![]() 27 Mar 2024
27 Mar 2024
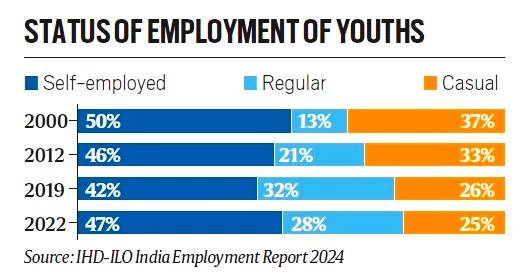
The India Employment Report 2024 recommends five key policy areas for youth in India,
About Institute of Human Development (IHD)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>