![]() 6 Feb 2024
6 Feb 2024
English
हिन्दी
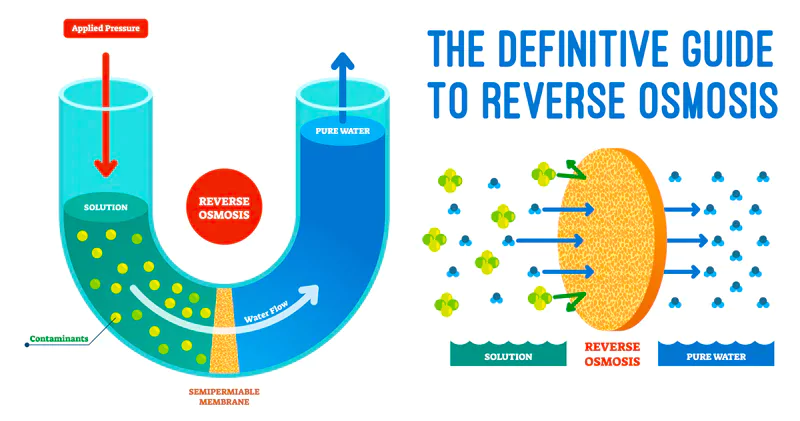
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) directs the government to regulate RO-based water Purification Systems.
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>