Context:
Recently, the intergovernmental negotiating committee (INC) of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) released a zero draft to end plastic pollution.
More on News:
- The text of the draft reflects the objective and mandate of UNEA resolution 5/14.The resolution requested INC to develop the instrument that addresses the full life cycle of plastic.
- Objectives Stated under Zero Draft:
- End plastic pollution, including in the marine environment.
- Protect human health and the environment.
- A comprehensive approach to address the full life cycle of plastic.
- Managing the utilization of plastics and plastic waste, while contributing to the achievement of sustainable development.
- Elimination of particularly harmful types of plastic and chemicals, problematic, avoidable, and short-lived plastics.
- Reduction in the production of primary plastic.
Significance:
- Global Coordination: It would facilitate global cooperation, ensuring that countries work together to address the problem of rising volume of plastic consumption collectively.
- According to the Peak Plastics: Bending the Consumption Curve report, the volume of plastic consumed across the G20 countries will grow to 451 million tonnes by 2050.
- Uniform Standards: It establishes uniform standards and guidelines for the management, reduction, and elimination of plastic pollution.
- For example, it provides elements for national plans which will ensure uniformity in standards for different countries.
- Resource Allocation: Facilitates financial and technological assistance to less-developed countries, helping them address the issue.
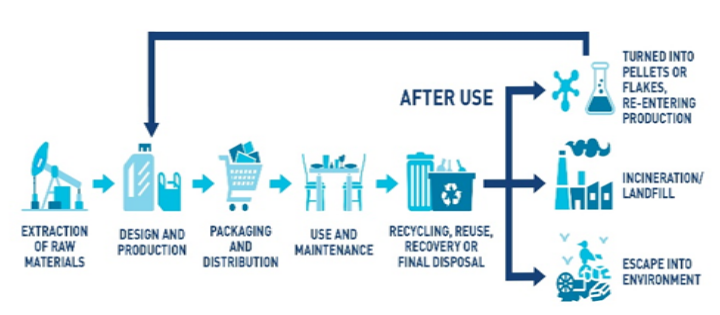
Challenges:
- Chemicals and Polymers of Concern: More than 13,000 chemicals are used in plastics, of which, around 3,200 are classified as hazardous viz. bisphenols, specific flame retardants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons etc.
- Only 4% of these chemicals are regulated globally.Problematic and Avoidable Plastic Products: Use of plastic products including short-lived and single-use plastic (SUP) products and intentionally added microplastics pose grave environmental concerns.
- SUPs like plastic straws, plastic water bottles, plastic coffee pod etc. have a life cycle of more than 200 years.
- Microplastic Contamination: Tiny plastic particles are a growing concern in the environment, potentially affecting both human health and ecosystems.
- For example: In India, microplastics have been found in rivers, soils, and even in some food items, raising concerns about their impact on the food chain.
- Informal Recycling Sector: They play a crucial role in collecting and recycling plastic waste, however, they often operate under unregulated conditions and face health hazards.
- For example: Informal waste pickers are exposed to health risks due to poor working conditions and limited access to safety equipment.
Initiatives to Address Plastic Pollution:
- Regulations by the MoEFCC: Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022 stipulating mandatory targets on EPR, recycling of plastic packaging waste, reuse of rigid plastic packaging and use of recycled plastic content.
- Regulations by the MoHUA: Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U) 2.0, efforts towards source segregation, collection, transportation, and processing of plastic waste.
- Other Measures: ‘Swachh Survekshan’ and ‘Star Rating Protocol’.
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Clean Seas Campaign and Global Partnership on Marine Litter: This campaign encourages governments, businesses, and individuals to take action to reduce plastic waste in the oceans.
Way Forward:
- Circular Plastics Economy: This approach offers several economic, social, and climate benefits.
Best Practices:
- Arunachal Pradesh: In Palin district, Waste is categorized into biodegradable waste and non-biodegradable waste. The biodegradable waste from household is reused as manure in kitchen garden
- Haryana: Swap Plastic to grain project to remove the littered plastic on road side.
- Chandigarh: Environmental compensation has been imposed for violation of Plastic Waste Management rules.
- Himachal Pradesh: Plastic waste used in waste to energy plants.
- Common Practices: Plastic Waste used for co-processing in cement mills, road construction etc.
|
-
- Circular plastic economy will reduce the annual volume of plastics entering our oceans by 80% by 2040 and greenhouse gas emissions by 25%.
- Private Sector Engagements: Using various innovative and scalable approaches through grants, technical assistance, and knowledge exchange platforms to manage plastic pollution.
- Global Plastic Action Partnership (GPAP) is a knowledge exchange network that brings together plastic pacts and National Plastic Action Partnerships (NPAP).
- Extended producer responsibility: It will incentivise increased recyclability, promote higher recycling rates, and enhance the accountability of producers and importers for safe and environmentally sound management of plastic products throughout their life cycle and across international supply chains.
- Just transition: Each Party shall promote and facilitate a fair, equitable and inclusive transition for affected populations, with special consideration for women and vulnerable groups.
Conclusion:
The Government of India must bring about a comprehensive and circular economy approach to reduce plastic waste, increase plastics value recovery, and tackle plastic pollution with a goal to achieve SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
(For more about plastic pollution, refer to the hyperlink)
News Source: Down To Earth
![]() 6 Sep 2023
6 Sep 2023
