Context
The chocolate industry is facing a big problem due to the rise in the price of cocoa beans, which are crucial for making chocolate.
Rising Cocoa Prices
- In April, it reached $12,000 per tonne, which is four times higher than last year.
- Cocoa processors, who process these beans into chocolate ingredients, have reduced production because they can’t afford the expensive beans.
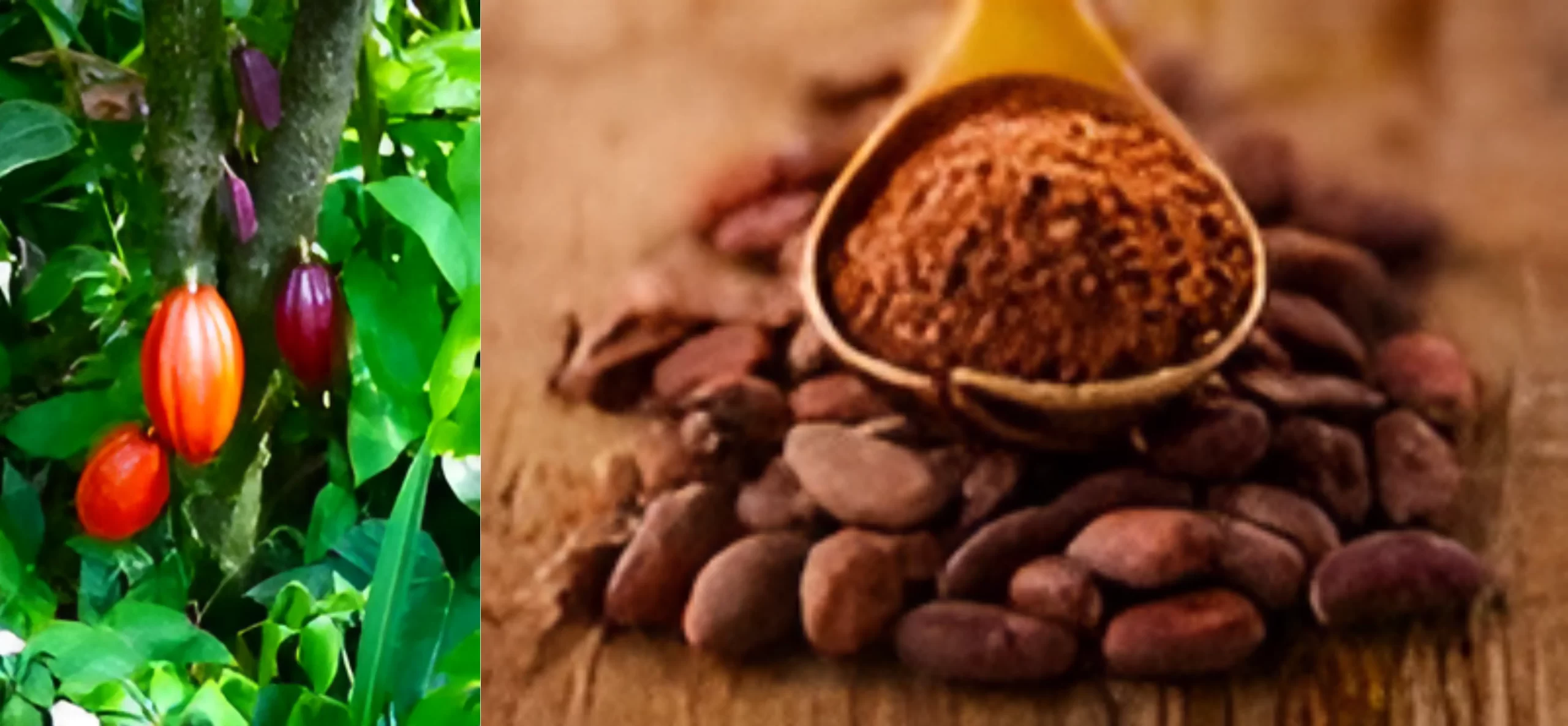

About Cocoa Plants
Cocoa plants are small trees originally from the American tropics but are now cultivated in tropical regions worldwide. It refers to the dried and fully fermented fatty seeds of the cacao tree. It is used in making chocolate. It can also refer to hot chocolate drinks, cocoa powder (the result of grinding cocoa seeds and removing cocoa butter), or a combination of both cocoa powder and cocoa butter.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
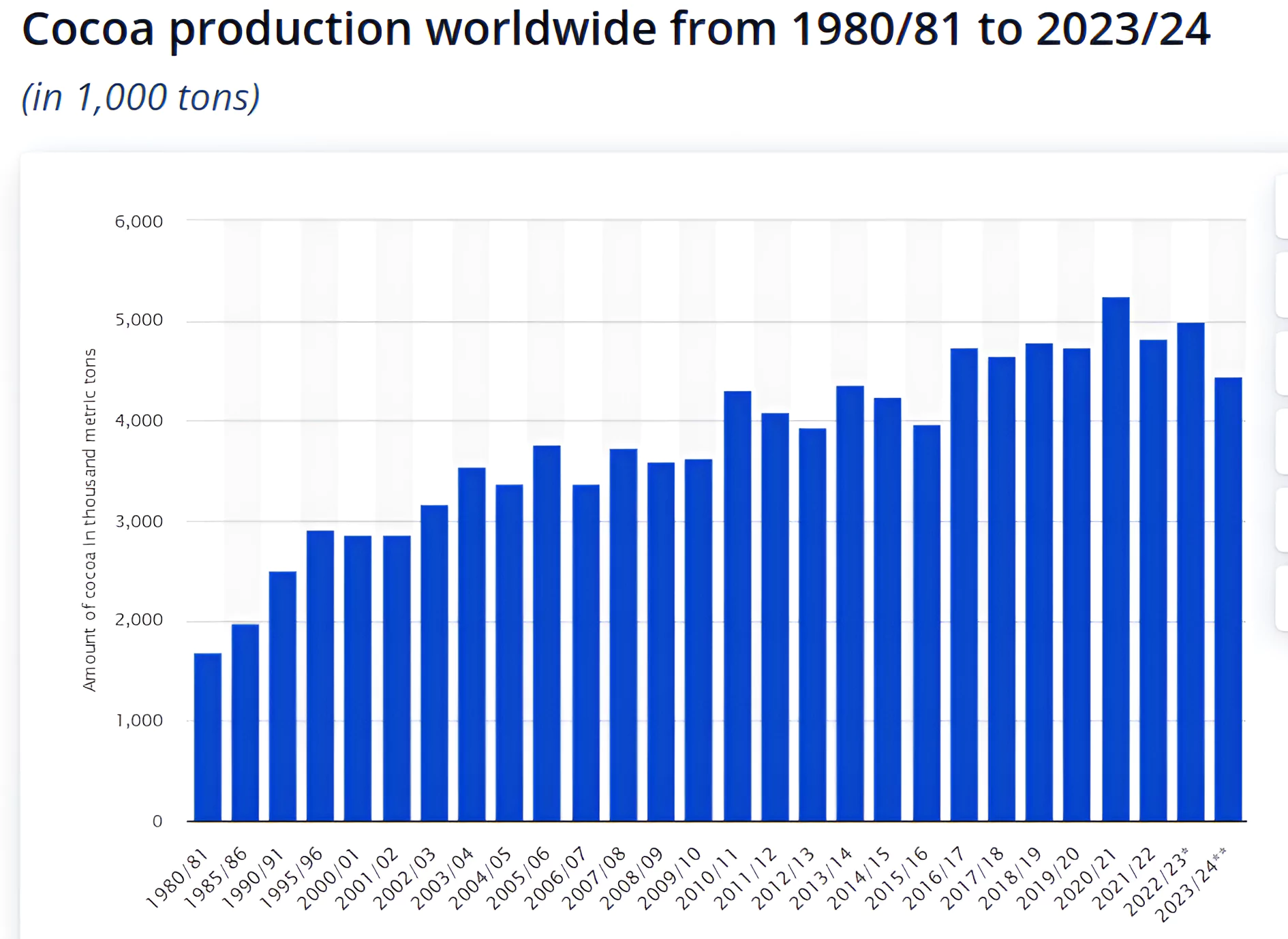
- Primary Producers: The main countries leading in cocoa production globally include Ghana, Nigeria, Ivory Coast, and Brazil.
Climate Requirements for Cocoa Plants
- Cocoa grows well up to 300 meters above sea level.
- Origin: It originated as a crop growing beneath the trees in the Amazonian forests.
- Cultivation of cocoa: It is cultivated under the shadow of forest trees or alongside other crops ( A practice known as intercropping).
- Annual Rainfall: It needs a minimum of 90-100 mm rainfall per month, with an annual rainfall of 1500-2000 mm.
- Equitable climate with well-distributed rainfall is essential, and irrigation may be necessary during prolonged dry periods.
| Black pod disease

- This Black pod disease is the primary ailment affecting cocoa.
- It is caused by a fungus, Phytophthora palmivora.
- It commonly occurs during the monsoon season.
- Infected pods develop a pale brownish color, leading to deterioration in the quality of cocoa beans.
- Preventive Measures:
-
- Phytosanitation and prophylactic spraying with a 1% Bordeaux mixture are effective methods for preventing black pod disease in cocoa.
|
-
- Ideal temperature: The ideal temperature range is 15°-39°C, with 25°C considered optimal.
- Soil Conditions: Most cocoa cultivation areas use clay loam and sandy loam soils.
- Shade Requirements: Commercial cocoa cultivation requires around 50% sunlight.
Cultivation of Cocoa in India
In India, cocoa is primarily grown in Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu, often as a secondary crop alongside arecanut and coconut.
- Ideal Environment:
- Cocoa cultivation thrives in India, particularly in coconut and arecanut gardens.
- These environments provide optimal conditions for cocoa growth.
- Sunlight Accessibility:
- Arecanut gardens allow 30-50% of sunlight to filter through their canopy.
- Cocoa plants benefit from this filtered sunlight, which supports their growth and development.
Factors Affecting Cocoa Prices
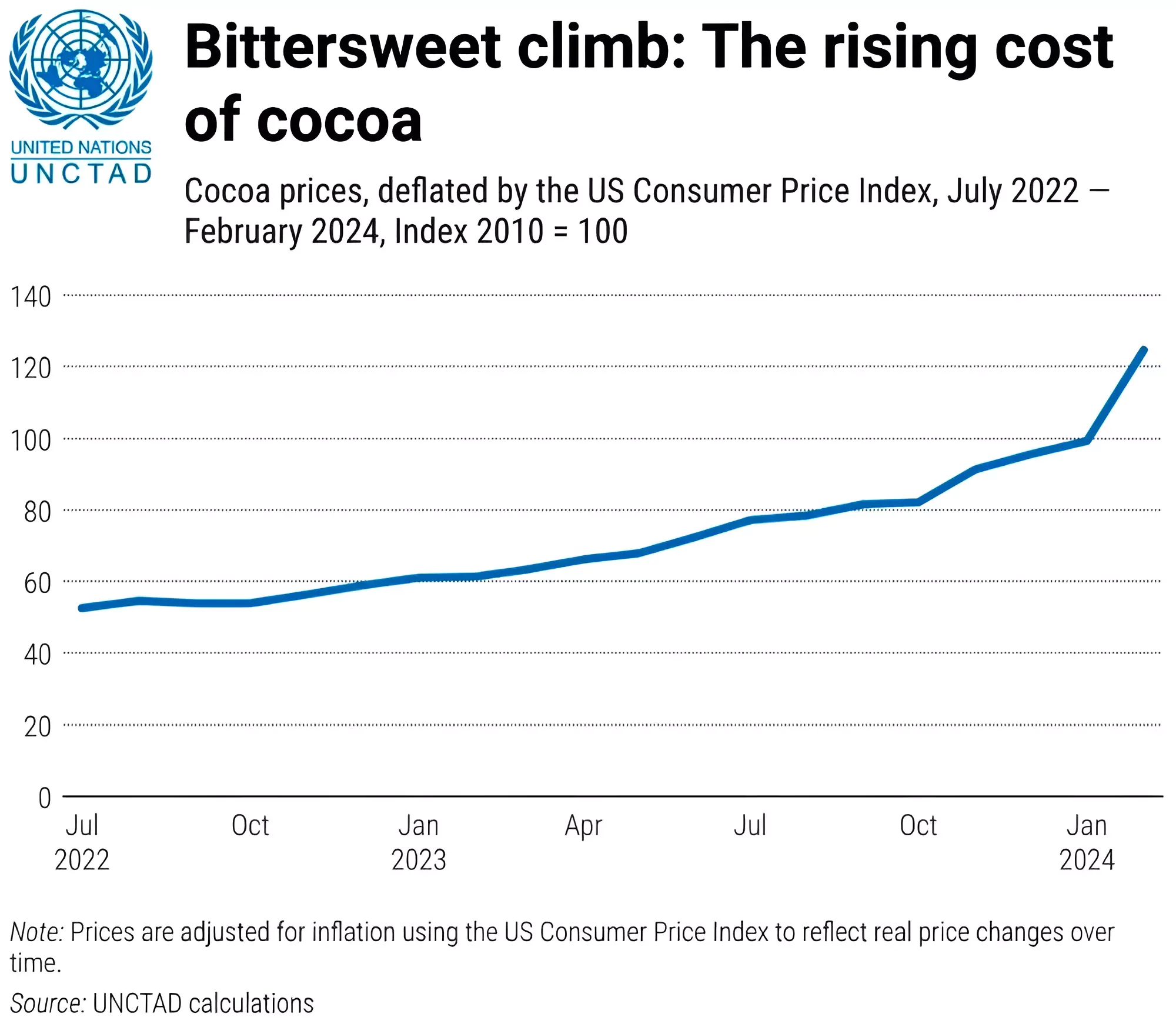
- Climate Factors:
- El Niño Influence: The immediate reason for the crisis is the bad harvest season in West African countries Ghana and Ivory Coast, where 60% of the world’s cocoa beans come from.
- Increased rainfall in West African cocoa-growing regions due to El Niño has facilitated the spread of black pod disease, leading to decreased crop yields.
- The International Cocoa Organization has predicted a shortage of about 374,000 tonnes cocoa beans for the 2023-2024 season than a shortage of 74,000 tonnes last year.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures leading to heat waves, droughts, and erratic rainfall patterns caused by climate change have made cocoa trees more vulnerable to diseases and environmental stress, further reducing yields.
- Economic Challenges for Farmers:
- Low Farmer Income: Cocoa farmers in West Africa earn significantly low incomes, often less than $1.25 a day, which hinders their ability to invest in their farms and improve productivity.
- It’s much lower than the United Nations’ poverty line of $2.15 per day.
- As a result, there is widespread use of slave and child labor on cocoa farms, and farmers are resorting to selling their land to illegal gold miners.
- As a result, there is widespread use of slave and child labor on cocoa farms, and farmers are resorting to selling their land to illegal gold miners.
 Poverty Cycle: Poverty among cocoa farmers perpetuates a cycle of exploitation, preventing them from adopting modern farming practices or adapting to climate change.
Poverty Cycle: Poverty among cocoa farmers perpetuates a cycle of exploitation, preventing them from adopting modern farming practices or adapting to climate change.
- In Ghana, a 2023 report by Oxfam found that around 90% of farmers can’t afford basic necessities like food, clothing, housing, and medical care.
- The survey, conducted among 400 farmers across the country, reveals a concerning trend. Since 2020, the average income of these farmers has decreased by 16%, with women experiencing an even steeper decline of nearly 22%.
- Nine out of ten farmers have been reported being worse off financially since the pandemic.
- Industry Practices:
- Lack of Fair Compensation: Major chocolate companies prioritize keeping consumer prices low, leading to minimal investment in improving the livelihoods of cocoa farmers.
- Sustainable Farming Challenges: With low income and limited resources, cocoa farmers struggle to implement sustainable farming practices or invest in resilience against climate change.
- Exploitative Practices: Despite substantial profits, chocolate companies have not adequately addressed the plight of cocoa farmers, contributing to ongoing exploitation and poverty.
- Potential Escalation: Unless there are substantial changes in how the industry operates, the cocoa price crisis is expected to continue. This could worsen the exploitation of farmers and potentially lead to higher chocolate prices.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Also Read: Agriculture Startups In Agriculture Sector
![]() 2 May 2024
2 May 2024


 Poverty Cycle: Poverty among cocoa farmers perpetuates a cycle of exploitation, preventing them from adopting modern farming practices or adapting to climate change.
Poverty Cycle: Poverty among cocoa farmers perpetuates a cycle of exploitation, preventing them from adopting modern farming practices or adapting to climate change.
