Context
Recently, the RBI had organised a conference for the directors and MD/ CEOs of ARCs in Mumbai that was attended by more than 80 participants representing all 27 ARCs.
- The Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has identified several supervisory concerns in the functioning of Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs).
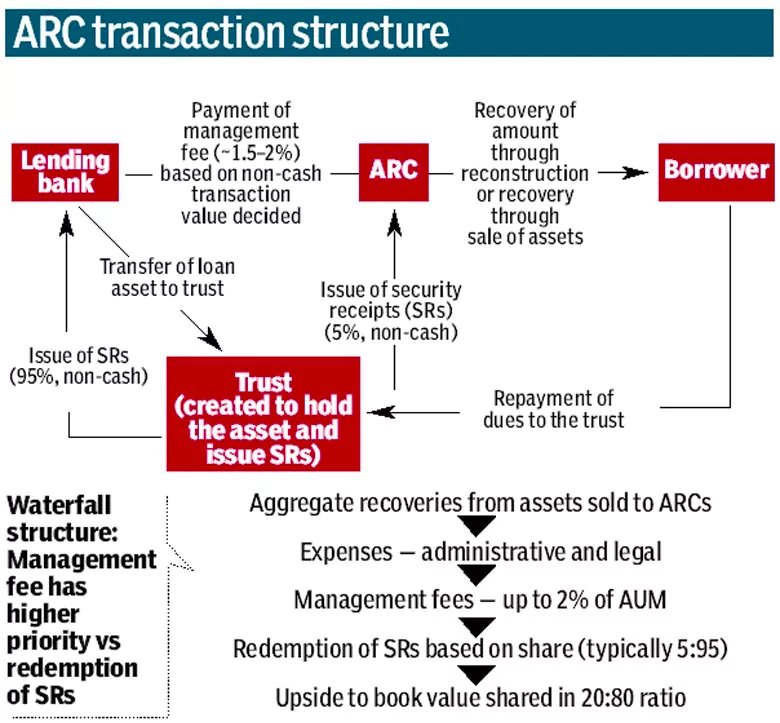
About Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC)
- A Type of Financial Institution: An asset reconstruction company is a type of financial institution that specializes in acquiring and managing distressed assets, typically loans or non-performing assets (NPAs) from banks and other financial institutions.
- When borrowers are unable to repay their loans, these loans become NPAs, and banks might decide to offload these troubled assets to ARCs.
- Importance: ARCs play a crucial role in the financial system by helping banks clean up their balance sheets and recover some value from the troubled loans.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Crucial Insights of the Conference
- To Adopt Regulation Plus Approach: RBI asked asset reconstruction company to adopt a “regulation plus” approach, ensuring compliance with both the letter and the spirit of regulations.
- Due Importance to Functions: Boards should accord due importance to assurance functions, namely, risk management, compliance and internal audit.
- These functions play a critical role in identifying and mitigating risks, ensuring compliance with laws and regulations as well as safeguarding the organisation’s reputation.
- Ethical Conduct & Integrity: Setting the right tone from the top is crucial in fostering a culture of integrity and ethical conduct.
- Emphasising the Importance of Sound Governance: The sound governance provides a strong foundation for ARCs to build a robust business model.
- Responsibility: The onus to develop sound governance lies largely with the Boards of the ARCs and the top functionaries who will have to develop a strong and institutional culture based on the above mentioned principles.
- Essence: Need for responsible conduct in the recovery process and emphasised that ARCs should follow transparent and non-discriminatory practices in line with the comprehensive fair practice code (FPC) put in place by the Reserve Bank.
About Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Formation: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was established through the Reserve Bank of India Act of 1934, based on the recommendations of the Hilton Young Commission, with a share capital of Rs. 5 crore.
- The Central Office of the Reserve Bank was set up in Kolkata but was permanently shifted to Mumbai in 1937.
- Initially, the RBI was owned privately but was nationalized in 1949. It is completely owned by the Government of India.
- Mandate: RBI is responsible for the control, issuing, and maintaining supply of the currency in the country. It also manages the country’s main payment systems.
- Organisation Structure: The operation of the Reserve Bank of India lies with a 21-member central board of directors consisting of:
- Governor
- 4 Deputy Governors
- 2 Finance Ministry representatives
- 10 government-nominated directors
- 4 directors to represent local boards’ headquarters of RBI
|
![]() 18 May 2024
18 May 2024

