Context:
- This article is based on an Editorial “Drawing lines in Cauvery waters” which was published in the Indian Express. Despite an official resolution, the Supreme Court has declined to get involved in the ongoing Cauvery or Kaveri river water dispute between Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- Article 262 of the Indian Constitution bars the jurisdiction of courts over interstate river water disputes. Hence, the Interstate River Water Disputes Act 1956 bars the jurisdiction of the courts, including that of the Supreme Court.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Kaveri river water dispute, Mekedatu Dam Project, Cauvery Water Management Authority (CWMA)’ and the Cauvery Water Regulation Committee.
Relevancy for Mains: Water resources, Kaveri river water dispute and associated agreements and challenges. |
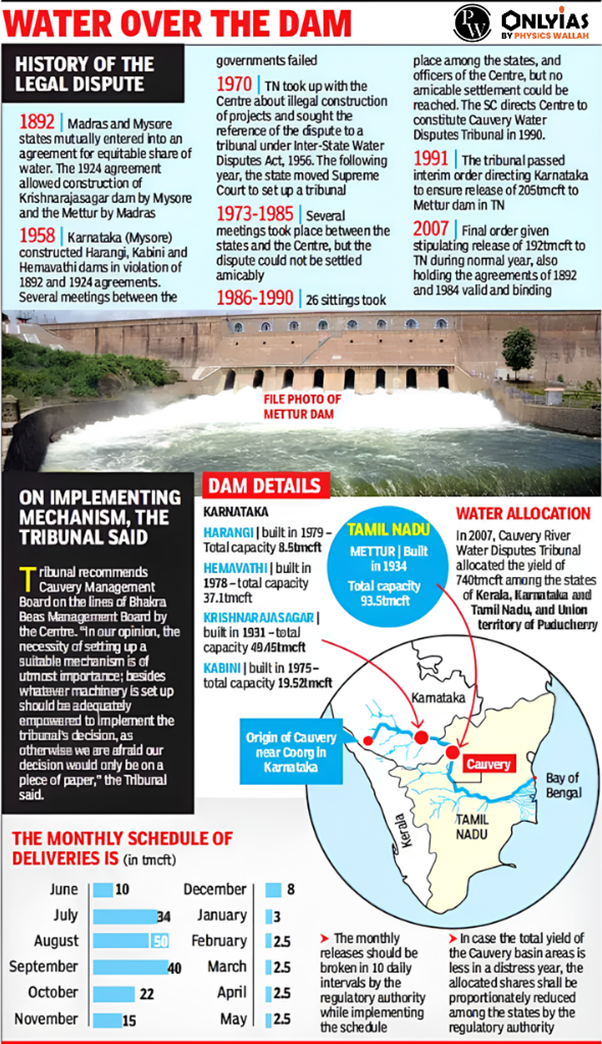
What is the Kaveri River Dispute?
- Agreement of the 19th century: Agreements were signed between the Madras Presidency and Mysore pertaining to the utilization of water resources.
- Obligation by Consent: According to the agreement, the upper riparian state was obligated to secure the consent of the lower riparian state for any infrastructure development, such as the construction of a reservoir on the Kaveri River.
- 1924 Cauvery River Water Agreement: The agreement was signed on February 18, 1924, which was brokered by the British government to resolve a dispute over the sharing of the Cauvery river water between the princely state of Mysore and the Madras Presidency, which stipulated the sharing of Kaveri river water in the following proportions;
- Madras: 75%
- Mysore: 23%
- Princely state of Travancore-Cochin: Remaining 2%
- Commencement of the Modern Phase of this Dispute: It started in 1974 when Karnataka initiated the diversion of Cauvery River water without obtaining the consent of Tamil Nadu.
- Establishment of Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT): Recognizing the escalating Kaveri river water-sharing conflict, the CWDT was established in 1990.
- Final Award by the Tribunal: In 2007, the CWDT issued its final award, delineating water allocations among the states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Puducherry.
- With a total availability of 740 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) in a typical year, the CWDT allocated water as follows;
- Tamil Nadu: Approximately 404 TMC
- Karnataka: Approximately 284 TMC
- Kerala: 30 TMC
- Puducherry: 7 TMC
- Declaration of the Kaveri River as a national asset by the Supreme Court: In 2018, the Supreme Court upheld the CWDT’s award, declaring the Cauvery River a national asset and mandating the establishment of the Cauvery Water Management Scheme.
- Cauvery Water Management Scheme: In June of the same year, the central government established the ‘Cauvery Water Management Scheme,’ which encompasses the ‘Cauvery Water Management Authority’ (CWMA) and the ‘Cauvery Water Regulation Committee’ (CWRA).
Also read: Important Rivers In India
What reasons are behind the Kaveri river dispute?
- Recent Developments
- Demand by Tamil Nadu: Tamil Nadu approached the Supreme Court to secure the release of 24,000 cusecs of water from Karnataka’s reservoir, as Karnataka had previously given up on agreed-upon water release commitments.
- The Mekedatu Dam Project: It has become a point of contention as Tamil Nadu contends that the project lacks authorization and poses a threat to its interests, thereby violating the directives of both the Kaveri river water disputes tribunal and the Supreme Court.
- Ineffectiveness of Tribunals
- Proven as ineffective: The government’s approach of establishing tribunals for each dispute has proven ineffective and ad hoc.
- Limited Legal Basis: The legal basis of tribunal decisions is often limited.
- Exacerbation of Conflicts: Furthermore, when states challenge the rulings of these tribunals, it tends to exacerbate the conflicts.
- Water Scarcity
- Associated Factors: The distress caused by climate change, unpredictable rainfall patterns, depletion of groundwater, and the adoption of water-intensive cropping practices have intensified disputes over river waters.
ALSO READ: INTER-STATE RELATIONS
The Path Ahead
- Enactment of Effective Legislation: It is essential to enact legislation that grants tribunals the authority to enforce their rulings, as this is pivotal for expediting and enhancing the resolution of these conflicts.
- In 2017, the Lok Sabha approved the Inter-State River Water Disputes (Amendment) Bill, aimed at establishing a single, permanent tribunal and a mediation committee.
- However, the implementation of this bill has not been realized to date.
- Need for Water Harvesting: Facilitating widespread water harvesting in both Karnataka and Tamil Nadu is necessary.
- Empowerment of Councils: Enhancing the interstate council and Zonal councils to bolster their capacity for resolving disputes is imperative.
Conclusion
The ongoing Kaveri River Water Dispute highlights an urgent requirement for legislation that empowers tribunals to enforce their judgments, thus expediting and improving the resolution of inter-state river water disputes.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
Recently, linking of which of the following rivers was undertaken? (2019)
- Cauvery and Tungabhadra
- Godavari and Krishna
- Mahanadi and Son
- Narmada and Tapti
Ans: B |
![]() 6 Oct 2023
6 Oct 2023


