![]() 14 Feb 2025
14 Feb 2025
English
हिन्दी

India has been ranked sixth in the Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2025, highlighting its high vulnerability to extreme weather events.
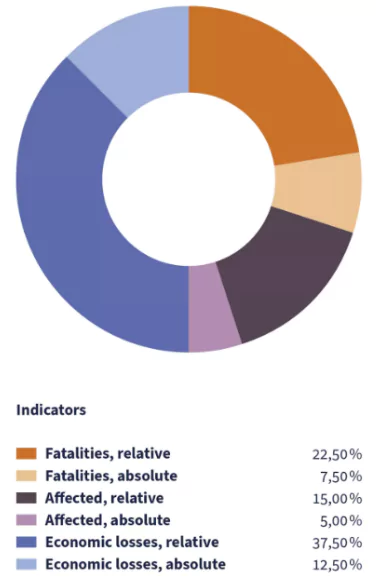 It has been published by Germanwatch since 2006.
It has been published by Germanwatch since 2006. 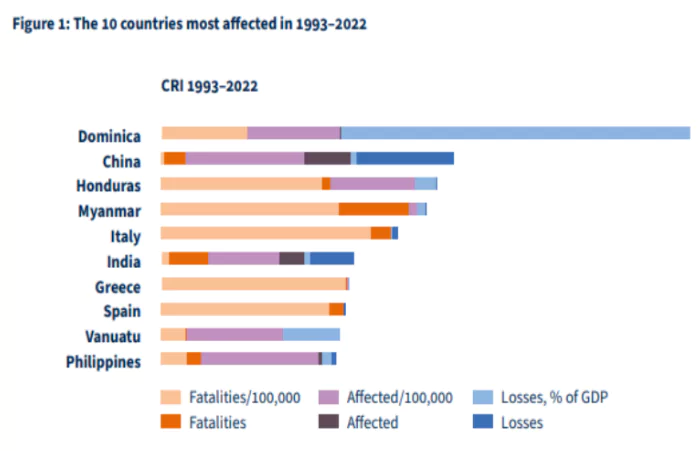
About Germanwatch
Key Publications and Reports
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>