![]() 2 Dec 2023
2 Dec 2023
An open economy is defined as one that interacts with other nations through various channels, unlike a closed economy, which has no linkages with the rest of the world. In an open economy, trade in goods, services, and financial assets with other countries is prevalent.
In an open economy, three crucial linkages influence its dynamics:
Foreign trade plays a crucial role in influencing aggregate demand in an open economy, operating through two ways:
There is a new classification in which the balance of payments have been divided into three accounts:
In an Open Economy, the Current Account records trade in goods and services as well as transfer payments. Components of Current Account (as illustrated in Figure):
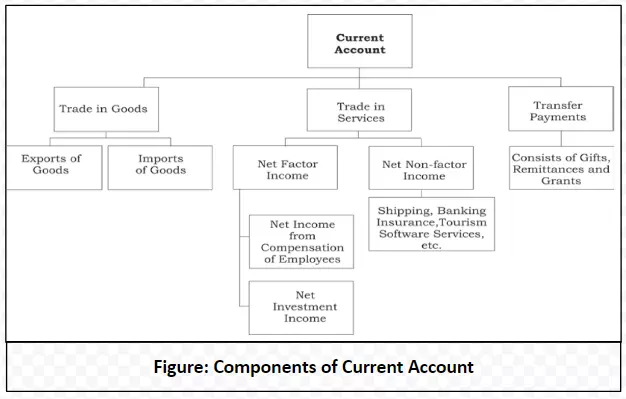

<div class="new-fform">
</div>