![]() 6 Apr 2024
6 Apr 2024

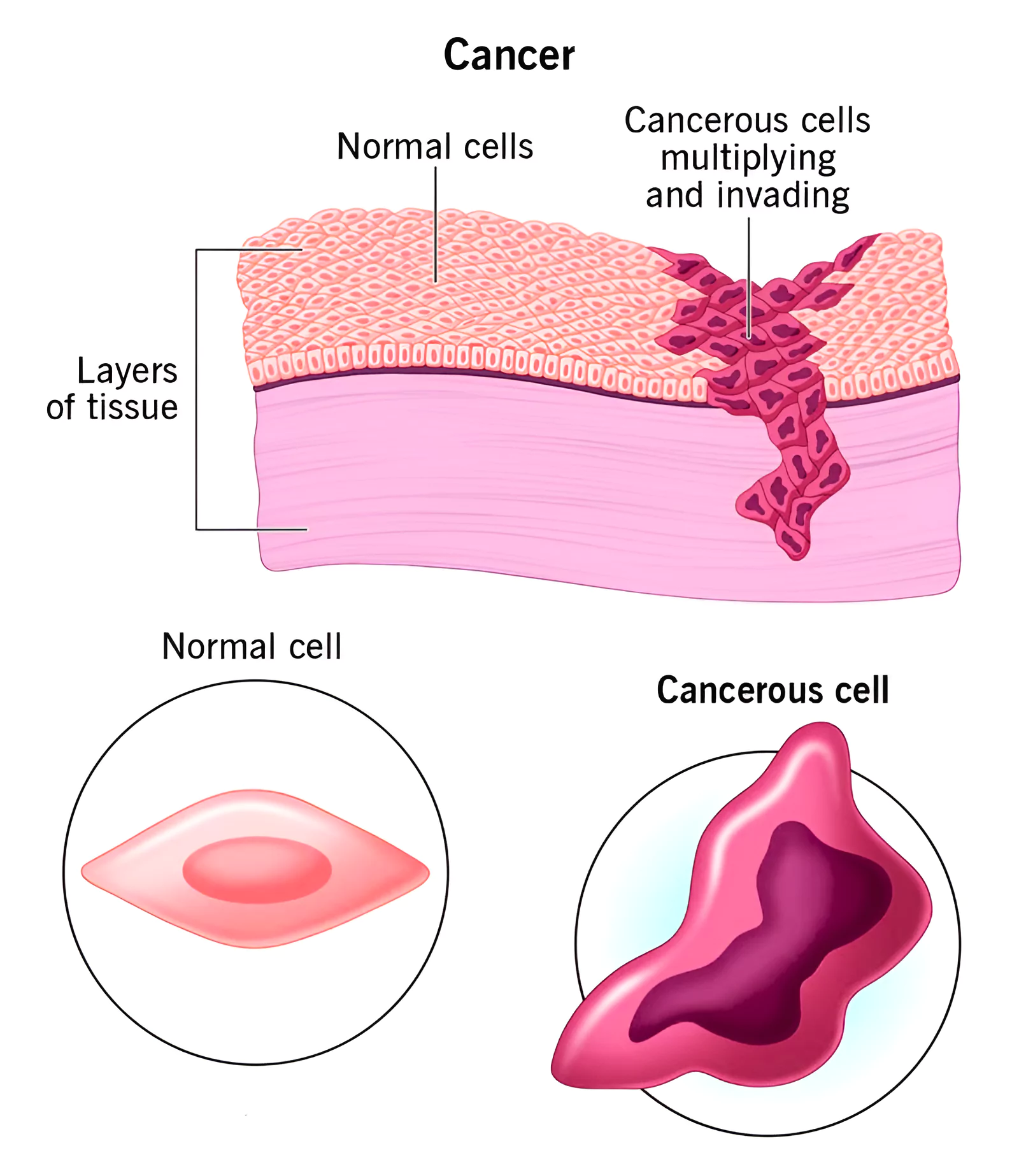
According to data shared by the annual Health of Nation report by Apollo Hospitals, India is rapidly emerging as the “cancer capital of the world”.
| Relevance for Prelims: DISEASES, Cancer Prevalence In India, India’s Fight Against Cervical Cancer, Latest Estimates Of Cancer Burden In India,, and Role Of Government In Health.
Relevance for Mains: Cancer Cases in India: Status, Reasons, Challenges, Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
|---|
| Prelims PYQ (2019):
‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why? 1. It is used in developing gene silencing therapies. 2. It can be used in developing therapies for the treatment of cancer. 3. It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies. 4. It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens. Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1 and 4 only Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

<div class="new-fform">
</div>