![]() 18 Mar 2024
18 Mar 2024
The haemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) test is widely used for prevention and early detection of non-communicable diseases, including diabetes (both type 1 and type 2).

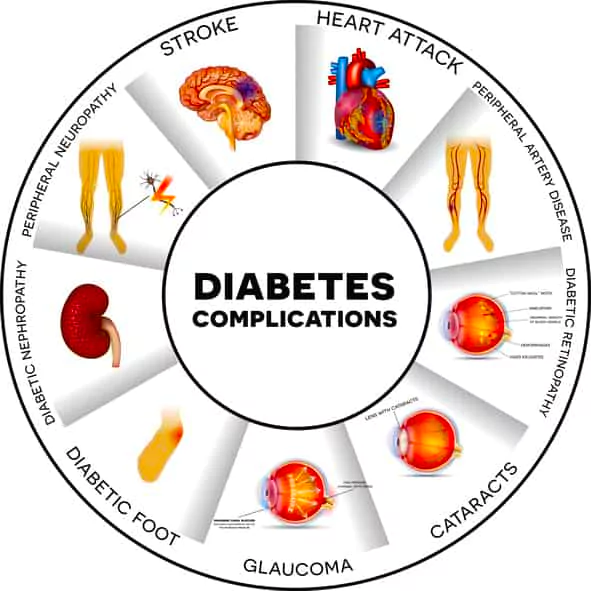 Medications: Use of medications including steroids, opiates, or dapsone (used to treat leprosy) can alter HbA1C readings.
Medications: Use of medications including steroids, opiates, or dapsone (used to treat leprosy) can alter HbA1C readings.News Source: Thehindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

<div class="new-fform">
</div>