![]() 10 Feb 2024
10 Feb 2024
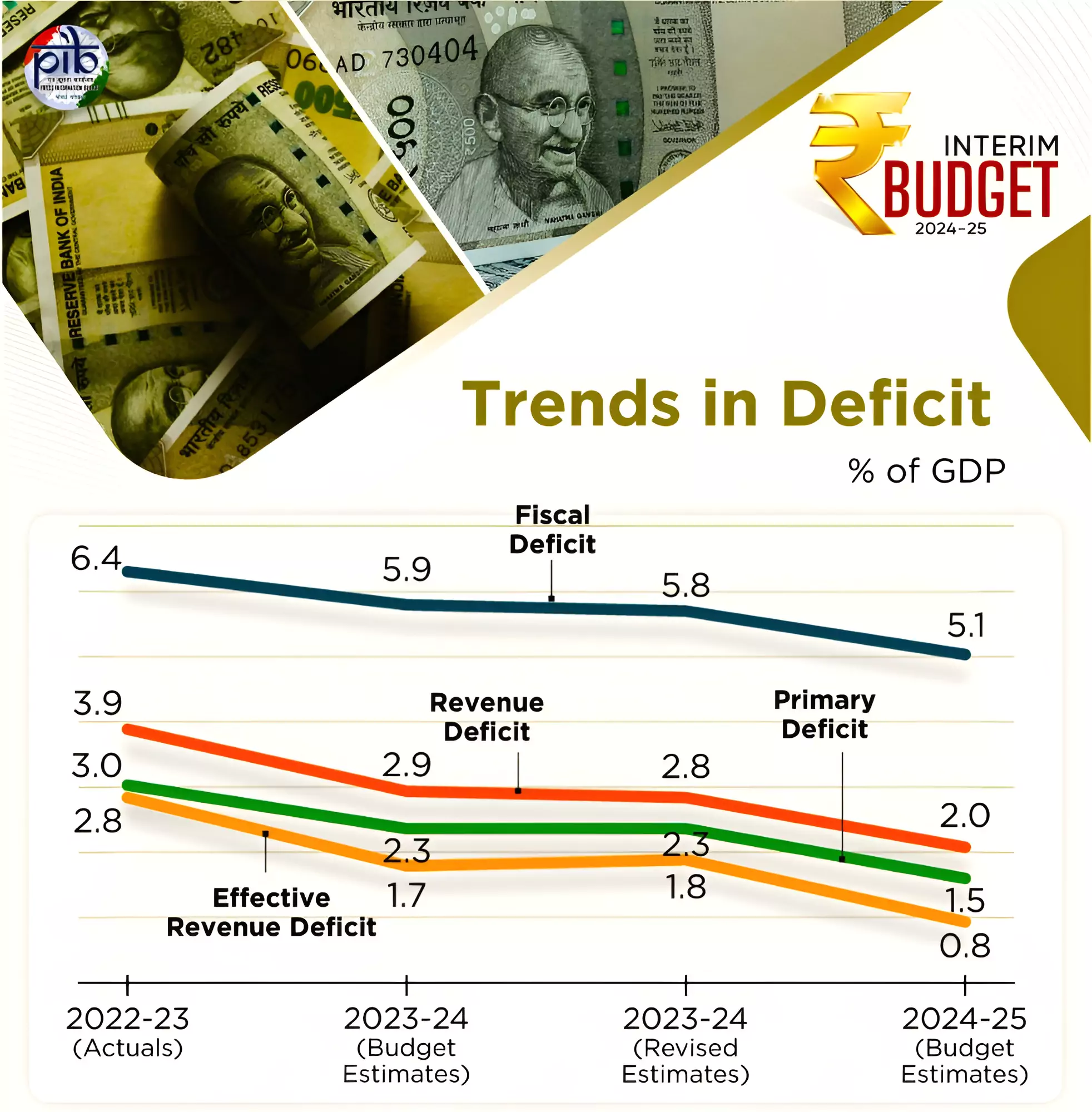
In her interim budget 2024-25 speech Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced that the centre would reduce its fiscal deficit to 5.1% of GDP in 2024-25.
Positive Aspect of Fiscal Deficit |
Negative Aspect of Fiscal Deficit |
|
|
Legislation Related to Fiscal Management in India
|
|---|
Fiscal consolidation measures can involve tough policy choices and may have short-term economic costs including reduced public spending but it underscores the importance of structural reforms to enhance productivity and competitiveness.
Also Read:
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>