![]() 30 Nov 2023
30 Nov 2023
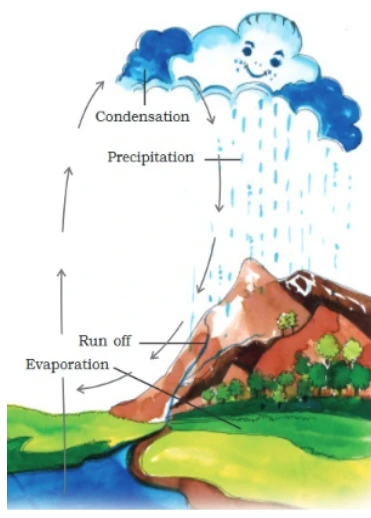
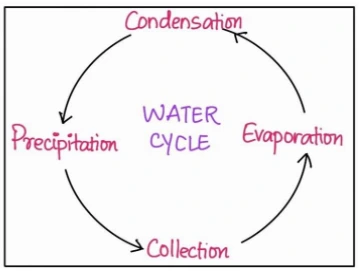
The Earth’s water cycle is a mesmerizing dance of elements, a continuous process that orchestrates the circulation of water between the Earth’s surface, the atmosphere, and the vast oceans. Initiated by the powerful influence of solar energy, this hydrological cycle governs the intricate balance of water on our planet. From evaporation and condensation to precipitation and the return of water to Earth’s surface, this perpetual cycle sustains life and shapes the availability of freshwater for a myriad of human and ecological needs.
Sources of Freshwater: Rivers, Ponds, Springs, and Glaciers
The hydrological cycle plays a crucial role in maintaining the Earth’s water balance and ensuring the availability of freshwater for various purposes.
Water vapor present in the air is known as humidity.
Forms of Condensation: Exploring Condensation Forms
Forms of Evaporation and condensation can be classified on the basis of temperature and location as dew, frost, fog and clouds as follows.

Cumulus Cloud

Stratus Cloud
<div class="new-fform">
</div>