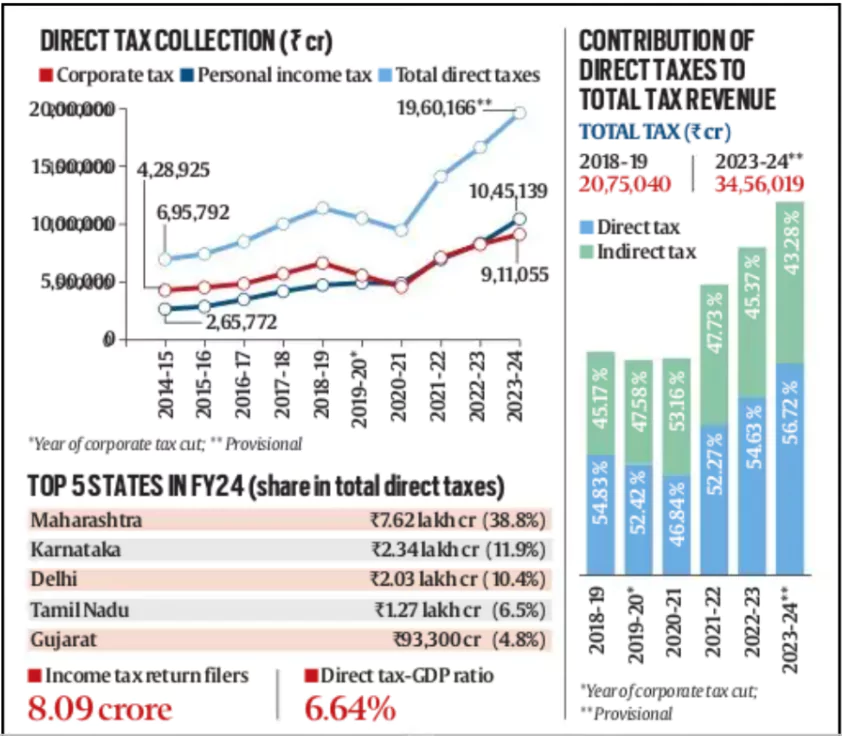
Data released by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) under the Ministry of Finance shows contribution of direct taxes to total tax revenue climbed to 56.72 per cent in FY24, the highest in 14 years.
Key Highlights of the Data
- Direct tax-to-GDP ratio is the share of direct taxes in the overall economic output in the country.
- Direct tax-to-GDP ratio jumped to over a two-decade high of 6.64 per cent
- Direct tax to total tax revenue : Increased to 56.72 % from last year 54.63 %
- Indirect taxes to total tax revenue: Reduced to 43.28% from last year’s 45.37%.
- In 2020-21 → Indirect Tax > Direct Tax
Tax Payer
- A taxpayer is a person who either has filed a return of income for the relevant Assessment Year (AY) or in whose case tax has been deducted at source in the relevant financial year but the taxpayer has not filed the return of income.
|
- State-wise Contribution in direct tax: Maharashtra (39 %) > Karnataka (12%) > Delhi (10.4%)
- Tax Buoyancy: Explains the relationship between the changes in the government’s tax revenue growth and the changes in Gross domestic product (GDP).
- When a tax is buoyant the revenue increases without increasing the tax rate.
- Tax Buoyancy grew to 2.12 in 2023-24 from 1.18 in the previous financial year.
- Increase in Income tax filers: The increase in collections was accompanied by an increase in returns filed, income tax return filers and taxpayers.
- Income tax return filers increased to 8.09 crore in FY24 from 7.4 crore in FY23.
- In the assessment year 2023-24 taxpayers increased to 10.4 crore(FY23) from 9.37 crore( FY22).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
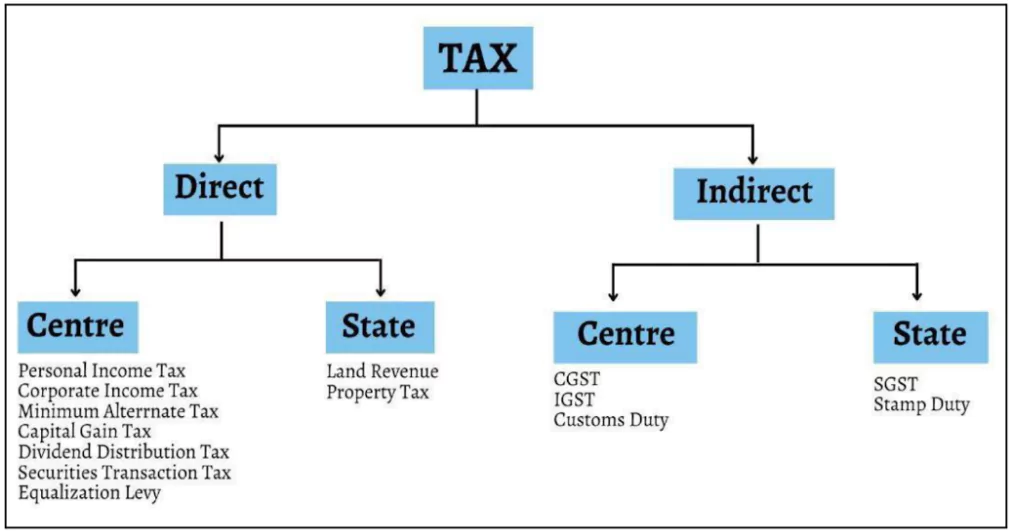
Classification of Taxation in India
| Parameter |
Direct Tax |
Indirect Tax |
| Liability |
- Direct taxes are levied directly on individuals and businesses based on their income, profits, or assets
|
- Indirect taxes are imposed on goods and services rather than directly on individuals or businesses.
|
| Payment |
- Paid entirely by a taxpayer directly to the government.
|
- Ultimately paid by the end-consumer of goods and services
|
| Nature |
- Progressive in Nature : Tax rate increases with increase in income level.
- So, Direct Taxes are considered as progressive tax.
|
- Regressive in Nature: Tax rate is the same for all, irrespective of the income level
|
![]() 18 Oct 2024
18 Oct 2024

