The crop of Maize has also undergone a Green Revolution in India with its annual output increasing more than 3 times between 1999-2000 and 2023-24, from 11.5 to over 35 million tonnes (mt), with average per-hectare yields also rising from 1.8 to 3.3 tonnes.
The Green Revolution in Maize
- Private Sector Led: The Green Revolution in maize has been, and continues to be, a private sector-led one with Private sector-bred hybrids accounting for more than 80% of the 10 million hectares-plus area planted to maize in India.
- First Generation Seeds: Their higher yields, from crossing two genetically dissimilar inbred plants, is however limited to the first generation only ie. the farmers cannot harvest the same yields if they save the grains from these and reuse as seed.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Maize
- Scientific name: Zea mays L.
- Native: Central America and Mexico
- Maize belongs to the tribe Maydeae of the grass family Poaceae and is widely cultivated as cereal grain
- Queen of Cereals: Maize is known as the queen of cereals because it has the highest genetic yield potential among the cereals.
- Types: It has many types like, normal yellow/ white grain, sweet corn, baby corn, popcorn, waxy corn, high amylase corn, high oil corn, quality protein maize, etc.
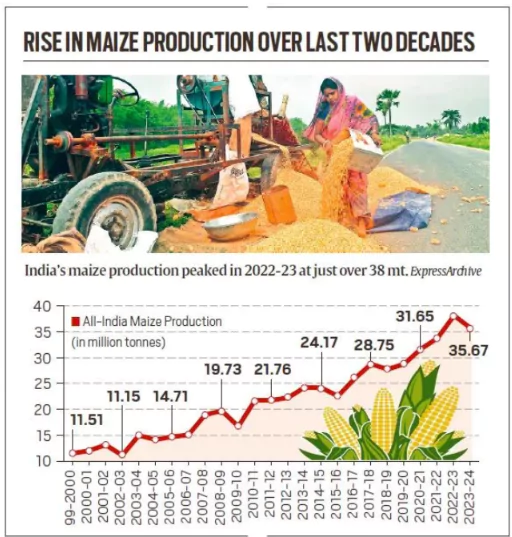 Maize Production In India:
Maize Production In India:
- India is the fifth largest producer of Maize in 2020 as per FAO data and India’s share in world production accounted for 2.59 per cent.
- Among cereals maize has witnessed highest growth rate in terms of area and productivity
- Productivity: Since 2010 maize productivity in India has increased at over 50 kg/ha/year, the highest among food crops.
- Area: It is principally grown in two seasons, rainy (kharif) season representing around 83% of maize area in India, and winter (rabi) corresponding to 17% maize area.
- Total Production: In financial year 2023, India’s production volume of maize was over 38 million metric tons which accounts for a close to around 10 percent of total food grain production in the country
- State-wise Share: The states of Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka have the highest area under production (15% each) followed by Maharashtra (10%), Rajasthan (9%), Uttar Pradesh (8%).
- Andhra Pradesh has the highest state productivity. Some districts like Krishna, West Godavari etc. records as high as 12 t/ha productivity.
- Exports: The country has exported 3,453,680.58 MT of maize to the world for the in 2022-23 with major export destinations being, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Nepal, Malaysia and Sri Lanka.
- Usage:
- Staple Food Consumption: Maize in the form of Corn, Corn Flour etc is a source of Food for humans, but hardly a fifth of India’s maize production is used for direct human consumption.
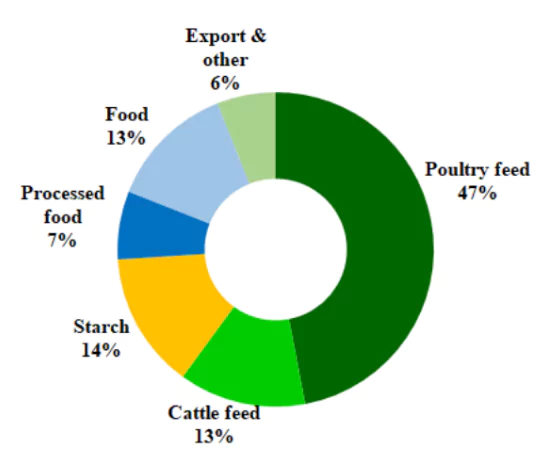 Feed Stock: An estimated 60% goes as feed for poultry birds and livestock.
Feed Stock: An estimated 60% goes as feed for poultry birds and livestock.
- Maize supplies carbohydrates, the principal energy source for poultry and livestock. Broiler feed for chickens itself contains 55-65% maize by weight, with these at 50-60% for egg-layer feed, and 15-20% in cattle feed.
- Industrial use: 14-15% of India’s maize utilisation is for industrial purposes. Maize grains have 68-72% starch, and 1-3% of other simple carbohydrates (sucrose, glucose and fructose). Starch has applications in the textile, paper, pharmaceutical, food and beverage industries.
- Feedstock for Ethanol: Maize is emerging as a feedstock for ethanol that is used for blending with petrol. Distilleries are considering the use of Maize to produce Ethanol in the off-season (May-October), when cane isn’t available.
Recent Developments in Maize Breeding Research
- Pusa Waxy Maize Hybrid-1: Indian Agriculture Research Institute (IARI) has bred India’s first “waxy” maize hybrid with high amylopectin starch content (at 93.9%) making it better suited for ethanol production.
- The starch in maize is a mixture of two polymers, comprising glucose molecules bonded together in a straight chain (amylose) and in branched form (amylopectin).
- Normal maize starch has 30% amylose and 70% amylopectin while the starch from IARI’s waxy maize hybrid (AQWH-4) has 93.9% amylopectin which will impart softness in the grain and would affect the starch recovery at 68-70% recovery and fermentation rates.
- Productivity: It has an average grain yield of 7.3 tonnes per hectare and potential of 8.8 tonnes.
- The higher recoverable starch from waxy maize should give 415-420 litres of Ethanol from one tonne of Maize grain, rising up from 390 litres of ethanol from one tonne of normal maize grain.
- Potential for Commercial Cultivation: The IARI-developed hybrid has been identified for release under the All-India Coordinated Research Project on Maize with future plans to move the Central Variety Release Committee, whose approval will pave the way for the hybrid to be officially released and notified for commercial cultivation.
- Field Trails: IARI has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Uttar Pradesh Distillers’ Association for field trials of its waxy maize hybrid
- Maize Doubled Haploid (DH) Facility: CIMMYT has opened a maize doubled haploid (DH) facility at Kunigal in Karnataka in partnership with the University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore producing 100% homozygous (i.e. having two identical copies of a single gene), and genetically pure inbred lines of maize that can be used as parents for further crossing and breeding of hybrids.
- Advantage: The Double Haploid technology enables production of completely uniform lines after just two cropping cycles and speeds up inbred line development, thereby improving the efficiency of maize breeding and shortening the process.
- Knowledge sharing: CIMMYT is sharing its improved inbred lines with both public sector institutions and 25-odd private seed companies including Mahyco, Shriram Bioseed, Advanta Seeds, Nuziveedu Seeds, Kaveri Seeds, Mahindra Agri Solutions, Rasi Seeds and Indo-American Hybrid Seeds.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Green Revolution
- The Green Revolution is the term given to the use of high-yielding varieties (HYVs) of wheat and rice particularly during the 1960s to increase food crop production, especially in India.
- Institutions and Leadership: The new seed varieties were bred by institutions such as the Mexico-based CIMMYT (International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center) and the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) in New Delhi, under the leadership of scientists like Norman Borlaug and M S Swaminathan.
- Funding: It was a government-driven agricultural modernization programme, majorly funded by international agencies, supplied farmers with high-yielding variety (HYV) or hybrid seeds, pesticides, fertilisers, and other inputs, specifically in areas with assured irrigation, mainly targeting wheat and rice cultivation.
- Unequal Beneficiaries:
- Regional Inequality: The Green Revolution was not a pan India phenomenon and predominantly benefited regions like Punjab, western U.P., coastal Andhra Pradesh, and parts of Tamil Nadu.
- Income Inequality: It mainly benefited medium and large farmers due to the high costs associated with the new inputs, further widening the economic disparity within rural communities.
- Why was the green revolution prevalent in certain areas?
-
- Assured Irrigation Support: Punjab and Haryana has a well developed water canals and dam network (Bhakra Nangal Dam and Indira Gandhi Canal) which provides irrigation support to the HYV seed crop.
- Economically viable land size: The average size of the farm land per capita was/is higher in the region like punjab and krishna- Godavari Delta which makes the application of chemical fertilizers and mechanical machinery more viable economically.
- Infrastructure location: Punjab and adjoining regions are located near Delhi where most of the research and scientific infrastructure was located during the 60s which benefitted them in terms of easier access to markets, research and testing labs etc.
- Enterprising Farmers: Green Revolution was a success in areas where large or middle farm owners lived who had the monetary bandwidth to invest in machines; seeds; fertilizers etc.
|
![]() 19 Jul 2024
19 Jul 2024
 Maize Production In India:
Maize Production In India:
 Feed Stock: An estimated 60% goes as feed for poultry birds and livestock.
Feed Stock: An estimated 60% goes as feed for poultry birds and livestock.