Context:
According to the latest global burden estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2022, India witnessed over 14.1 lakh new cancer cases and recorded more than 9.1 lakh deaths attributed to the disease.
Cancer Burden In India: WHO Estimates
- According to the Report Cancer Prevalence among Men were majorly affecting the lip, oral cavity, and lungs, comprising 15.6% and 8.5% of the new cases, respectively.
- While among women, breast and cervical cancers were the most frequent, accounting for approximately 27% and 18% of the new cases, respectively.
- WHO also published survey results from 115 countries, showing a majority of countries do not adequately finance priority cancer and palliative care services, as part of universal health coverage (UHC).
Universal Health Coverage (UHC)
- It means that all people have access to the full range of quality health services they need, when and where they need them, without financial hardship.
- It covers the full continuum of essential health services, from health promotion to prevention, treatment, rehabilitation and palliative care.
|
Major Findings of WHO On Cancer Burden In India & World
- Cancer Burden In India: In 2022, nearly 32.6 lakh people in India survived within 5 years of a cancer diagnosis.
- The risk of developing cancer before 75 was 10.6%, and the risk of death from cancer by the same age was 7.2%.
- Cancer Burden Globally: It estimated around 2 crore new cancer cases and 97 lakh deaths, with about 5.3 crore people surviving 5 years post-diagnosis.
- Cancer Incidence: 1 in 5 people worldwide develops cancer in their lifetime, and 1 in 9 men and 1 in 12 women die from the disease.
- Cancer management Scenario: Only 39% of surveyed countries covered cancer management in their core health services, and 28% covered palliative care.
- Most Common Type of Cancer: Lung cancer cause of global cancer deaths (19%). Breast cancer in women is 7% of global cancer deaths.
- Cervical cancer was the eighth most common globally.
- Highest age-standardized rate of cancer deaths: Europe (82 per 1 lakh people).
- Highest risk of developing cancer before 75 (38%) : Oceania
- Highest death risk from cancer (11.5%) : Europe
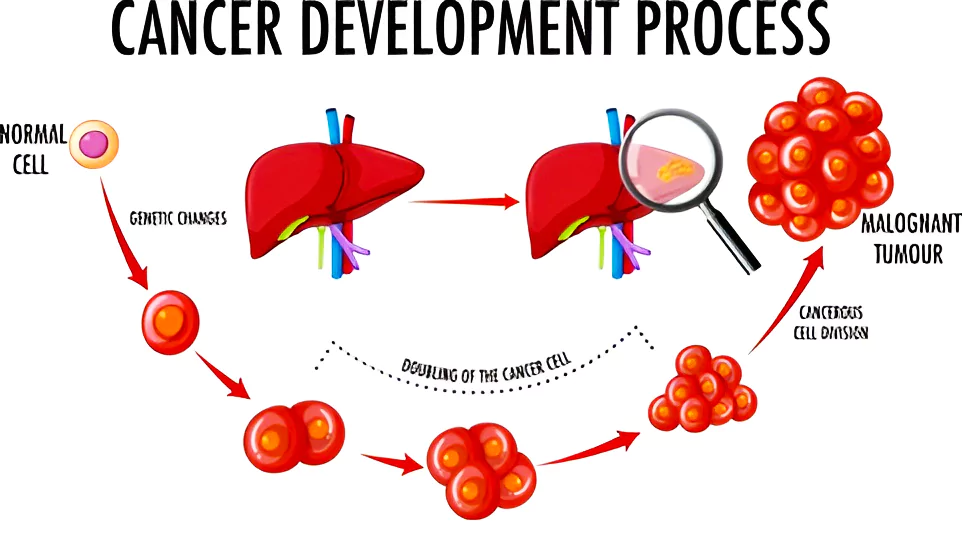
What is Cancer ?
- Cancer is a disease of the genome which is caused by changes in genes that cause some cells to divide in an uncontrolled way through a process known as metastasis.
- Metastasis is the movement or spreading of cancer cells from one organ or tissue to another.
- Treatment varies based on cancer type and includes surgery, radiotherapy, and systemic therapy and Palliative care.
Cause of Cancer
Cancer arises from the transformation of normal cells into tumor cells in a multi-stage process which are the result of the interaction between a person’s genetic factors and three categories of external agents, including:
- Physical carcinogens, such as ultraviolet and ionizing radiation;
- Chemical carcinogens, such as asbestos, components of tobacco smoke, alcohol, aflatoxin (a food contaminant), and arsenic (a drinking water contaminant); and
- Biological carcinogens, such as infections from certain viruses, bacteria, or parasites.
Prevention From Cancer
- Maintaining a healthy body weight, incorporating fruits and vegetables into the diet, and engaging in regular physical activity are effective preventive actions.
- Limiting or abstaining from alcohol consumption is another means of lowering cancer risk.
- For those recommended, vaccination against HPV and hepatitis B is advised.
- Avoiding exposure to ultraviolet radiation, from the sun or artificial tanning devices.
- Ensuring the safe use of radiation in healthcare, both for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, is crucial.
- Occupational exposure to ionizing radiation should be minimized.
- Individuals should limit exposure to outdoor and indoor air pollution, including the radioactive gas radon, which can accumulate in buildings.
Government Initiative for Preventing & Reducing Cancer Burden in India
- The National Cancer Grid is another significant effort aimed at coordinating cancer care and research across the country.
- The National Tobacco Control Programme focuses on raising awareness about the harmful effects of tobacco, aiming to decrease both demand and supply of tobacco products.
- The Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN) was initiated to address the financial requirements associated with cancer treatment.
- The government also supports the HPV vaccine program as a preventive measure against cervical cancer.
- FSSAI‘s new labeling regulations target cancer-causing chemicals in food, promoting inter-sectoral action.
WHO Global NCD Action Plan 2013–2020
- This plan serves as a roadmap, offering policy options for Member States, international partners, and WHO to collectively implement between 2013 and 2020. The goal is to achieve 9 global NCD targets by 2025, including a 25% relative reduction in premature mortality from NCDs
|
Global Efforts to Reduce Cancer Burden
WHO Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs 2013–2020 provides a road map.
Observance of World Cancer Day on 4th February.
Focusing on Scientific Research for the treatment of various types of cancer.
Way Forward to Reduce Cancer Burden In India
- Risk Reduction: About 50%-60% of cancer cases can be prevented by managing known risk factors.
- Behavior promotion can mitigate factors like tobacco use (27% of cases), alcohol, poor diet, low physical activity, obesity, and pollution.
- Awareness Generation: A multisectoral approach involving government, private practitioners, and civil society is vital for enhancing health literacy on cancer.
- Promotion of Health Infrastructure: Strengthening health systems is crucial for better access to screening, early detection, and timely, affordable treatment.
- Focus on Scientific Research & Data-Driven Policies: Designating cancer as a notifiable disease could enhance research by providing access to accurate data for informed policy decisions.
Also Read:
News Source: ET
![]() 3 Feb 2024
3 Feb 2024

