Context
Dengue fever is spreading across regions such as southern Europe and the United States as the planet is getting warmer.

- Aedes is increasing risk of getting dengue by 2bn people
About Dengue fever
This fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease.
- Transmission of disease: A bite from Infected Aedes can transmit dengue fever if the mosquito is carrying a flavivirus pathogen.
- The Aedes species is a mosquito, such as Ae. aegypti or Ae. albopictus.
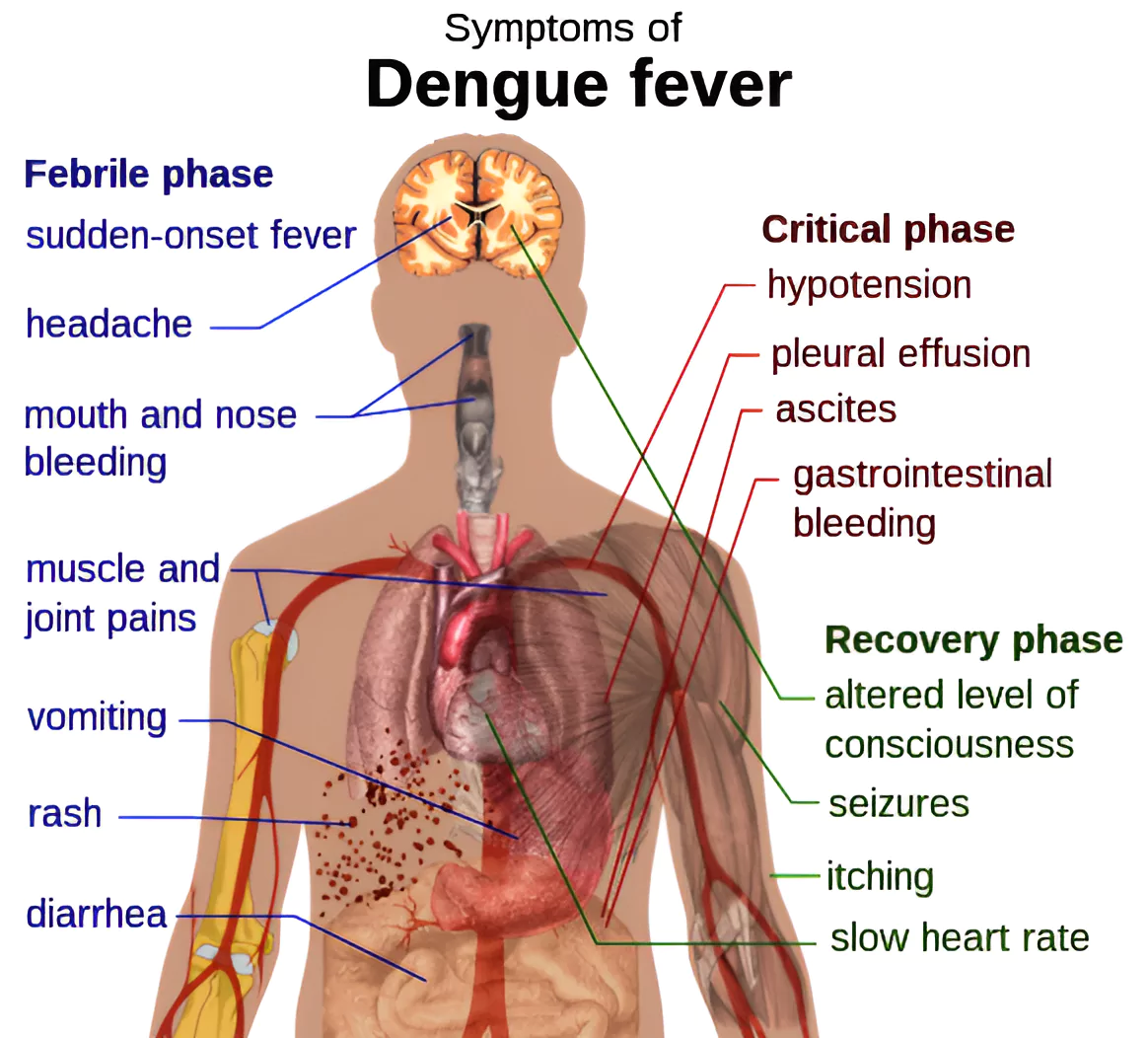
- Its symptoms typically begin 3 to 14 days after infection.
Statistics of Dengue fever
Dengue feveris common in tropical and subtropical regions due to various reasons
- The climatic conditions of Tropical and subtropical regions are warm and humid.
- Tropical and Subtropical regions are dense.
- Increase in Dengue fever Deaths: In 2000, approximately 20,000 people died from dengue, as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Current Year Data: This year, the death toll is expected to reach at least 40,000, marking a significant rise in fatalities.
- Contrast with Malaria:
- In contrast, malaria deaths decreased by 30% between 2000 and 2022, according to WHO data.
- Impact of Dengue fever on India
- 1950 and 1960: Dengue fever was concentrated in southeast Asian countries.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Year |
Dengue cases in India |
| 2017 |
188,401 |
| 2018 |
101,192 |
| 2019, |
157,315 |
| 2021. |
193,245 |
| 2022 |
110,473 |
-
-
- It started prevailing worldwide in 1970
- In India, This disease spread by 2012–13.
- Decade Trend
- Over the decades from 1951–60 to 2012–21, the number of favorable months for dengue transmission in India increased annually by 1.69%.
- Dengue cases in India: Each year, dengue cases surpass lakhs cases in India.
- It causes tremendous pressure on the Indian healthcare system.
- During pandemic 2020, dengue incidence had decreased by 56-60%.
- Highest Dengue cases: Dengue cases were highest in 2021.
- Again in 2022, the case declined
Factors Contributing to Dengue fever Spread
-
Climate Change and Mosquito Range:
- Higher temperature sensitivity: Higher temperatures and humidity create favorable conditions for mosquito breeding.
- Due to current climate trends, Aedes could spread to southern Europe and the United States.
-
Urbanization:
- Favorable condition: Urbanization facilitates the spread of dengue as mosquitoes find more hosts in densely populated areas.
- Dengue cases are increasing in previously unaffected regions like Bangladesh, India, California, southern Europe, and subtropical Africa.
-
Water Storage Practices:
- Breeding in stagnant water: Aedes mosquitoes breed in stagnant water, which is commonly found in containers and water storage vessels.
- Improper water storage practices, such as open containers and neglected water sources, create ideal breeding sites for mosquitoes, leading to higher dengue transmission rates.
-
Lack of Effective Vector Control:
- Inadequate vector control: lack of measures, such as mosquito surveillance and elimination programs, contribute to the continued spread of dengue.
- Limited resources and infrastructure: lack of proper infrastructure and limited resources in some regions hinder efforts to effectively control mosquito populations and prevent dengue outbreaks.
Innovative Approaches to Dengue Control
- Singapore’s Approach:
- Singapore uses both traditional methods and innovative strategies like releasing mosquitoes infected with wolbachia bacteria.
- Since 2016, Singapore has implemented a technologically advanced dengue program.
- This method, combined with vaccine development, offers a promising alternative to traditional mosquito control.
 Vaccine in India: Currently, there is no approved vaccine in India.
Vaccine in India: Currently, there is no approved vaccine in India.
- However, Initiatives are going on for “Dengusiil”.
- Impact of Wolbachia:
- Trials in Colombia: These trials have shown a significant reduction in dengue cases where wolbachia-infected mosquitoes were released.
- largest wolbachia-mosquito factory: Brazil is set to host the world’s largest wolbachia-mosquito factory.
- This initiative will help other regions to combat dengue.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Also Read: Cancer Prevalence In India
![]() 29 Apr 2024
29 Apr 2024


 Vaccine in India: Currently, there is no approved vaccine in India.
Vaccine in India: Currently, there is no approved vaccine in India.
