![]() 21 Mar 2024
21 Mar 2024
A recent study ‘Enabling a Circular Economy in India’s Solar Industry – Assessing the Solar Waste Quantum’ has been conducted by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
Pros of Addressing Solar Waste
|
Challenges in Addressing Solar Waste
|
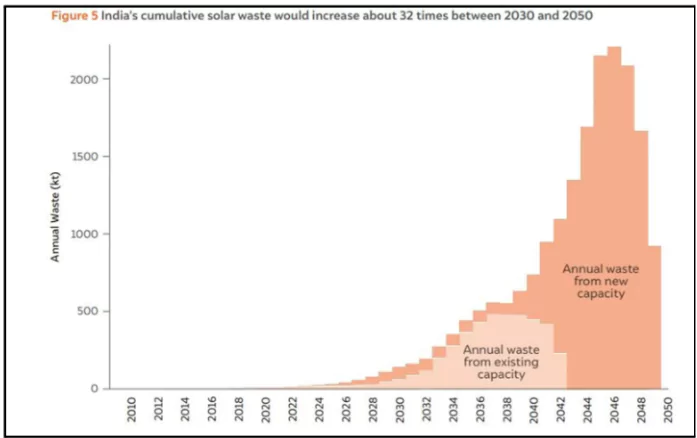 2030 Waste Projection: This waste is projected to increase significantly to 340 kilotonnes by 2030.
2030 Waste Projection: This waste is projected to increase significantly to 340 kilotonnes by 2030.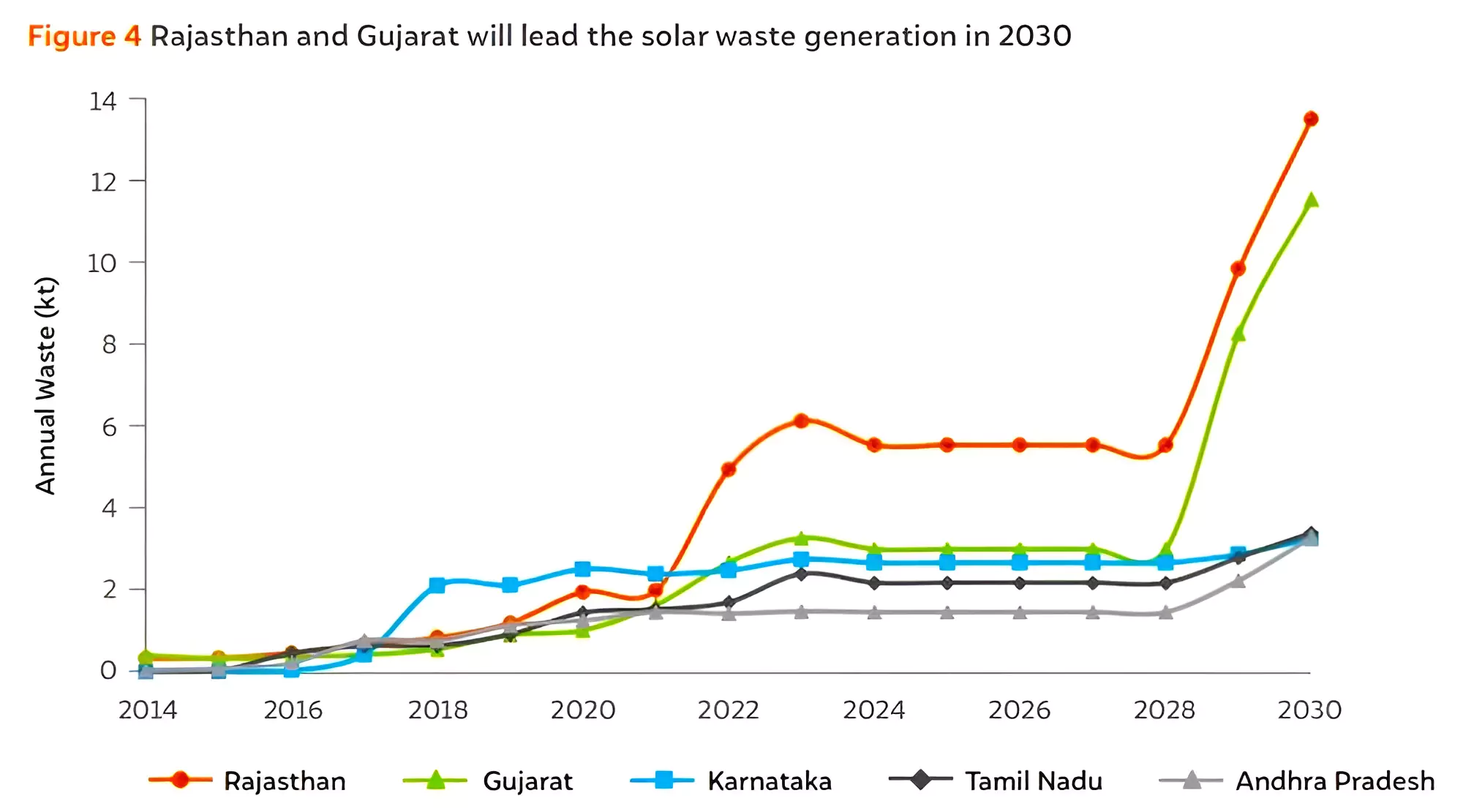
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>