Context

Recently, under the aegis of Strategic Forces Command a new version of Medium-Range Ballistic Missile successfully launched in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
About Crystal Maze 2
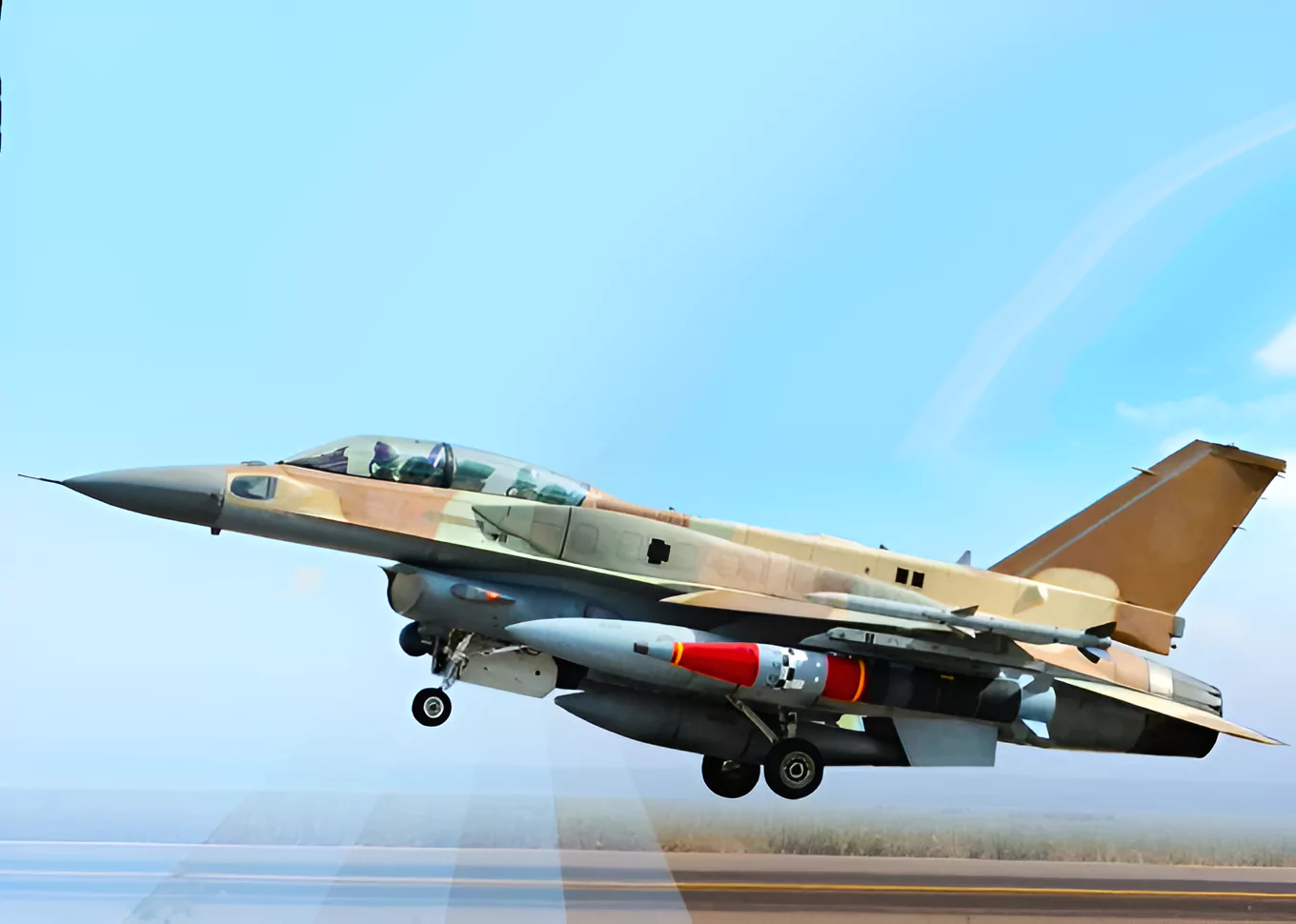
Crystal Maze 2 is an extended stand-off range air-to-surface ballistic missile of Israeli origin, also known as ROCKS.
- The missile, launched from a Su-30 fighter jet by the IAF.
- This missile inherits many technologies from Popeye and SPICE which was used in the Balakot strike.
- Popeye Missile : The Israeli-built Popeye is a medium-range conventional missile which can be fired from a stand-off distance of around 90 km, i.e., the aircraft doesn’t need to be vertically above the target to hit it.
- SPICE : SPICE (Smart Precise Impact and Cost Effective guidance kit)-2000 is mounted on a standard 2000-pound Mk 84 unguided bomb. This converts it into smart guided air-to-surface munition that can be dropped from a stand-off distance of up to 60 km.
- It is a “fire and forget” weapon that automatically goes to its target once launched relying only on its navigation/seeker system.
|
Crystal Maze 2 Features:
- This missile has the ability to strike targets located at distances exceeding 250 kilometers.
- It is designed for precision strikes on high-value targets.
- It is capable of engaging heavily fortified positions from long distances, ensuring minimal collateral damage.
- It is renowned for its accuracy and reliability in combat scenarios, making it a preferred choice for missions requiring surgical precision.
- The missile’s integration into various platforms enhances its operational flexibility and effectiveness in diverse combat environments.
- It operates effectively in GPS-denied areas like the one India faced during the Kargil War.
- It can breach regions secured by air defense systems.
- This system allows for the choice between penetration or blast fragmentation warheads, making it suitable for targeting both surface and heavily fortified underground facilities.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Significance for India: The Indian Air Force (IAF) has successfully conducted tests on this missile and aims to procure it in large numbers under the Make in India initiative. This move highlights India’s dedication to achieving self-sufficiency in defense manufacturing.
What is a Ballistic Missile and Why is it Named So?
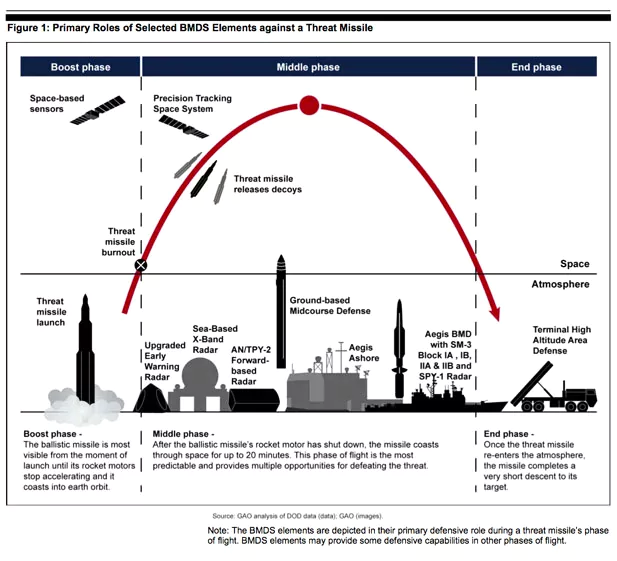
- A Ballistic missile follows a ballistic flight path which comprises three phases of flight:
- First phase or the Boost Phase: The solid-fuel rocket engine propels the missile upward, requiring it to swiftly attain velocity and altitude as it penetrates through the dense layers of Earth’s atmosphere.
- Second and unpowered phase of flight: It happens in the upper reaches of the earth’s atmosphere or in space, where the missile travels along its pre-determined path, but without the power of its engines.
- It is known as the coast phase or mid-course phase and during this time, it travels along a horizontal path.
- During the coasting, the missile is either in space or the upper atmosphere, where it faces minimal resistance or drag.
- Third and final phase or the terminal phase: The missile descends and gets back into the earth’s atmosphere and flies towards its target, while being guided by its on-board systems.
Strategic Forces Command (SFC):
- It is also sometimes known as Strategic Nuclear Command, forms part of India’s Nuclear Command Authority (NCA ,which is responsible for command and control decisions regarding India’s nuclear weapons programme).
- The SFC is incharge of handling the country’s nuclear arsenal, while the DRDO is responsible for developing weapons systems and related military technologies.
- It was created on 4th of January, 2003
- It comprises personnel from the Indian Army, Navy and Air Force.
- The Commander-in-Chief (CinC), a 3-star General, is appointed on a rotational basis from the three services.
|
Also Read: List of Indian Missiles
![]() 26 Apr 2024
26 Apr 2024

