![]() 19 Dec 2023
19 Dec 2023
Animal Physiology and Environmental Response Systems
Control and coordination in animals involve intricate systems that manage physiological functions and respond to environmental stimuli.
Facilitating Control and Coordination:
Mechanisms of Nervous Impulse Transmission: From Information Acquisition to Synaptic Transmission
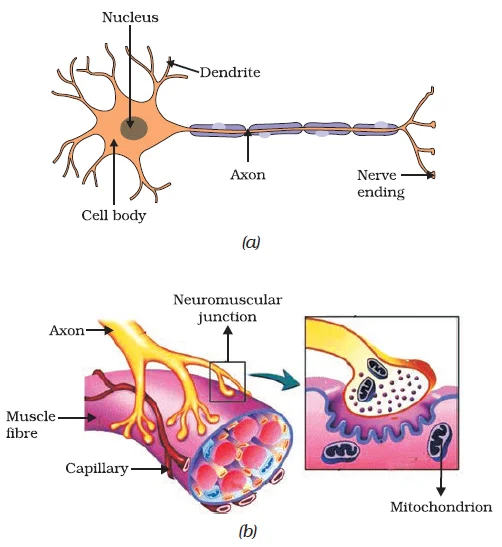
Structural Dynamics of Nervous Tissue: Neuronal Information Transmission
Neural Information Processing: The Coordinated Functionality of the Nervous System
Reflex Actions
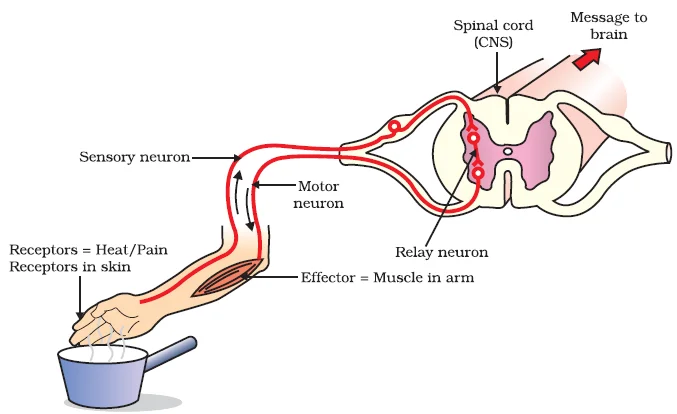
Reflex Actions and Neural Efficiency: Rapid Responses in the Nervous System
Understanding the Reflex Arc and Its Evolutionary Significance in Rapid Responses
Neuroanatomy and Functional Complexity: the Intricacies of the Human Brain
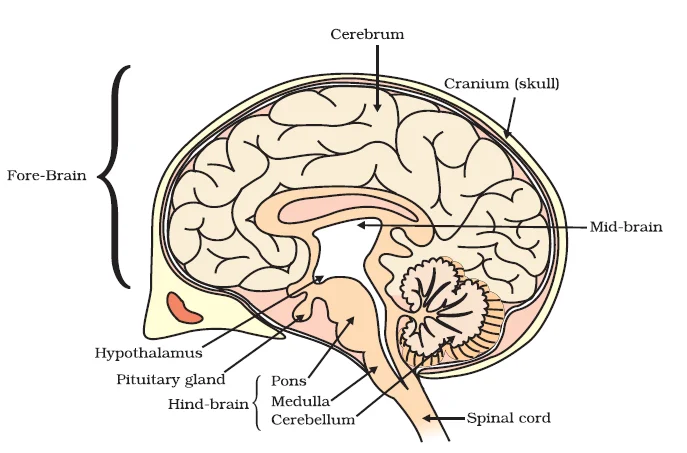
Protection of Delicate Organs
Integration of Nervous Tissue and Muscle Function: Precision in Action
<div class="new-fform">
</div>