Context: The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the UN Women recently released a report Gender Related Killings Of Women And Girls (Femicide/Feminicide).
Gender Related Killings Of Women And Girls – Key Findings From the Report
- Surge in Female Homicide: Globally, nearly 89,000 women and girls were killed intentionally in 2022, marking the highest annual figure in the past two decades.
|
What is femicide?
- It can be defined as intentional killings committed on the grounds of gender related factors.
- Ideology: These can include the ideology of men’s entitlement and privilege over women, social norms regarding masculinity, and the need to assert male control or power, enforce gender roles, or prevent, discourage or punish what is considered to be unacceptable female behavior.
- Outcome: Femicide represents the lethal endpoint of a continuum of multiple, overlapping and interconnected forms of gender based violence.
- For example: Such homicides usually follow prior experiences of physical, sexual or emotional abuse.
About the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC):
- Mandate: UNODC is mandated to assist Member States in their struggle against illicit drugs, crime, and terrorism.
|
- Despite an overall decline in global homicide numbers in 2022 following a spike in 2021, the incidence of female homicides shows no signs of reduction.
- Homicide refers to the killing of one human being by another.
- Violence Perpetrator: Female homicides perpetrated by current or former intimate partners account for an average of 63% of all female intimate partner/family-related killings.
- In 2022, approximately 48,800 women and girls globally were killed by their intimate partners or other family members.
- Gender dimension of homicide: Women and girls are disproportionately affected by homicidal violence in the home.
- They represent approximately 53% of all victims of killings in the home and 66% of all victims of intimate partner killings.
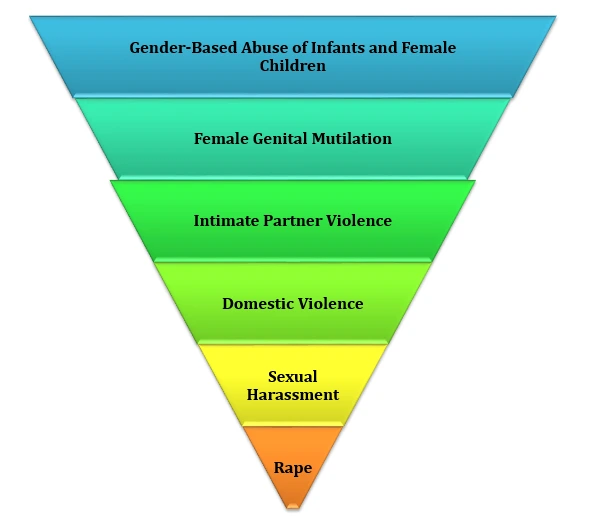
- Regional differences: In Africa, women and girls are at greatest risk of being killed by their intimate partners or other family members.
- In 2022, the female intimate partner/family-related homicide rate in Africa was estimated at 2.8 per 100,000 female population, compared with 1.5 in the Americas, 1.1 in Oceania, 0.8 in Asia and 0.6 in Europe.
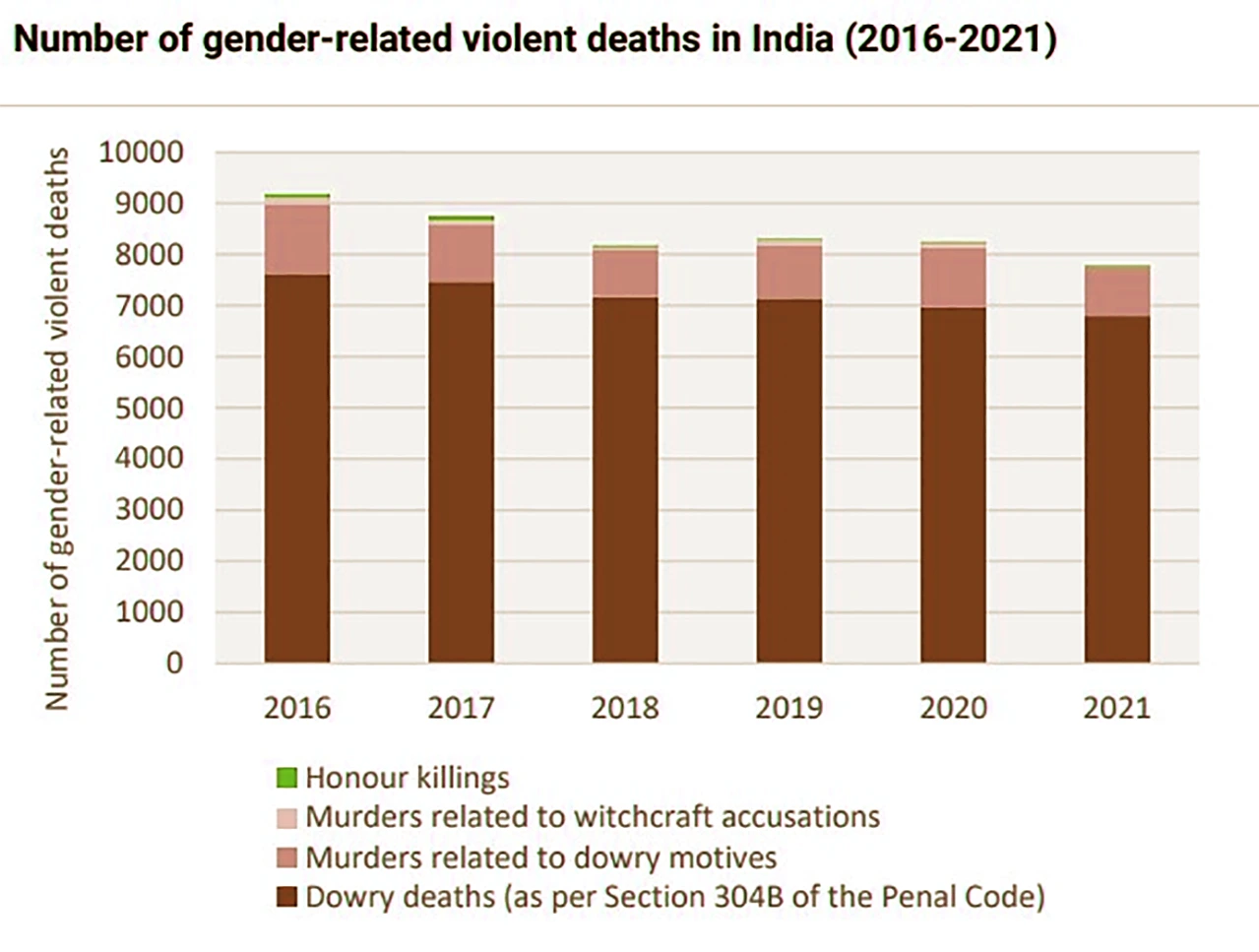
- Status in India: In India, fatalities linked to dowry disputes, allegations of witchcraft, and other gender-related factors have exhibited a gradual decrease over the past decade.
National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) Report 2021:
- Status of gender related crime in India: Rise in crime rate: The rate of crime against women (the number of incidents per 1 lakh population) increased from 56.5 percent in 2020 to 64.5 percent in 2021.
About National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB):
- It was established in 1986 as a repository of information on crime and criminals based on the recommendations of the Tandon Committee under the Ministry of Home Affairs (1985).
|
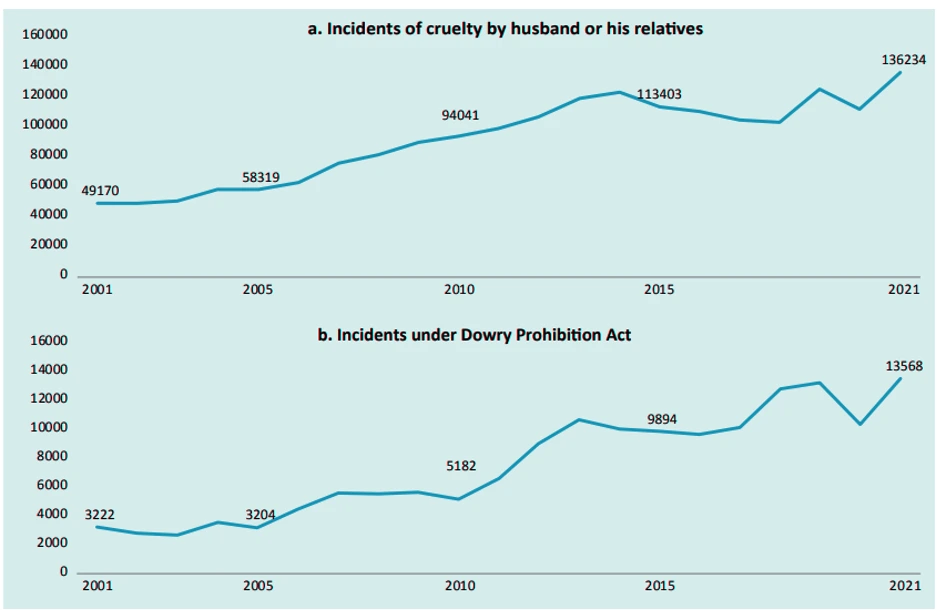
- Gender Based Violence: The majority of cases (31.8%) are classified under “Cruelty by husband or his relatives,” followed by “Assault on women with intent to outrage her modesty” (20.8%), kidnapping and abduction (17.6%), and rape (7.4%).Cases registered: Uttar Pradesh (UP) registered the highest number of cases (56,083) in 2021 although the rate is comparatively lower at 50.5%.
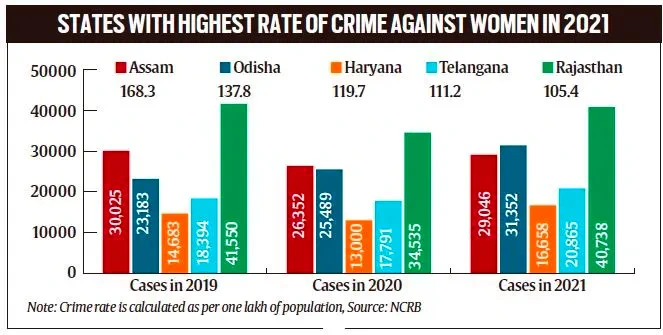
- State with highest crime rate: In 2021, Assam recorded the highest rate of crime against women at 168.3% although there was a slight decrease over the past three years.
- Other states with high rates include Odisha, Haryana, Telangana, and Rajasthan (See Graph).
- State with lowest crime rate: Nagaland distinguished itself with the lowest number of registered crimes against women in the past three years—43 in 2019, 39 in 2020, and 54 in 2021.
- It also recorded the lowest crime rate against women for 2021, at 5.5%.
- Status of U.T: In the category of Union Territories(U.T.), Delhi reported the highest crime rate against women in 2021 at 147.6%.
- Delhi also recorded the highest number of actual cases in the past three years increasing from 13,395 in 2019 to 14,277 in 2021.
Data for crime against women in 19 cities with a population of over 2 million
- Crime rate: Among these cities, Jaipur had the highest crime rate at over 194%, followed by Delhi, Indore, and Lucknow.
- On the contrary, Chennai and Coimbatore, both in Tamil Nadu, exhibited the lowest rates.
- In actual numbers, in 2021, Delhi led with 13,982 cases, followed by Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad.
- Rape cases: In 2021, Rajasthan recorded the highest rape rate at 16.4% and topped the list in actual numbers with 6,337 registered cases.
- Following closely were UP, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
- Rajasthan also reported the highest number of minor girls raped in 2021, with 1,453 cases registered.
What are the reasons behind Gender Based Violence in India?
- Patriarchal Structure of society: Gender based violence against women results from the interplay between discriminating behaviors at the level of the individual, cultural and institutions of societies.
- Examples include discriminatory rules, laws, traditions and customs, as well as misogynistic language.
- Gender norms legitimize and defend gender inequality and violence against women.
- Deep rooted patriarchal mindset in the society foster a cultural environment where gender norms reinforce expectations of male dominance and female subordination.
- Traditional and cultural practices: These are another cause of violence against women. Ex-Age-old practices like Dowry, Child Marriage, and Caste discrimination.
- According to the recent statistics available from the NCRB, in India, there were 25 honor killings reported in each of the years 2019 and 2020 and 33 in 2021.
- Ineffective implementation of laws: Despite existing laws aimed at preventing sexual harassment, their effectiveness in protecting women remains limited.
- Despite the prohibition of the dowry Act, in 2021 alone, 6,589 dowry-related deaths were recorded.
- Lack of awareness: Unawareness about rights, laws, and regulatory mechanisms within the legal system contributes to increased crimes.
- If individuals were well-informed about legal matters, such crimes could be mitigated.
- For instance, an informed victim could use legal knowledge to approach competent authorities, ensuring that justice is pursued and the perpetrator is held accountable.
- Substance abuse: This has emerged as a significant factor contributing to crimes against women such as drug addiction and Alcoholism.
- As per NCRB, in India, domestic violence has been implicated in one-third of suicides among women, and alcohol consumption by the husband has been shown to be strongly associated with the perpetration of violence against the wife.
- Women’s Economic dependence: The economic dependence fosters a perception of superiority among men, leading to the vulnerability of women, who are then subjected to various crimes.
Suggestions From The Report/ Preventing Gender Related Killings Of Women And Girls:
- Enhancing national data collection systems:
- In the current global context, it is imperative to strengthen data systems for assessing the impact of conflicts, environmental crises, and humanitarian emergencies on gender based violence as a whole, with specific attention to gender related killings of women and girls.
- especially, those in public life—politicians, women human rights defenders, and journalists.
- Primary Prevention Initiatives: These multifaceted efforts should aim to establish an evidence-based, comprehensive response to prevent and eliminate gender related killings of women and girls effectively.
- This should be coupled with enhanced social, health, and criminal justice responses and robust victim support and assistance.
- Comprehensive review mechanism: In-depth multistakeholder reviews of gender related killings of women and girls are imperative to improve institutional responses and prevent future killings.
- Several countries, including Australia, Canada, and the United States, have established multi-sectoral committees that conduct regular in-depth reviews of deaths or homicides related to domestic violence.
Respect Women: Comprehensive framework to address gender based violence: It is a comprehensive framework by the UN to address gender based violence against women and girls, Respect Women. It entails the adoption of more than one of the seven strategies, which should not be regarded as silos.
- Relationship skills strengthened
- Empowerment of women
- Services ensured
- Poverty reduced
- Environments made safe
- Child and adolescent abuse prevented
- Transformed attitudes, beliefs and norms
|
- Addressing gaps in the response system: As recommended by the UN Special Rapporteur on Violence Against Women, the femicide watch panels or observatories on violence against women should analyze all cases of femicide, including court cases systematically.
- This will determine gaps in the response system to such violence, and establish risk factors to prevent such violence.
- Strengthening civil society and women’s rights organizations: They play a vital role in preventing gender based violence by advocating normative and policy changes, providing psycho-social support services, and holding governments accountable.
- Ex-The UN’s Spotlight Initiative, funded by the European Commission actively involves civil society, particularly grassroots women’s organizations, in program development, implementation, and monitoring. Also Read: A Safe Workplace for Women
Statutory Provisions related to women in India:
- Dowry Prohibition Act (1961)
- Indecent Representation of Women (Prohibition) Act (1986)
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act (2005)
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act(2006)
- Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention Prohibition and 5 Redressal) Act (2013)
Government Initiatives to check violence Against Women:
- One Stop Centre and Universalization of Women Helplines
- Swadhar Greh Scheme
- Ujjawala Scheme
- Working Women Hostel
- Mahila Shakti Kendra (MSK)
- Nirbhaya Fund
|
Way forward:
-
- Addressing Patriarchy in Institutions: The police, lawyer and other judicial officers need to be sensitised regarding gender equality norms in order to address the deeply entrenched patriarchy and create a gender neutral society.
- Gender Based Legislation: The gender based laws should contain measures to provide women with legal rights to property, land, inheritance, employment and income. This will allow a woman to walk out of an abusive relationship.
-
-
- The Standing Committee on the Empowerment of Women submitted its report, on August 10, 2023, and noted that there is an urgent need to review the National Commission for Women Act, 1990 to make the NCW more independent, and effective.
- It recommended empowering the NCW with a certain degree of accountability over the police to implement their directions and penalties for non-compliance.
- Political and Economic Empowerment of Women: Empowering women involves reclaiming spaces to enhance their visibility by fostering political and economic participation and expanding their involvement in non-traditional sectors.
- Justice Verma’s Committee (2012) Recommendation: The three-member committee constituted to recommend amendments to the Criminal Law so as to provide for quicker trial and enhanced punishment for criminals accused of committing sexual assault against women.
- A Rape Crisis Cell should be set up. The Cell should be immediately notified when an FIR in relation to sexual assault is made. The Cell must provide legal assistance to the victim.
- All police stations should have CCTVs at the entrance and in the questioning room.
- Police officers should be duty-bound to assist victims of sexual offenses irrespective of the crime’s jurisdiction.
- Members of the public who help the victims should not be treated as wrongdoers.
- The police should be trained to deal with sexual offenses appropriately.
- The number of police personnel should be increased. Community policing should be developed by providing training to volunteers.
Conclusion
Addressing the alarming surge in gender related killings of women and girls demands a multifaceted approach, combining legal reforms, societal awareness, and comprehensive support systems, with an urgent need for global collaboration to dismantle the deeply rooted structures perpetuating such violence.
![]() 30 Nov 2023
30 Nov 2023




