A large number of people from the Bhil tribe recently gathered at a rally in Rajasthan and raised the “long due” demand for an independent ‘Bhil state’.
| Relevancy for Prelims: About Bhil Pradesh, Adivasi Jallianwala, Govind Guru, Need, Significance and Challenges of Creation of Small States in India, etc.
Relevancy for Mains: Bhil Pradesh, Creation of Small States in India- Need, Significance, Challenges, and Consequences, etc. |
About Bhil Pradesh
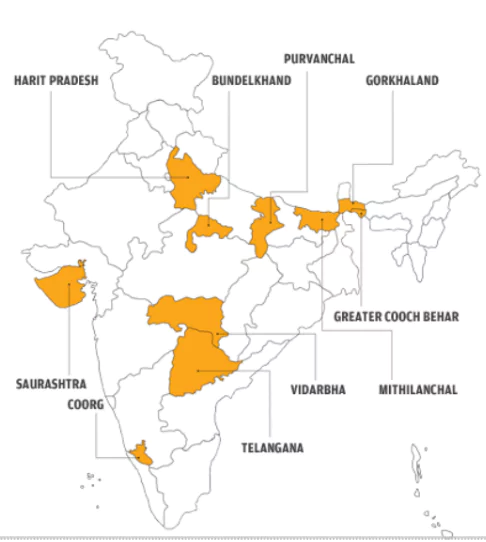
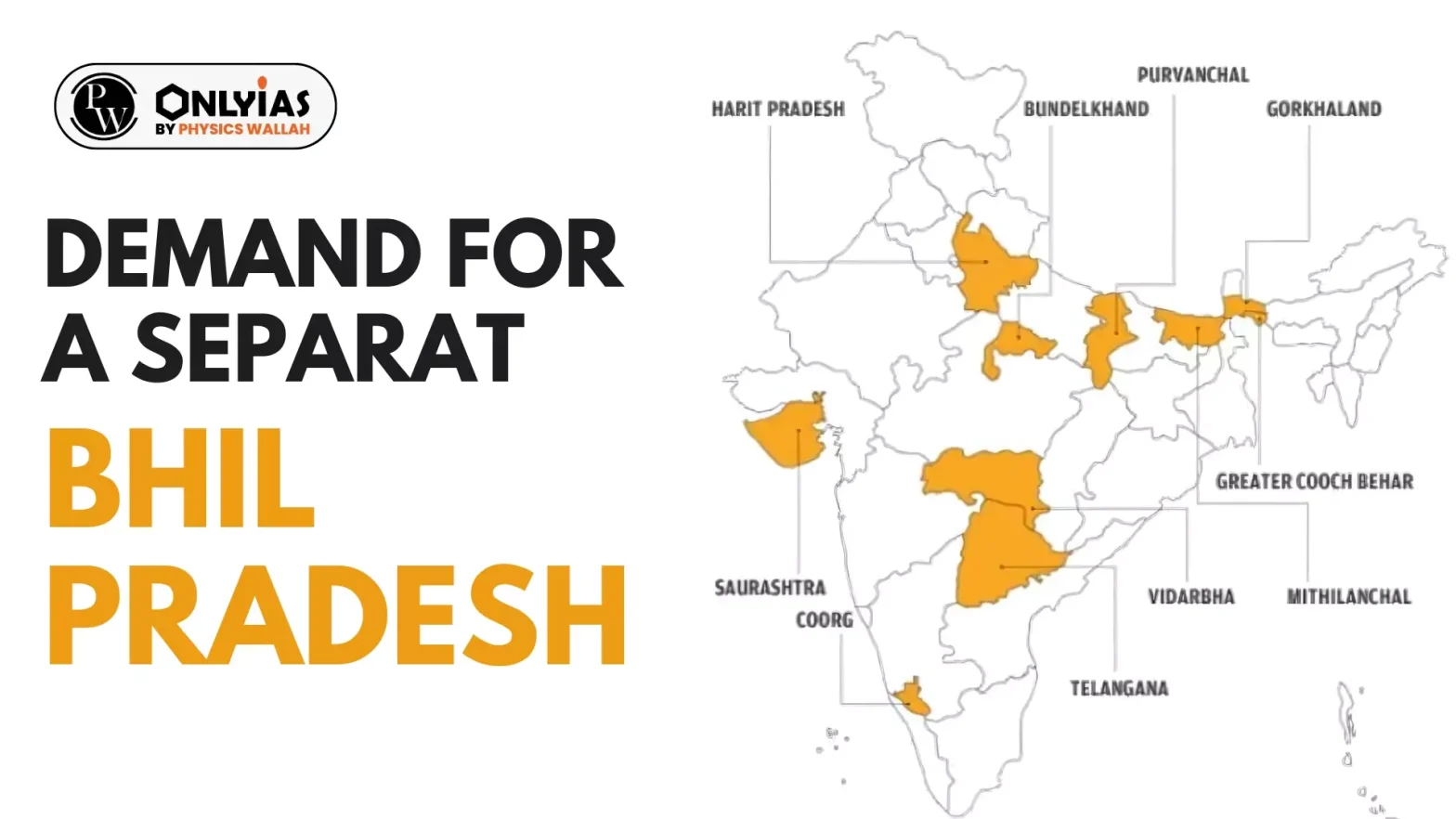
- Demanding Regions: The Bhil community has been demanding that 49 districts be carved out of the four states comprising parts of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Maharashtra, to establish Bhil Pradesh.
- Historical Background: Bhil social reformer and spiritual leader Govind Guru first raised the demand for a separate state for tribals back in 1913.
- This was after the Mangarh massacre, which took place six years before Jallianwalla Bagh and is sometimes referred to as the “Adivasi Jallianwala”.
- It saw hundreds of Bhil tribals being killed by British forces on November 17, 1913, in the hills of Mangarh on the Rajasthan-Gujarat border.
- The sacrifice of the tribals in 1913 wasn’t just for the Bhakti movement but for the demand of Bhil Pradesh.”
- Post-Independence, the demand for Bhil Pradesh was raised repeatedly.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Why do the tribals want a Separate State?
- Earlier, a Single Entity: Earlier, the Dungarpur, Banswara, Udaipur region in Rajasthan and Gujarat, MP, etc. was part of a single entity. But post-Independence, the tribal majority regions were divided.
- Delay on Implementation: Several Union governments brought various “laws, benefits, schemes, and committee reports” on tribals over time, but went slow on their execution and implementation.
- Example: The Provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 law was enacted in 1996. However,the Rajasthan government adopted it in 1999, and came out with its Rules in 2011.
- But even in a few villages, people don’t even know about this law. Even the legislatures and executives do not have proper knowledge about the law.”
- The Provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996, a law meant to decentralise governance and empower gram sabhas in tribal areas.
Arguments in Creation of Small states in India
- Better Governance and Administration: Smaller states are easier to manage and administer, as they have a smaller population and geographical area. This can lead to better public services and development.
- More Equitable Distribution of Resources: Smaller states can ensure that resources are more equitably distributed among different regions and communities. This is because there is less competition for resources and the government is more accountable to the people.
- Increased Participation in Democracy: Smaller states can encourage greater participation in democracy, as people feel more connected to their government and have a greater say in decision-making.
- Cultural and Linguistic Preservation: Smaller states can help to preserve and promote distinct cultures and languages. This is because people are more likely to feel a sense of identity and belonging to a smaller state.
Arguments against Creation of Small States in India
- Increased Administrative Costs: The creation of new states can lead to increased administrative costs, as new government institutions need to be set up and maintained.
- Inter-State Disputes: Smaller states can lead to an increase in inter-state disputes, as there is more competition for resources and territory.
- Loss of National Unity: The creation of new states can lead to a weakening of national unity, as people may identify more with their state than with the country as a whole.
- Regional Imbalances: Smaller states may not be able to generate enough resources to sustain themselves, which can lead to regional imbalances.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Conclusion
The creation of new states is a double-edged sword. While it holds significant potential, it also comes with multiple challenges. An informed, sensitive, and participatory approach, keeping the larger national interest in mind, is crucial when taking such a significant step. There is a need to empower local governance and determine the demands of state creation on a case to case basis.
![]() 20 Jul 2024
20 Jul 2024