Context:
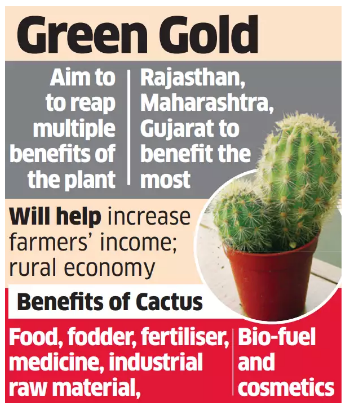
The Government is looking at promoting cactus plantations in low-irrigation areas to rejuvenate degraded land.
About Cactus:
- Geographical Distribution: Cacti are unevenly distributed. Its largest concentration is found around latitude of 30-degree north and 30 degree south of the equator.
- It is found in semi-arid regions of Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh.
 Species: Saguaro cactus, Cereus cactus.
Species: Saguaro cactus, Cereus cactus.- Cactus cultivation will help in achieving Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for the country as well.
- For Example: Cacti are drought-tolerant plants that can store water in their tissues. This water can be used to photosynthesise, which produces oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Thus they help in Carbon sequestration.
- Economic Importance:
- Food production: Many cacti are edible, and their fruits, pads, and flowers can be used to make a variety of dishes.
- For example, the prickly pear cactus is a common food crop in many parts of the world, and its pads can be cooked or pickled.
- Fodder: The pads of some cacti are high in fiber and nutrients, and they can provide a valuable source of food for animals during times of drought.
- Biofuel production: The starch and sugars in cactus can be fermented to produce ethanol, which can be used as a fuel for cars and other vehicles.
- Water conservation: Cacti are drought-tolerant plants that can store water in their tissues. This makes them a sustainable way to use land in arid regions, where water is scarce.
News Source: The Print
![]() 5 Sep 2023
5 Sep 2023
 Species: Saguaro cactus, Cereus cactus.
Species: Saguaro cactus, Cereus cactus.