Context
IRDAI is devising a new affordable bundled product to give citizens protection against multiple risks, and seeking to expedite claim settlements by linking death registries onto a common industry platform.
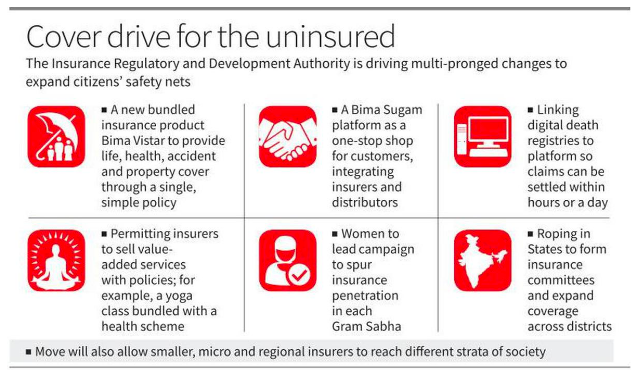
Image Source: The Hindu
IRDA’s Plan for Affordable and Comprehensive Insurance Coverage in India:
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) aims to expand insurance penetration in India.
- Plans include creating a bundled product that covers health, life, property, and accident insurance.
- Claims settlement process to be expedited by linking death registries onto a common industry platform.
-
- RDA’s chief striving to create an “UPI-like moment” in insurance through a plan worked out with general and life insurance firms that he termed “Bima Trinity”.
- Bima Sugam platform to integrate insurers and distributors, providing a one-stop shop for customers.
- Bima Vistar, a bundled risk cover, to offer defined benefits for each risk and faster claim settlements.
- Swift Claim Settlements:
- Parametric triggers implemented to assess losses without the need for surveyors.
- Defined benefits transferred directly to policyholders’ bank accounts.
- Integration of birth and death registries to expedite claim settlement within hours.
- Women-centric Workforce:
- Bima Vaahaks (carriers) to meet with women heads of households to promote composite insurance products.
- Encouraging women to consider Bima Vistar for financial security during distress.
- Legislative Amendments and Value-Added Services:
- Proposed amendments to insurance laws to attract more investments and allow value-added services.
- Differentiated capital requirements for niche insurers to accommodate specialized players.
- The amendments will also enable the entry of new players in the form of micro, regional, small, captive players, specialised players, and even composite licences.
- Formation of State-Level Insurance Committees:
- IRDA plans to establish State-level insurance committees for effective implementation.
- Collaboration with State governments to develop district-level insurance plans.
- Comparison to Banking Sector:
- Drawing parallels with the banking sector’s differentiated licenses for niche players.
- Different types of banks catering to diverse geographies and segments of the population.
- Similar approach in the insurance sector to cater to different regions and population segments.
| Additional Information
About Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI):
- An autonomous and statutory body established under the IRDA Act 1999.
- An apex body that supervises and regulates the insurance sector in India.
- A 10-member body- a Chairman, five full-time members, and four part-time members appointed by the Government of India.
- Objective: To protect the interests of policyholders, to regulate, promote and ensure orderly growth of the insurance industry in India.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Finance.
- Headquarters: Hyderabad.
|
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 26 May 2023
26 May 2023
