Context:
The recent announcement of India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has the potential to make India an Asian hub in global supply chains.
About Supply Chains:
- It is described as global production networks, production fragmentation, or global value chains — refers to the geographical location of stages of production (such as design, production, assembly, marketing, and service activities) in a cost-effective manner.
- Evolution of Supply Chains: Global supply chains emerged as the dominant model in industrial production around the 1980s.
- This shift from local and regional to global supply chains occurred gradually over the last century.
- Scope: Supply chains are prevalent in both simple (e.g., textiles, food processing) and complex industries (e.g., automobiles, electronics, pharmaceuticals).
Factors Driving the Shift in Global Supply Chains Away from China:
- Rising Wages: China’s labor costs have been steadily increasing over the years, reducing its cost advantage as a manufacturing hub.
- Supply Chain Bottlenecks: China’s rapid economic growth led to supply chain bottlenecks, particularly in transportation and logistics.
- Regulatory Concerns: Foreign firms operating in China have faced increasing regulatory scrutiny.
- Recently, the Beijing office of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu was fined 211.9 million yuan ($30.8 million) on charges that it failed to adequately audit state-owned China Huarong Asset Management Co.
- Trade War with the US: The trade tensions and tariffs resulting from the trade war between China and the United States have created uncertainties and risks for companies with supply chains heavily reliant on China.
- In 2018, the Trump administration initiated a trade dispute with Beijing. This led to a series of actions, including the imposition of tariffs by the United States on over $300 billion worth of Chinese goods. In retaliation, China imposed import levies on approximately $100 billion worth of American goods.
- Significant Export Declines: Mainland China and Hong Kong represent 20% of world exports of intermediate goods.
- In the last quarter of 2022:
- Exports from mainland China decreased by 15% year-on-year.
- Hong Kong experienced a more substantial decline, with a 27% year-on-year drop in exports.
- The United States, comprising 8.1% of world exports of intermediate goods, saw a 3% decline in shipments.
- Japan, with a 4% share, faced a 13% decrease in exports.
India’s Emergence as an Attractive Supply Chain Hub:
- Competitive Factors:
- Lower Costs in Southeast Asia: India, like Southeast Asian countries, offers cost advantages to foreign companies, including cheap labor and fiscal incentives.
- Potential Complement to China: India can complement China as a manufacturing hub, benefiting from technology transfers and creating value-added jobs.
- Sophisticated Manufacturing Sectors: India’s automotive, pharmaceutical, and electronics assembly sectors are already advanced, positioning them as potential winners in the global supply chain landscape.
- This is seen in the ramped-up manufacturing of iPhones in the country, early technology transfer in the product cycle of the technologically advanced Mercedes Benz EQS to India, and Foxconn Technology Group developing a chip-making fabrication plant in Gujarat.
Government Initiatives to Boost Manufacturing and Supply Chains
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: Introduced in sectors like automobiles, electronics, and medical devices to incentivize both multinational enterprises and domestic manufacturers.
- PM Gati Shakti Plan and National Logistics Policy: Focus on developing world-class infrastructure and improving logistics capabilities.
- Aims to reduce the cost of logistics from 13-14% of GDP to less than 8%.
- Digital Payments and E-commerce Initiatives: Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has encouraged even street hawkers to adopt digital payments.
- The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) initiative aims to empower small-scale firms in the e-commerce sector, offering various goods and services.
- National Logistics Policy (NLP): In 2022, the central government launched the NLP to ensure the required efficiency in the logistics sector.
- The country has set a goal of raising its LPI score to rank among the top 25 by the year 2030.
|
- Global Perspective:
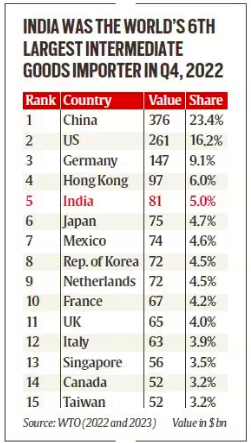
- Shifting Perception: India’s ranking as the fifth-largest importer of intermediate goods in 2022 Q4 suggests a changing perception of its supply chain potential.
- Export Growth Potential: India has the potential to double its 1.5% share of world exports of intermediate goods, indicating its growing role in global supply chains.
- The countries ahead of India are China (23.4%), the US (16.2%), Germany (9.1%), and Hong Kong (6.0%).
- Service Sector Opportunities: India’s service sector, including IT, back-office operations, financial services, and logistics, holds growth potential.
- Trade Policy Initiatives:
- Bilateral Trade Deals: The Indian government’s emphasis on preferential trade through bilateral agreements with partners like the UAE and Australia.
- The UAE-India Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement entered into force in May 2022.
- Australia-India free trade agreement (FTA), and talks are ongoing to conclude the full FTA by the end of 2023.
- Negotiations for a UK-India and EU-India FTA are in process.
| China-Plus-One, or just Plus One refers to a strategy in which companies avoid investing only in China and diversify their businesses to alternative destinations. |
Benefits for South Asia:
- Regional Stability and Economic Growth: As the focus on China+1 increases, India has a historic opportunity to promote industrialisation in South Asia, which would stabilise the region, increase jobs, and make it less vulnerable to Chinese enticements.
- Spillover Effects: Market-led spillovers from India’s supply chains can naturally benefit neighboring countries like Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, leading to job creation and economic growth.
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation: Leveraging India’s dynamic start-up culture and fintech capacity can attract young entrepreneurs from other South Asian nations, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship.
Challenges in Integrating India into Global Value Chains:
- Domestic Policy Challenges: Enterprises in India grapple with complex tax policies and procedures. The substandard quality of infrastructure poses significant obstacles.
- Uncertainty in trade policy adds to the challenges of scaling up production in the country.
- Quality and Institutional Support: Indian firms struggle to meet international quality standards. They often lack the necessary institutional support.
 Inadequate access to essential information further hinders their integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs).
Inadequate access to essential information further hinders their integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs).
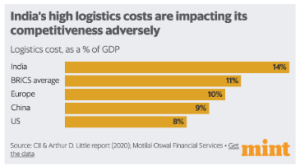
- High Logistics Costs: High logistics costs in India, accounting for around 13-14% of GDP, are impacting its competitiveness adversely compared to developed nations where logistics costs are lower (8-10% of GDP).
Strategies for India’s Future in Supply Chains: Learn from China’s experience
- Promotion of Export-Oriented FDI:
- Maintain an open-door policy for foreign direct investment (FDI) in manufacturing.
- Offer competitive fiscal incentives and create modern special economic zones through public-private partnerships.
- Simplify business processes through digitalization of tax, customs, and administration.
- Pursue high-quality free trade agreements to facilitate global trade.
- Smart Business Strategies for Local Companies:
- Small and mid-sized enterprises should act as industrial suppliers and subcontractors to larger exporters.
- Consider business strategies such as mergers, acquisitions, and alliances with multinationals and large local companies.
- Invest in domestic technological capabilities to meet international standards in terms of price, quality, and delivery.
- Caution in State Intervention:
- Exercise caution when replicating China’s state interventionist model, as it carries the risk of government failure and cronyism.
- Engage with think tanks to gain insights into effective policies and practices.
- Focus on targeted interventions in new industrial activities with comparative advantages.
- Improve coordination between central and state governments.
- Investment in Education:
- Invest in tertiary-level education, particularly in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields to enhance the skill base.
- Policy Initiatives for South Asia: The Indian government should consider two policy initiatives to promote regional supply chains.
- Make in South Asia Programme: Expand the “Make in India” initiative to a “Make in South Asia” program.
- Offer fiscal incentives to Indian manufacturers to expand into Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, focusing on industries like food processing, textiles, apparel, and automotive.
- Comprehensive FTAs: Establish comprehensive bilateral Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with Bangladesh and upgrade the Indo-Sri Lanka FTA.
- Strengthen regional rules-based trade and investment to integrate these countries into supply chain activities centered on India.
Conclusion:
- Unless India creates channels for South Asia, it has no offer for the Global South. The fresh supply chains opening up with the US are a good place for India to start its global integration journey, Neighborhood First.
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 14 Sep 2023
14 Sep 2023

 Inadequate access to essential information further hinders their integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs).
Inadequate access to essential information further hinders their integration into Global Value Chains (GVCs).