Context:
India’s Net Direct Tax Collection rises 20.25% YOY to Rs.15.60 lakh crore, reaches over 80% of FY24 Target.
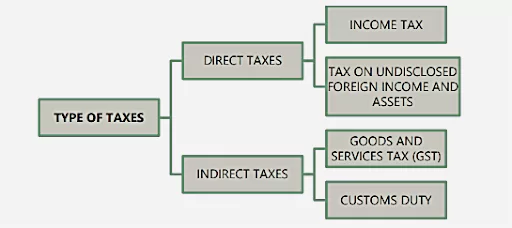
About Direct Tax
- Direct taxes are imposed directly on individuals and organizations based on their income, wealth, or ownership of property. i.e. Individuals and organizations pay taxes directly to the government (e.g., tax agency) without any intermediary.
-
Characteristics of Direct Taxes:
-
- Tax Incidence on the same entity: it can’t shift the burden to someone else.
- Progressive in Nature : The tax rate increases as income or wealth increases. Which promotes a sense of fair distribution of the tax burden based on ability to pay.
- Regulated by: Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT).
|
Key Data On Direct Tax Collection: By Finance Ministry
-
Overall Growth & Performance:
- Gross collections amount to Rs. 18.38 lakh crore, showing year-on-year growth of 17.30%.
- Net collections at Rs. 15.60 lakh crore, up 20.25% year-on-year. Represents 80.23% of revised target for FY 2023-24.
-
By Tax Type:
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT):
- Gross growth rate is 9.16% year-on-year. Net growth rate is 13.57% year-on-year. Personal Income Tax (PIT):
- Gross collections up 25.67% (PIT only) / 25.93% (including STT) year-on-year.
- Net collections up 26.91% (PIT only) / 27.17% (including STT) year-on-year.
- Refunds: Rs. 2.77 lakh crore issued in refunds between April 1st, 2023 and February 10th, 2024.
Also Read: Direct Tax To GDP Ratio Rose To 15-year High In FY23
Corporate Income-Tax (CIT):
- The income-tax paid by domestic companies, and foreign companies on their income in India is corporate income-tax (CIT).
5 heads of Personal Income Tax (PIT):
- Income from salary
- Income from house property
- Income from profits and gains from business or profession
- Income from capital gains
- Income from other sources
STT ( Security Transaction Tax): It is a direct tax levied on every purchase and sale of securities that are listed on the recognized stock exchanges in India. |
Government Initiatives to Improve Direct Taxes:
-
Reduction in tax rates:
- Corporate Tax Rates were Reduced : from 30% to 25.17% (including surcharge and cess) for existing domestic companies.
-
Promotion of Technology in Tax Department:
- Faceless E-assessment Scheme (2019) & Faceless Appeals(2020): It removes direct interaction between taxpayers and assessing officers/ appellate authorities fostering transparency and reducing bias.
- Document Identification Number (DIN): (2019), a unique DIN is assigned to every communication related to tax matters, facilitating easy tracking and verification
-
Reducing litigation by providing tax certainty:
-
- Advance Pricing Agreements (APAs): It allows taxpayers and tax authorities to pre-agree on how to price international transactions, minimizing future disputes and fostering certainty.
- FY 2022 saw a record 95 APAs signed, highlighting the program’s success in reducing litigation
- Vivad se Vishwas Act, 2020: This initiative provides a window for settling pending direct tax disputes, offering reduced penalties and fees for timely resolution.
- By offering a streamlined process and reducing litigation costs, the Act promotes certainty and encourages dispute resolution.
Overall, the direct tax collection figures indicate robust growth revenue, with both Corporate & personal income tax contributing a steady increase. The Steady growth in tax collections reflects positively on the fiscal health of the country during the current fiscal year.
Also Read: Regional Disparity In GST Collections
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 12 Feb 2024
12 Feb 2024