Temperate grasslands proved ideal for animal farming. Cattle, sheep, pigs, and horses were introduced, thriving in these conditions.