Context
The Commonwealth Secretariat has recognized Centralised Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) of India as a best practice in Commonwealth Secretaries of Public Service meeting held at Marlborough House, London.
Commonwealth Secretariat Recognises India’s Public Redress System as Global best practice
- Theme: The Institutionalisation of SMART Government to enhance public service delivery with focus on adopting AI in governance.
- The forum brought together Commonwealth Heads of Public Service, Secretaries to Cabinet, Senior Public Officials, industry champions, and eminent scholars.
- Objective: It is to share contemporary knowledge, ideas and experiences on how to leverage technology to support provision of e-services for optimal service delivery and to achieve the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development across the Commonwealth
- Outcome Statement: At the Third Biennial Pan-Commonwealth Heads of Public Service Meeting, the commonwealth Secretariat Shared with member countries certain future-ready governance best practices from across the Commonwealth, these are,
- The Centralised Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) of India
- The Civil Registration and Vital Statistics System (CVRS)
- Identity management systems of Namibia
- Human Resource Management and E-Citizen models of Kenya
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Actions taken:
 A stocktaking exercise: To conduct a stock taking exercise on the status of smart governance within the Commonwealth countries and to identify both the success stories as well as the gaps/demand for digital services.
A stocktaking exercise: To conduct a stock taking exercise on the status of smart governance within the Commonwealth countries and to identify both the success stories as well as the gaps/demand for digital services.- A Road Map: To facilitate implementation of agreed actions at country level including the establishment of a Smart Governance Working Group at the Commonwealth Secretariat
- Sharing technology and best practise: To share the work being conducted by the Commonwealth AI Consortium amongst members also the future-ready governance best practices, such as the Centralised Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) of India etc with member countries.
- Assistance: To Continue the provision of technical assistance to support implementation of GAPP principles, including capacity building in government performance management.
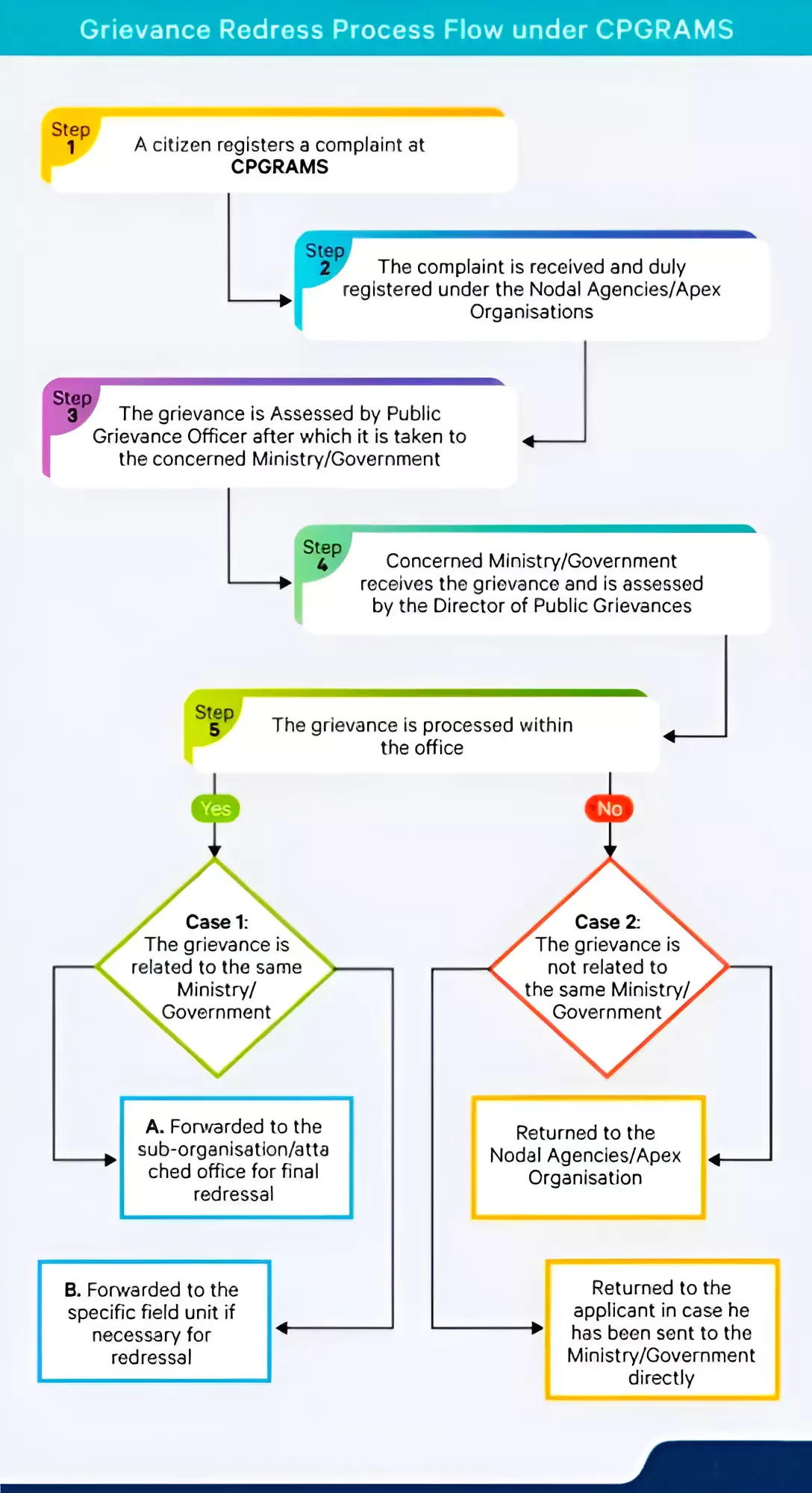
About Centralised Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS)
- It is an online platform available to the citizens 24×7 to lodge their grievances to the public authorities on any subject related to service delivery.
- Implementation Agency: Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievance, Ministry of personnel. Public grievance and Pension.
- Single window: It is a single portal connected to all the Ministries/Departments of Government of India and States.
- Accessibility: Every Ministry and States have role-based access to this system and is accessible to the citizens through standalone mobile application downloadable through Google Play store and mobile application integrated with UMANG.
- Features:
- Tracking: The grievance status can be tracked with an unique registration ID provided at the time of registration of the complainant.
- Feedback and appeal: After closure of grievance if the complainant is not satisfied with the resolution, he/she can provide feedback. If the rating is ‘Poor’ the option to file an appeal is enabled.
- The status of the Appeal can also be tracked by the petitioner with the grievance registration number.
- Exempted Issues:
-
- RTI Matters
- Court related / Subjudice matters
- Religious matters
- Grievances of Government employees concerning their service matters including disciplinary proceedings etc. unless the aggrieved employee has already exhausted the prescribed channels.
The Commonwealth
The Commonwealth is often described as a ‘family’ of nations. It is one of the world’s oldest political associations of states (beginning 1887) with roots in the British Empire.
- Modern Commonwealth of Nations: It was born at the Commonwealth Prime Ministers meeting in London in 1949 with the London Declaration opening up the membership of commonwealth to all.
- Membership: It is a voluntary association of 56 independent and equal countries including India.
- The membership is open to all countries with the last two countries to join the Commonwealth being Gabon and Togo in 2022.
- Commonwealth member countries are also supported by a network of more than 80 intergovernmental, civil, cultural and professional organisations
- Vision and Goals: Shared goals like development, democracy and peace were agreed upon by Member countries with the values and principles of Commonwealth expressed in the Commonwealth Charter.
- Intergovernmental organizations:
- The Commonwealth Secretariat: It supports member countries to achieve the Commonwealth’s aims.
- The Commonwealth Foundation
- The Commonwealth of Learning: It promotes open learning and distance education.
- International Headquarters: Marlborough House on Pall Mall in London.
|
Also Read: SEBI Scores 2.0: Complaint Redress System Of SEBI
![]() 26 Apr 2024
26 Apr 2024
 A stocktaking exercise: To conduct a stock taking exercise on the status of smart governance within the Commonwealth countries and to identify both the success stories as well as the gaps/demand for digital services.
A stocktaking exercise: To conduct a stock taking exercise on the status of smart governance within the Commonwealth countries and to identify both the success stories as well as the gaps/demand for digital services.