![]() 3 Jan 2024
3 Jan 2024
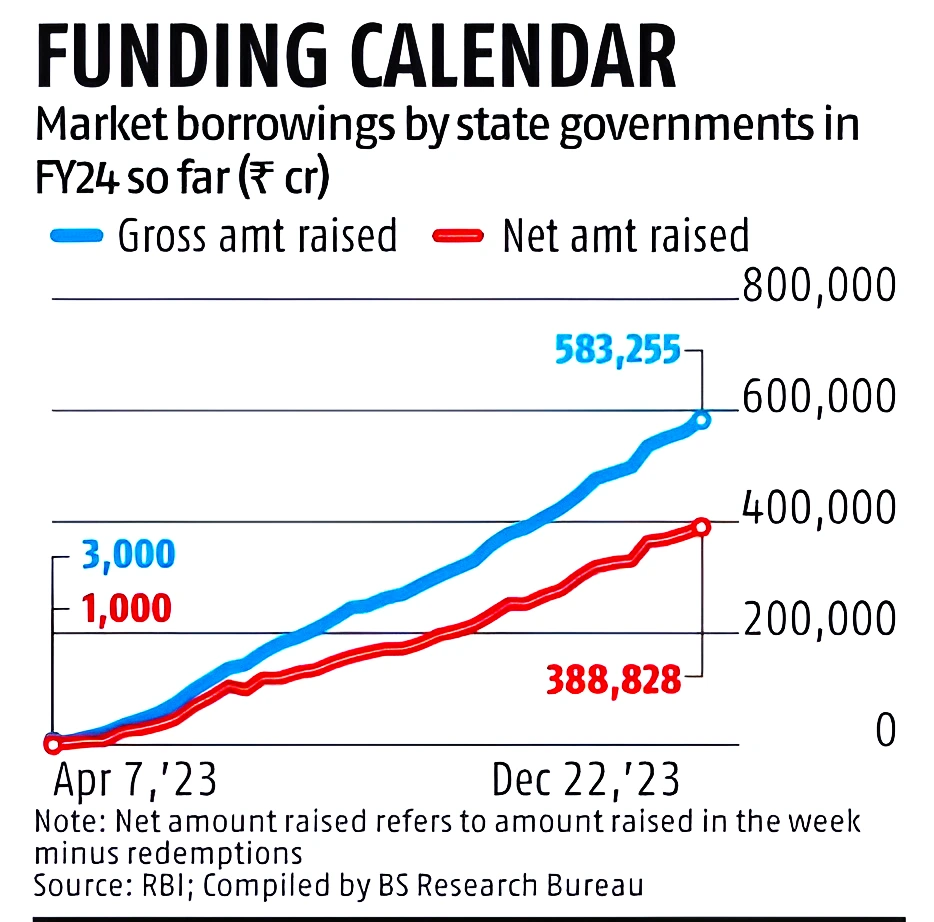
Context: The spread between yields on the 10-year state development loans (SDL) and the Centre’s G-sec (government securities) widened to a two-year high.
About Bonds
|
|---|
Source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>