PM Fasal Bima Yojana
Context:
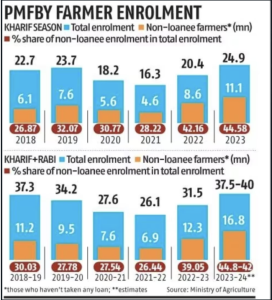
In the recently concluded Kharif season, the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) saw a surge in farmer enrollment, reaching 25 million farmers.
- Of these, 44.5% (11.1 million) are non-loanees, indicating a growing voluntary acceptance of the scheme.
- This enrollment figure is the highest since 2018.
Expected Enrollment and Crop Coverage for 2023-24:
- It is estimated that in the fiscal year 2023-24, 37.5-40 million farmers may enroll in the scheme.
- Of these, 42-45% could be non-loanee farmers.
- The scheme is expected to cover 57.5-60 million hectares of land, an increase from 49.7 million hectares in 2022-23.
About PMFBY:
- Launched: 2016
- Administered by: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
- Eligibility: Farmers, including sharecroppers and tenant farmers, cultivating notified crops in designated areas
- Objectives: Provide insurance coverage and financial support in case of crop failure due to natural calamities, pests, or diseases.
- Premium Rates: Uniform premium rates: 2% for Kharif crops, 1.5% for Rabi crops.
Share of Women in Workforce
Context:
The government has introduced the Narishakti Vandan Adhiniyam to provide 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and state assemblies.
- This effort aims to increase women’s representation in politics, addressing gender disparities in political participation compared to their declining participation in the economy.
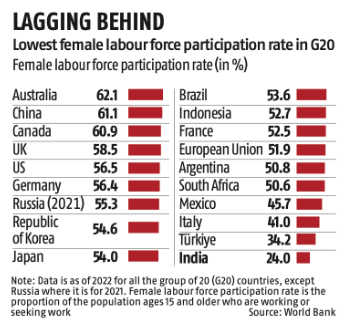
Declining Female Labor Force Participation:
- India’s female labor force participation rate is just 24%, the lowest among G20 countries.
- In contrast, Australia, China, and Canada have rates exceeding 60%, while even BRICS peers like Brazil, South Africa, and Russia have rates over 50%.
- Female labor force participation rate measures the proportion of the population aged 15 and older who are either working or seeking employment.
Decline in Employed Women:
- Over the past seven years, the number of employed women in India has fallen by a third.
- In 2016-17, there were 68 million women in a labor pool of 446 million (15%).
- In FY23, there were 45 million women out of a total labor force of 439 million (10%).
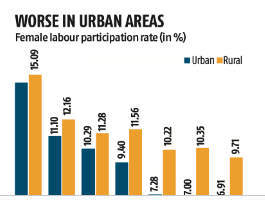
Urban and Rural Disparities:
- In FY17, female labor participation was around 15% in both urban and rural India.
- By FY23, their share in the total workforce dropped to 7% in urban areas and 9.7% in rural regions.
Ownership of Assets:
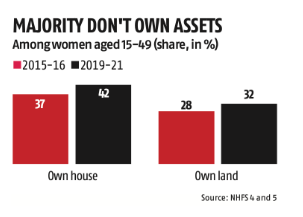
- According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS), female land ownership increased from 37% in 2015-16 to 42% in 2019-21.
- House ownership also increased from 28% to 32%, but these figures remain relatively low.
![]() 20 Sep 2023
20 Sep 2023



