![]() 16 Dec 2023
16 Dec 2023
In assessing the purity of consumables like milk, ghee, butter, salt, spices, mineral water, or juice, we often encounter the term ‘pure’ on their packaging, but scientifically nothing is pure rather it’s just a mixture. For instance, milk is a blend of water, fat, proteins, and more.

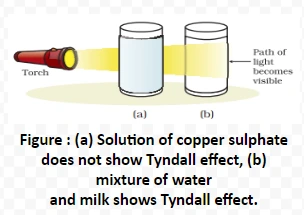
Tyndall Effect
Common Examples of Colloids
| Dispersed phase | Dispersing medium | Type | Example |
| Liquid | Gas | Aerosol | Fog, clouds, mist |
| Solid | Gas | Aerosol | Smoke, automobile exhaust |
| Gas | Liquid | Foam | Shaving cream |
| Liquid | Emulsion | Milk, face cream | |
| Solid | Liquid | Sol | Milk of magnesia, mud |
| Gas | Solid | Foam | Foam, rubber, sponge, pumice |
| Liquid | Solid | Gel | Jelly, cheese, butter |
| Solid | Solid | Solid gel | Coloured gemstone, milky glass |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>