![]() 24 Feb 2024
24 Feb 2024
English
हिन्दी
Recently, the Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) payload onboard the Aditya-L1 detected solar wind impact of Coronal Mass Ejections.
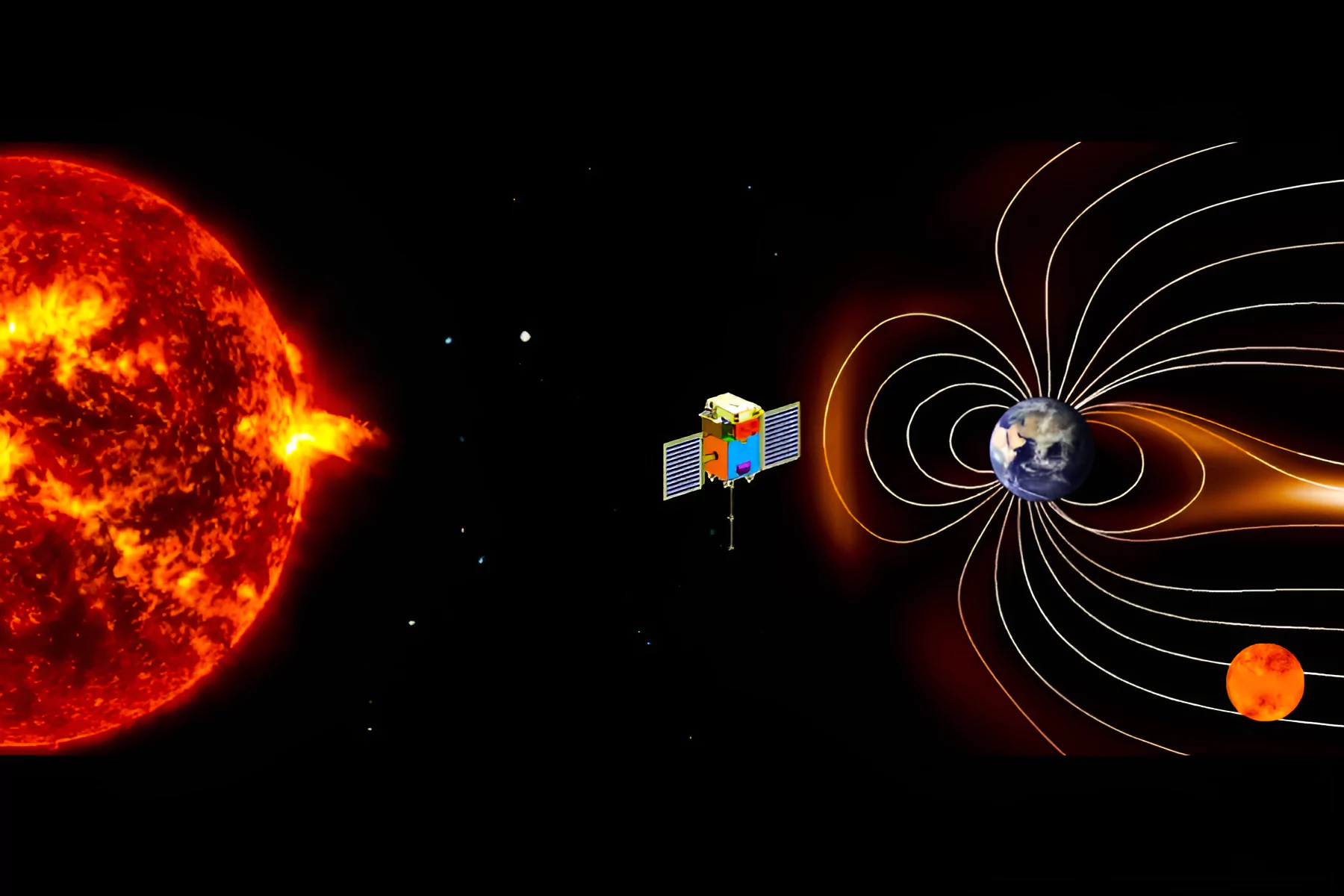
Aditya L-1 Mission |
| Mission Objective: Aditya-L1 endeavours to conduct a comprehensive solar study, encompassing the corona, photosphere, chromosphere, solar emissions, solar winds, flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs). |
| Launch Vehicle: Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV C-57) |
| Primary Payload: Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) |
| Secondary Payload: Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT), Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS), High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS), Aditya Solar wind Particle EXperiment (ASPEX), Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) |
Purpose:
|
L 1 Point/ Lagrange Point 1:
|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>