![]() 3 Apr 2024
3 Apr 2024
The Steel Ministry has initiated efforts to develop a thorough green steel policy to reduce carbon emissions.

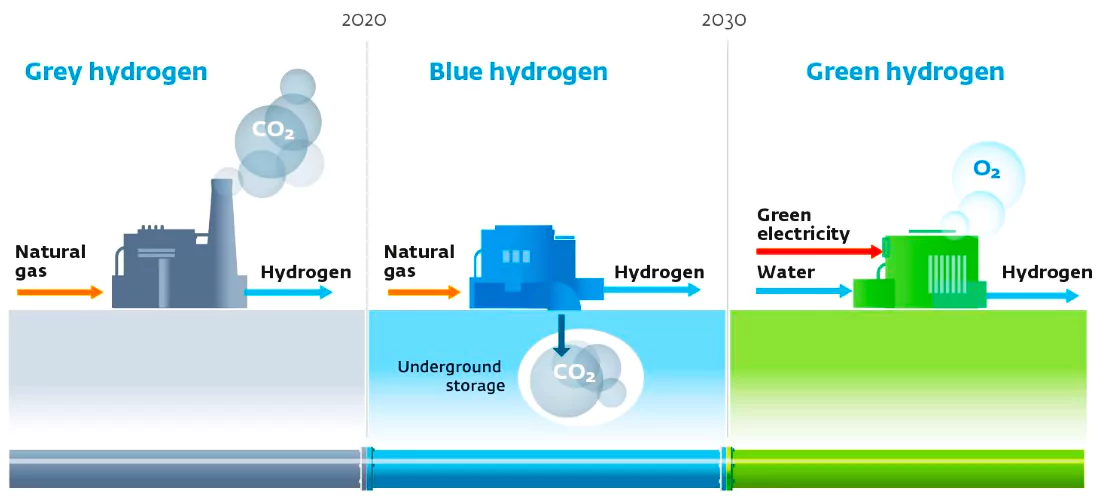 Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen is a solution that emits only water when it’s burned.
Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen is a solution that emits only water when it’s burned.| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|
|
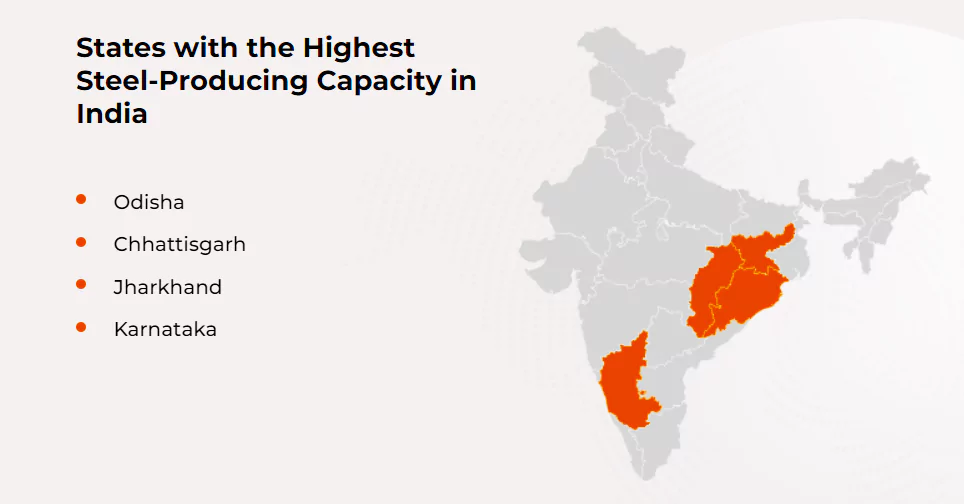 Finished steel production stood at 121.29 MT during the same period.
Finished steel production stood at 121.29 MT during the same period.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>