Context: Recently, the forest officials in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve rescued a wild elephant calf found separated from the herd.
About Anamalai Tiger Reserve
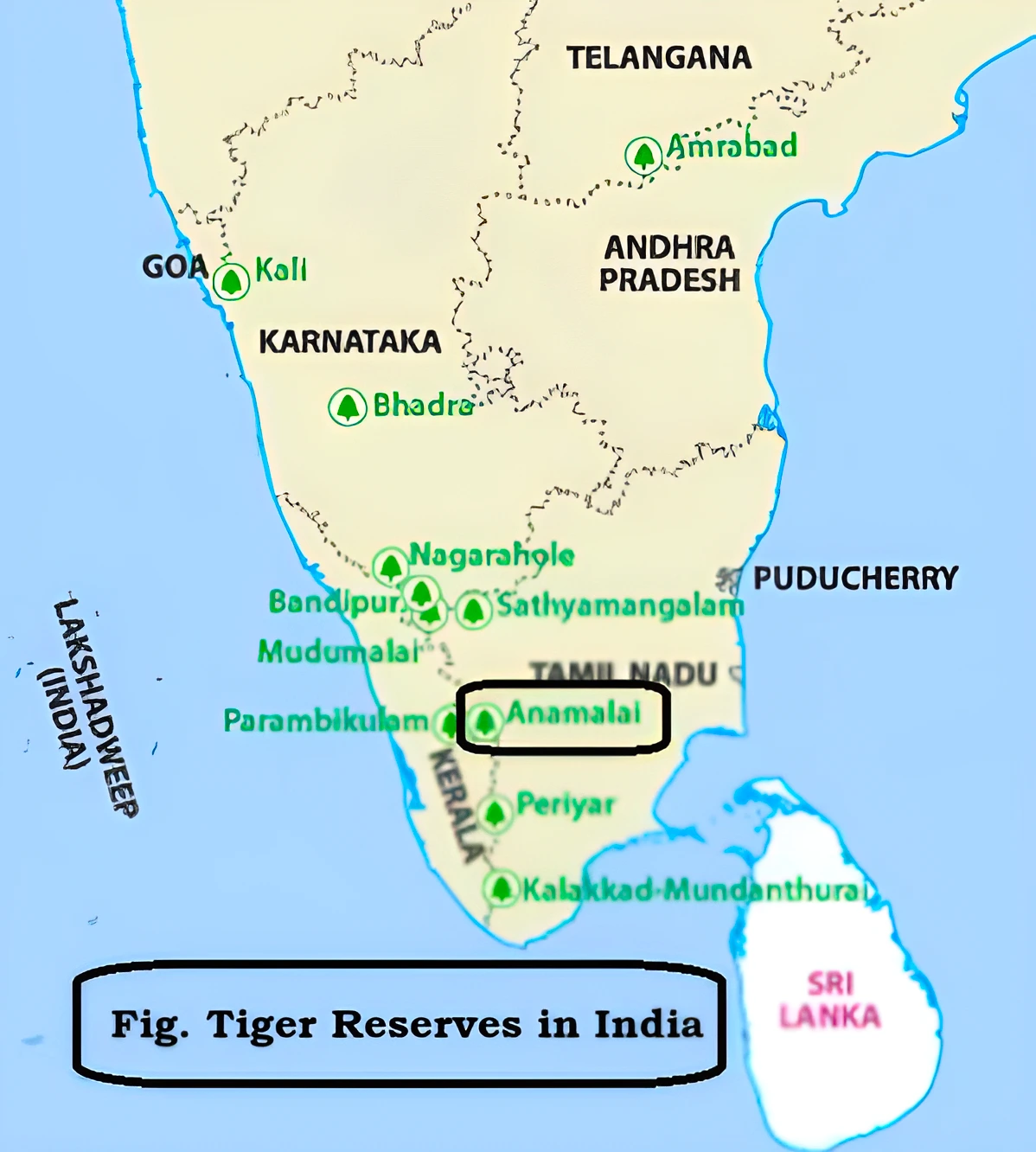
- Location: Anamalai Tiger Reserve lies South of the Palakkad gap in the Southern Western Ghats along with the Kerala and Tamil Nadu border, surrounded by Parambikulam Tiger Reserve on the East, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary and Eravikulam National Park on the South Western side.
- The reserve is also surrounded by Nenmara, Vazhachal, Malayattur and Marayur reserved forests of Kerala.
- Recognition:
- Tiger Reserve: It was declared as a Tiger reserve in the year 2007.
- The Kariyan shola, Grass hills and Manjampatti of Anamalai Tiger Reserve has been identified as a world heritage site by UNESCO.
- Area of the Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Core/critical tiger Habitat: 958.59 sq km.
- Buffer/Peripheral Area: 521.28 sq km.
- Total: 1479.87 sq km.
- Flora: The Anamalai Tiger Reserve is rich in wild relatives of cultivated species like turmeric (Curcuma longa), pepper (Piper longum), cardamom, solaipuli, nutmeg, cinnamom, etc.
- Fauna: The important mammals include Asiatic elephant, Sambar, Spotted deer, Barking deer, Mouse deer, Gaur, Nilgiri tahr, Lion Tailed Macaque, Nilgiri langur, and Common langur. Other
- Common wild animals include wild pigs (Sus scrofa) and sloth bears (Melursus ursinus).
- Wildlife Corridors: There are several wildlife corridors which include Navamalai, Punachi, Siluvaimedu, Sethumadai–Nenmara.
- Anthropological Reserve: As it supports 6 indigenous people viz. Malasar, Malai malasars, Kadars, Eravallars, Pulayars and Muduvars.
- Best Practices:
- Innovative alert system for addressing human-wildlife conflict.
- Anti-poaching strategy.
- Control over illegal ganja cultivation.
- Smart patrolling using M-STrIPES protocol.
Also Read: Tiger Reserves In India
News Source: Mint
![]() 30 Dec 2023
30 Dec 2023
