![]() 6 Mar 2025
6 Mar 2025

The cotton industry in North India is facing severe challenges due to whiteflies and pink bollworms.
Bt Technology
|
|---|
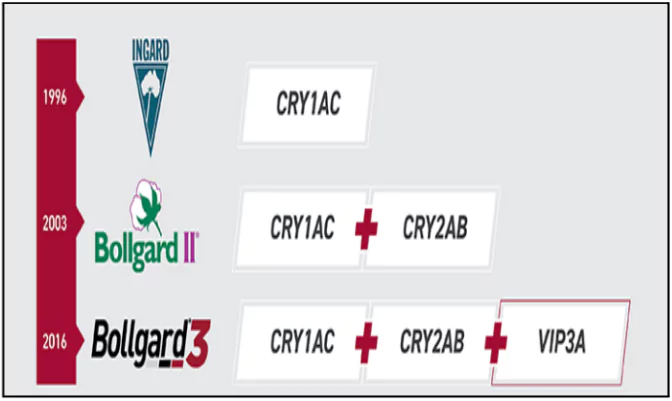
About Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac, and Vip3A
|
|---|
About Whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci)
Impact on Productivity
About Pink Bollworms (Pectinophora gossypiella)
Impact on Productivity
|
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>