![]() 21 Jun 2024
21 Jun 2024
The southwest monsoon season, a vital meteorological phenomenon in the Indian subcontinent, marks the arrival of seasonal winds laden with moisture from the Indian Ocean. Characterized by its onset in June and withdrawal by September, this annual weather pattern plays a pivotal role in shaping the region’s climate, influencing agriculture, water resources, and overall livelihoods. The southwest monsoon brings widespread rainfall, crucial for sustaining ecosystems and supporting the agrarian economies of countries like India.
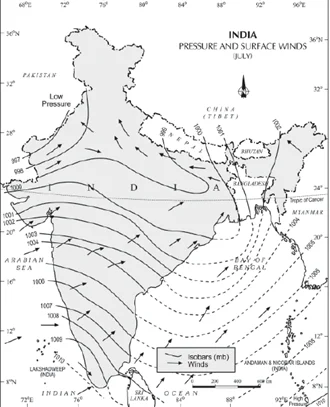
Pressures and Surface wind (July)
The monsoon winds originating over the Arabian Sea further split into three branches:
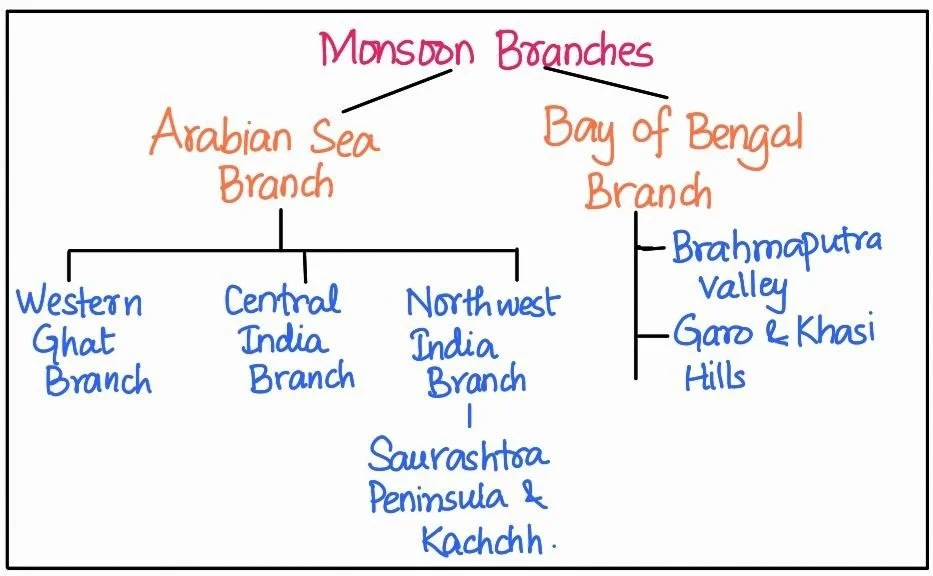
|
Do You Know? The Tamil Nadu coast remains dry during the southwest monsoon season due to two main factors:
|
|---|
Retreating Southwest Monsoon Season: October-November Transition
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>