Context:
“The Global Cooperation Barometer 2024” has been released by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
About the Global Cooperation Barometer 2024 Report
- McKinsey & Company has collaborated with WEF to prepare it.
- Methodology: It used 42 indicators from 2012 to 2020 to measure five pillars of global cooperation namely:
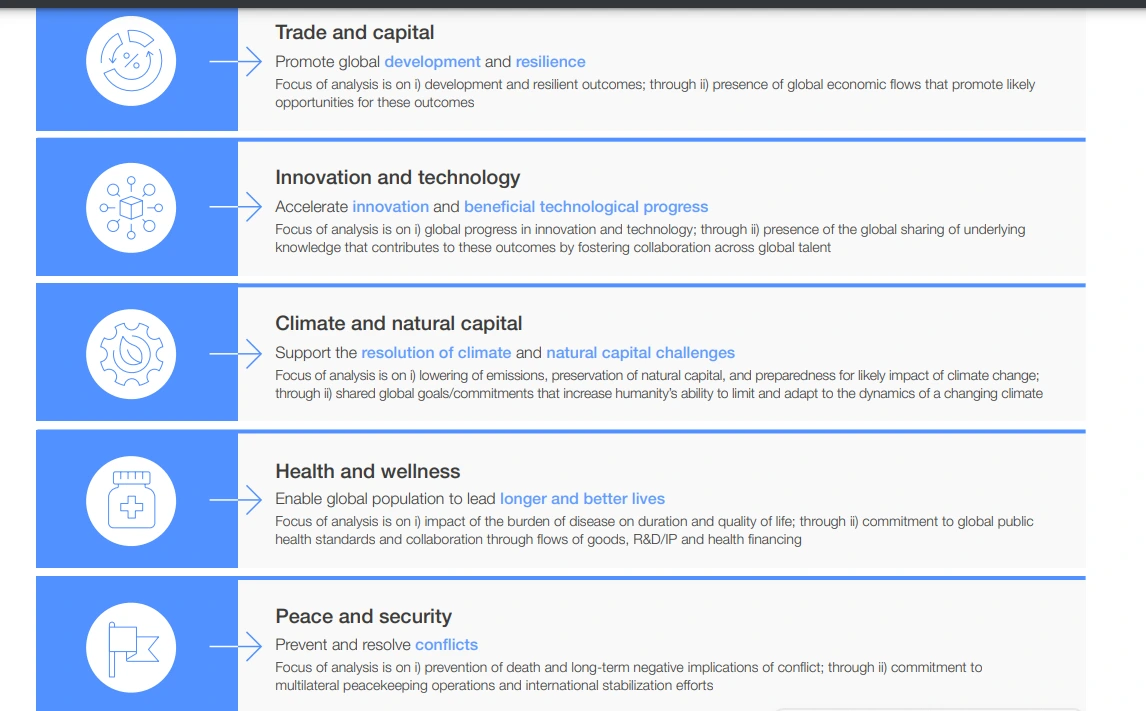
- Utility: It is meant to serve as a tool for leaders to better understand the contours of global cooperation.
Frontier Technology
- Frontier technologies are defined as potentially disruptive technologies that can address large-scale challenges or opportunities.
- Example: Artificial Intelligence.
|
- Challenges: New power dynamics, changing demographic realities and breakthrough frontier technologies.
- They are bringing back the long-simmering distrust rather than fueling opportunities for benefit.
Global Cooperation Barometer 2024 Report Findings
- Broad Trend: Despite demonstrating resilience, cooperation saw a 2 percent decline from 2020 to 2022.
- Trade and capital: Trade and capital cooperation grew through the pandemic disruption, but slowed in 2023; geopolitical tensions and new restrictions make the future path unclear.
- Innovation and technology: Flows of data, IP and international students increased cooperation until 2020, but new questions have arisen about how to work together to harness opportunities.
- Climate and natural capital: The level of cooperation for climate and natural capital has been rising steadily, due largely to increased commitments, but emissions also continue to rise.
- Health and wellness: Cooperation in health and wellness rose swiftly in response to the pandemic, but appears to be returning to historical patterns.
- Peace and security: Cooperation in peace and security has declined since 2016 and has plummeted recently.
- Health Cooperation:
- Positives: Freely available COVID-19 genome, accelerating vaccine development, and health-related aid flowed to emerging economies. GAVI, the Vaccine Alliance, also played a pivotal role in providing basic life-saving vaccines.
- Health outcomes like life expectancy, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and maternal and child mortality improved from 2012 through 2019.
- Before 2020, most indicators of health cooperation, such as health development assistance, trade in health goods and health-related R&D and IP flows, grew slowly and steadily.
- Negatives: Overall life expectancy and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) suffered due to COVID-19-related deaths and the diversion of resources from other health priorities.
- Life expectancy at birth declined to 71 in 2021 from 72.8 in 2019.
- As the immediate impact of COVID-19 subsides, global health cooperation appears to be decreasing but remains above 2019 for certain metrics.
- Communicable Diseases: This means that 14 million more people contracted malaria and 69,000 more people died from it than in 2019.
Global Cooperation Barometer 2024 Report’s Key Recommendations
- The entities prioritizing strong cooperative arrangements are more likely to recover effectively from supply disruptions.
- International partnerships will be crucial for deepening basic research on a variety of health conditions, ranging from chronic disease to clinical trials.
- Sustained cooperation is needed against synthetic drugs globally. Eg- fentanyl, tramadol, methamphetamine, captagon, and ketamine.
Also Refer: Global Risks Report 2024
News Source: DTE
![]() 16 Jan 2024
16 Jan 2024
