A decade on, the Andhra-Telangana bifurcation, several issues relating to the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014 (APRA) remain still pending.
- India’s return to the coalition system of government has seemingly seen old demands rise again. Both Bihar and Andhra Pradesh want special category status.
| Special category status is a classification of regions or states by the central government to provide special assistance in the form of tax benefits and financial support for development of the region. |
About Andhra-Telangana Bifurcation
- Background:
- Formation of Andhra Pradesh, 1956: Andhra Pradesh was formed in 1956 by merging Andhra State with the Telangana region of the erstwhile Hyderabad State on linguistic basis (both regions primarily spoke Telugu).
- Gentlemen’s Agreement (1956): To address the concerns of the Telangana region, this Agreement was signed, promising safeguards in areas like employment, education, and development.
 Bifurcation: The Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act was passed in February 2014, outlined the division of assets, liabilities, and administrative details.
Bifurcation: The Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act was passed in February 2014, outlined the division of assets, liabilities, and administrative details. -
-
- Hyderabad was designated as the joint capital for both states for a period of up to ten years.
- In June 2014, Telangana was formed by separating the northwestern part of Andhra Pradesh by following the States Reorganisation Act of 1956.
- It merged Telugu-speaking areas of Hyderabad state with Andhra to create the enlarged Andhra Pradesh.
- In 1953, the government of India was forced to create the first linguistic state known as Andhra Pradesh by separating the Telugu speaking areas from Madras state.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Demand: The push for a separate Telangana arised due to regional development inequalities.
- Issues: The division of assets and liabilities between Andhra Pradesh and Telangana as outlined in the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act of 2014 is still unresolved.
- Economic and Developmental Issues: Andhra Pradesh had to establish a new capital, Amaravati, and faced significant financial challenges, while Telangana focused on addressing regional disparities and development issues.
- Telangana, with Hyderabad as a major IT hub, had a relatively strong economic base compared to many other regions.
- Political Issue: The bifurcation reshaped political dynamics in both states. The bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh into Telangana posing new challenges for governance and development.
- The Telangana Rashtra Samithi provided stable governance initially, but political challenges remain, especially regarding resource sharing with Andhra Pradesh.
- According to official sources, the division of various institutions and corporations, listed in Schedule 9 and Schedule 10 of the Act, between the two states, has not been completed as there was no consensus over several issues.
- Though an expert committee headed by retired bureaucrat Sheela Bhide gave recommendations on bifurcation of Schedule IX and X institutions, the matter remained unresolved.
- Other Significant Issues: The states are embroiled in some other disputes as well, including over competing claims on pending power generation dues, division of the AP State Financial Corporation’s assets, and over the sharing of Krishna and Godavari waters.
- Raised Questions:
- Aftermath Unresolved Issues: It raises questions about disorderly bifurcation process, unfulfilled promises, and mishandling of asset distribution.
- Other Criteria: As most states are based on language, people are asking if this principle should change such as territory or population instead.
- About the unity of Telugu speaking persons, which seem to be less unified than in other regions such as Kannada and Marathi-speaking.
- Speculation has been arising whether other linguistic groups may encounter similar challenges in the future because of common regional disparities.
- Impact on the Federal Structure: In India, most states are organized based on language. The different sizes of states affects the numbers of seats in the central legislature and hence the unequal representation might strain the federal structure.
- Actions that need to be Taken:
- Establishment of a Permanent Inter-State Council to facilitate communication and resolve disputes.
- Mechanism for Special Financial Assistance to grant special status and economic packages for both states.
- Grant of allocation should be provided for the development of backward regions in both states.
- Establishment of a Judicial Mechanism for Asset Division to resolve disputes as early as possible.
- Need for Governance Reforms such as fixing terms for governors, better representation, and continuous dialogue to bring stability in both regions.
- Prioritize Infrastructure Projects such as connectivity, power, and education to provide economic stability and social justice to the citizens.
Other Inter-State Disputes in India
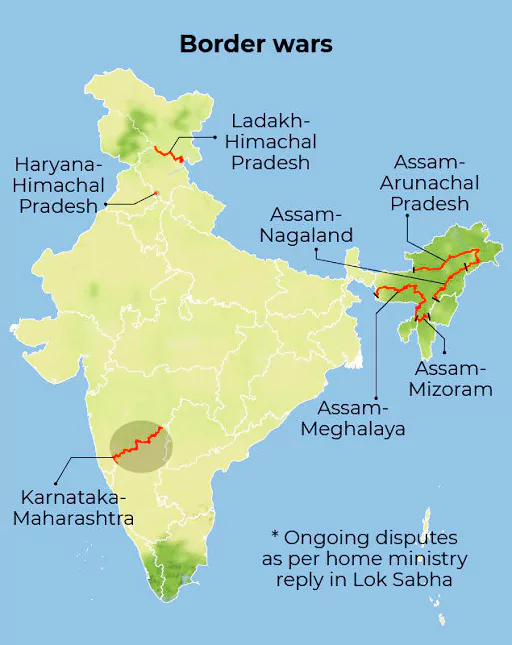
There are border disputes mostly arising out of claims and counter-claims over territories between Assam-Meghalaya, Assam-Nagaland, Assam-Mizoram, Assam-Arunachal Pradesh and Maharashtra- Karnataka.
Mechanisms to Resolve Inter-State Boundary Conflicts
- By Cooperation: Inter-state disputes can be resolved with the cooperation of both sides, with the Centre working as a facilitator or a neutral mediator.
- If issues are resolved amicably, Parliament can bring a law to alter state boundaries, such as the Bihar-Uttar Pradesh (Alteration of Boundaries) Act of 1968 and the Haryana-Uttar Pradesh (Alteration of Boundaries) Act of 1979.
- Judicial Redressal: The Supreme Court in its original jurisdiction decides disputes between states.
- Article 131 of the Constitution: It states that “Subject to the provisions of this Constitution, the Supreme Court shall, to the exclusion of any other court, have original jurisdiction in any dispute:
- between the Government of India and one or more States; or
- between the Government of India and any State or States on one side and one or more other States on the other; or
- between two or more States, if and in so far as the dispute involves any question (whether of law or fact) on which the existence or extent of a legal right depends.
- Inter-State Council: Article 263 of the Constitution gives powers to the President to set up an Inter-state Council for resolution of disputes between states. The Council is envisaged as a forum for discussion between the states and the Centre.
- In 1988, the Sarkaria Commission suggested that the Council should exist as a permanent body, and in 1990 it came into existence through a Presidential Order.
- In 2021, the Council was reconstituted.
- Zonal Councils: Under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, five Zonal Councils have been set up. Besides this, a North Eastern Council has been set up under the North Eastern Council Act, 1971.
- The idea of creation of Zonal Councils was mooted by the first Prime Minister of India, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru in 1956.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Formation of States in India
- Constitutional Provision: Article 3: Deals with the formation of new states in India. Parliament can enact laws to create new states with a simple majority.
- Power & Recommendation:
- Parliament: Holds the power to create new states through legislation.
- President Recommendation: Required to introduce such a bill.
- State Consultation: The President must consult the respective State Legislatures but the centre is not bound by them.
- Reasons for Demand:
- Linguistic: The State Reorganization Commission recommended the formation of 14 states and 6 Union territories based on factors such as language, culture, financial viability, and national welfare.
- These recommendations were implemented through the 7th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1956.
- Development: States like Uttarakhand, Chhattisgarh, and Jharkhand, formed in 2000, and Telangana in 2014, were created based on developmental considerations.
- The Eleventh Plan document provides some data which support that the smaller newly carved states grew at a rate faster than their parent states.
- The existence of new states would mean the creation of new capital cities and the associated infrastructure and will attract private investors, resulting in employment opportunities and eventually better standard of living for citizens.
- Other Factors:
- The reorganization of states in India’s northeastern region was influenced by factors such as race, culture, and customs, reflecting the diverse socio-cultural landscape of the country.
- Competition for local resources
- Government negligence towards certain regions
- Improper allocation of the resources
- The economy’s failure to create enough employment opportunities
- Popular mobilization and the democratic political process is also one of the reasons
- The sons of the soil sentiments
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Challenges Associated with Formation of States in India
- Demand for Further Disintegration: The creation of one new state will lead to the demand for and creation of other new states.
- Based on the earlier experience, linguistic homogeneity has not proven to be effective in keeping the states integrated such as in the cases of Bihar, UP and Madhya Pradesh.
- These conflicts are rooted in reorganisation of states. Initially the states were reorganised on linguistic lines and later over other issues. It left many matters unresolved over borders and river water sharing.
- Economic Concerns:
- Revenue Generation: New states often struggle with generating adequate revenue and may lack established industries, infrastructure, and resources, which are crucial for economic self-sufficiency.
- Allocation of Assets and Liabilities: Dividing assets (like infrastructure) and liabilities (debts) between the parent state and the new state can be contentious and complex.
- Establishment of New Setup: Establishing new administrative structures, including government offices, educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and public services, requires significant investment and planning.
- Political & Governance Issues:
- Stability: New states need to establish stable political environments. Power struggles and factionalism can impede governance.
- Integration: Integrating diverse ethnic, linguistic, and cultural groups within the new state while fostering a cohesive identity can be challenging.
- Bureaucratic Transition: Transferring and training bureaucrats, police, and other officials to the new administrative setup takes time and resources.
- Interstate Relations:
- Resource Sharing: Issues related to sharing natural resources, such as water from rivers, can lead to conflicts between the new state and its parent state.
- Border Disputes: Determining clear and accepted boundaries can be contentious, especially in regions with historical disputes.
- Cultural Issues:
- Minority Rights: Protecting the rights and interests of minority groups within the new state is crucial for social harmony and is a challenging task for a newly formed state.
- Language and Education: Establishing language policies and educational systems that respect the diversity of the population can be a complex task.
- Ineffective Zonal Councils: The zonal councils, although met regularly, lack imparting effective solutions.
- Example: Maharashtra and Karnataka fall in different zones.
- Ineffective Inter-State Councils: The national level mechanisms like Inter-State Councils are ineffective. In the last 16 years, just two meetings have been held.
- Also, it is merely an advisory body, hence, often its recommendations are ignored by the government at the centre as well as the states.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way Forward
- Careful Consideration: The formation of new states in India is a multi-faceted process that requires careful consideration of economic, administrative, social, and political factors.
- Effective Planning & Governance: It is desirable to include effective planning, inclusive policies, and strong governance to address the challenges and ensure the successful integration and development of new states.
- Regular meetings of Inter-State Councils: These must be held to address the challenges faced by states.
- More Effective Zonal Councils: Zonal councils need to be revived to discuss the matters of common concern to states in each zone such as matters relating to social and economic planning, border disputes, etc.
- Environmental Factors:
-
- Sustainable Development: There is a need to ensure that development projects in the new state are environmentally sustainable.
- Resource Management: Managing natural resources effectively is needed to avoid depletion and degradation.
Also Read: Inter-State Relations in India
![]() 10 Jun 2024
10 Jun 2024

 Bifurcation: The Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act was passed in February 2014, outlined the division of assets, liabilities, and administrative details.
Bifurcation: The Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act was passed in February 2014, outlined the division of assets, liabilities, and administrative details. 