India will apply for licenses to explore for deep-sea minerals in the Pacific Ocean as it competes to secure supplies of minerals critical for energy transition technologies.
- India’s Ministry of Earth Sciences is gearing up to apply for exploration of seabed minerals in the Pacific.
- China, Russia, and some Pacific Island nations have already secured exploration licenses for the Pacific Ocean.
Deep Sea Exploration Licence
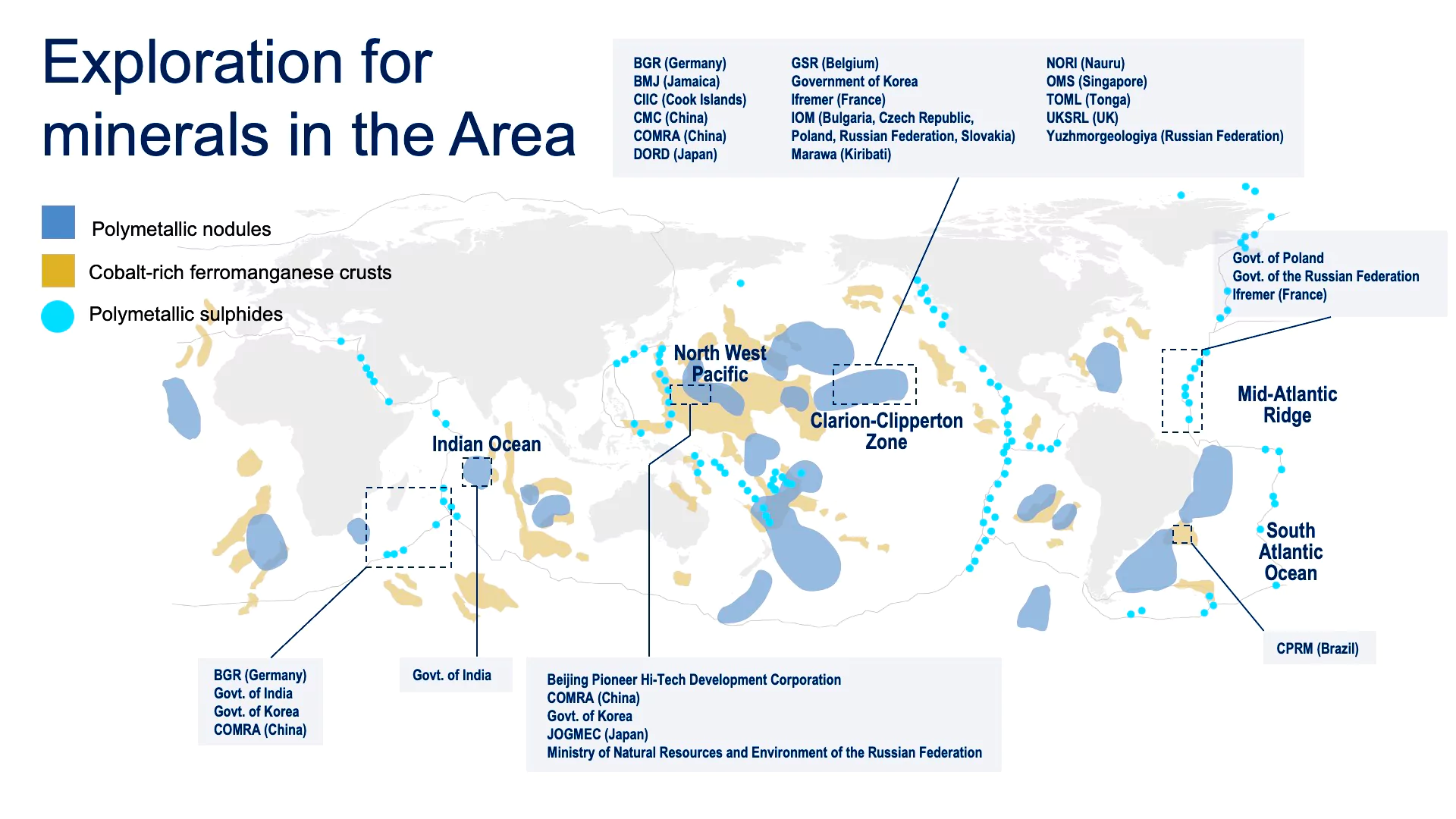
- The UN-backed International Seabed Authority (ISA) has issued 31 deep-sea exploration licences in total, including two for India in the Indian Ocean, but is yet to allow mining.
- Total Area Assigned: More than 1.5 million km2 of international seabed, roughly the size of Mongolia, has been set aside for mineral exploration.
- Present Status of India: India has been allotted a site of 75,000 sq. km. in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB) by ISA for the exploitation of polymetallic nodules (PMN).
- Technology Demonstrator: India’s National Institute of Ocean Technology conducted trials of its mining machine at a depth of 5,270m in the central Indian Ocean basin and collected some polymetallic nodules in 2022 as part of the Deep Sea Ocean Mission.
- India’s Plans: India is planning to get a licence to explore the Clarion-Clipperton Zone (a vast plain between Hawaii and Mexico containing large volumes of polymetallic nodules)
- India has submitted applications to ISA for exploration focused on the Carlsberg Ridge and Afanasy-Nikitin Seamount regions, known for polymetallic sulphide deposits and ferromanganese crusts.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
The International Seabed Authority (ISA):
- Establishment: The International Seabed Authority came into existence on 16 November 1994, established under the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the 1994 Agreement relating to the Implementation of Part XI of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.
- Headquarters: Kingston, Jamaica.
- Membership: It has 169 Members in total, including 168 Member States and the European Union. USA is not a member
- Article 156(2) of the UNCLOS, states that all States Parties to UNCLOS are ipso facto members of ISA.
- Mandate: ISA organizes and controls all mineral-resources-related activities in the High Seas Area and ensures the effective protection of the marine environment from harmful effects that may arise from deep-seabed-related activities.
- The High Seas Area: It is an area in international waters comprising all parts of the sea that are not included in the exclusive economic zone, the territorial sea or the internal waters of a State, or in the archipelagic waters of an archipelagic State
- It covers around 54 per cent of the total area of the world’s oceans.
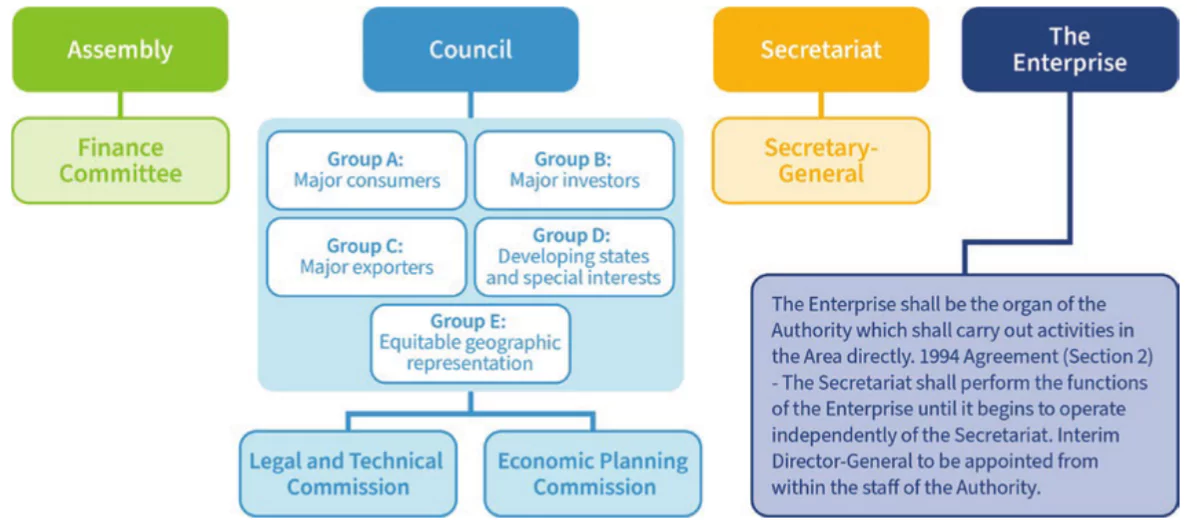
- Governance Structure: The ISA is composed of four principal organs ie,
- The Assembly: It is the supreme decision-making and political organ of the ISA formed by all members of the ISA, with the power to establish the general policies of the ISA and approve the rules and regulations recommended by the Council.
- The Assembly also elects the Finance Committee, which oversees the financial management of the ISA
- The Council: It is the executive organ of the ISA with the power to establish the specific policies of the ISA and to recommend rules, regulations and procedures.The Council has two organs, namely,
- The Legal and Technical Commission (LTC) and The Economic and Planning Commission
- The Secretariat: It provides administrative and legal services, as well as scientific and technical input, through its offices of Administrative Services, Legal Affairs and Environmental Management, Mineral Resources
- The Enterprise: It is the operational arm of the ISA, which shall carry out mineral-related activities in the Area
- Exploration Contracts: With the establishment of ISA in 1994, exploration activities for mineral resources in the Area began to be regulated under exploration contracts.
- ISA has entered into 15-year contracts for the exploration for polymetallic nodules (PMN), polymetallic sulfides (PMS) and cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts (CFC) in the deep seabed with 31 contractors
- The ISA has only issued exploration contracts, but is developing regulations to govern the transition to exploitation.
- Polymetallic Nodules: Found in the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone (17), and Central Indian Ocean Basin (1), and Western Pacific Ocean (1).
- Polymetallic Sulphides: Seven contracts for exploration in the SouthWest Indian Ridge, Central Indian Ridge and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge are given.
- Cobalt-rich Ferromanganese Crusts (CFC): Five contracts are awarded for exploration for cobalt-rich crusts in the Western Pacific Ocean.
Polymetallic Nodules
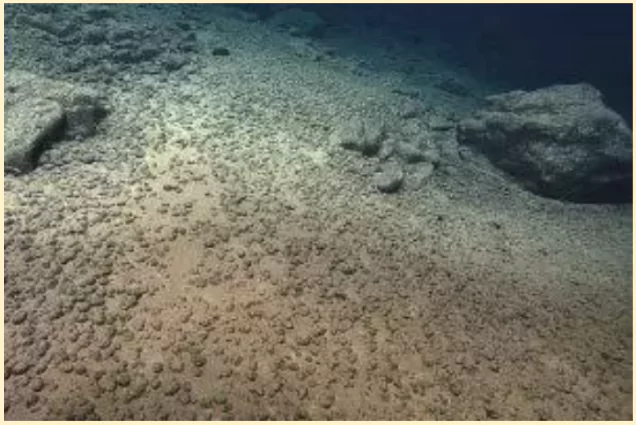

- Formation: Nodules require a nucleus (A piece of pumice, a shark tooth, basalt debris or even microfossils) around which it starts forming
- Process: The metals get enriched around the nucleus either hydro genetically by the precipitation of metals from the seawater or through release from the interstitial spaces between the underlying sediments
- Occurrence: The deposits of economic importance occur mostly at 4,000-6,000 meters depths in areas of extremely low sedimentation rate.
- Found:They are found in areas off the west coast of Mexico in the Pacific (known as the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone), the Central Indian Ocean Basin, and the Peru basin.
- Composition:These are potato-shaped rocks that lie on the seafloor and are composed mainly of Manganese, Iron, silicates and hydroxides but also rich in cobalt, nickel, and copper (The Rare Earth Elements)
- Size: The nodules vary from micro-nodules to about 20 cm, the common size being two to eight centimeters.
|
Polymetallic Sulphides

- Found: Massive polymetallic sulphide deposits are 3D deposits and are most commonly formed along tectonic plate boundaries and volcanic provinces in water depths from <500 to 5000m.
- Process: Seawater seeps into the volcanic rock through cracks and fissures, this hot fluid then circulates through the sub-seafloor, dissolving metals and other elements from the surrounding rocks.
- Convection carries this hot (up to 450°C), acidic, metal-rich fluid back up towards the surface where it is expelled at the seafloor, creating hydrothermal vents
- As this hot fluid reacts with the cold seawater particles of metal sulphide minerals precipitate from the fluid and settle out on the seafloor.
- Composition: These metalliferous muds contained large amounts of copper, zinc, lead, iron, silver and gold.
- Occurrence: Massive Sulphides deposits occurs along the mid-ocean ridges, backarc environments, submarine volcanic arcs and in basins near volcanic arcs.
|
Cobalt-rich Ferromanganese Crusts
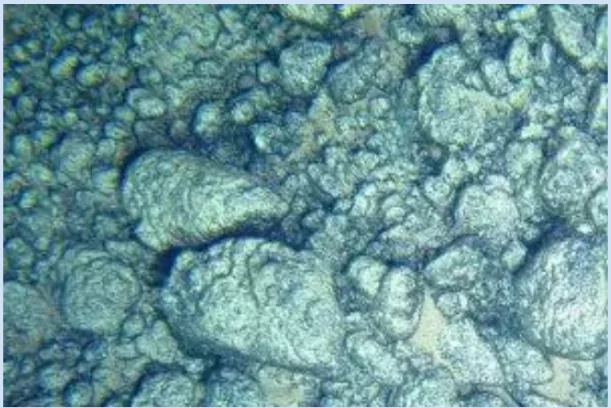

- Occurrence: They are found at shallower depths of <400 to about >5,000 meters in areas of significant volcanic activity.
- The crusts grow on hard-rock substrates of volcanic origin by the precipitation of metals dissolved in seawater in areas of seamounts, ridges, plateaus and where prevailing currents prevent deposition of unconsolidated sediments and occupy large areas on top of these topography highs.
- In many cases, the deposits occur within the exclusive economic zone of the countries.
- Composition: They are similar in general composition to the polymetallic nodules but have higher cobalt percentage (up to 2%), platinum (0.0001%) and rare earth elements besides nickel and manganese.
|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Deep Sea Mining
- Deep-sea mining is the process of extracting and often excavating mineral deposits (Cobalt, copper, gold, lead, manganese, nickel, silver, zinc and other rare metals) from the deep seabed achieved through methods such as dredging sand or lifting materials in various ways.
- The deep seabed is the seabed at ocean depths greater than 200m, and covers about two-thirds of the total seafloor.
India’s EEZ and Mineral Exploration Rights
- India’s Exclusive Economic Zone spreads over 2.2 million sq. km. holding significant recoverable resources which lies unexplored and unutilized.
- Union List: The entry at serial No. 54 of List I mandates the central government to own the minerals within the exclusive economic zone of India (EEZ).
- Legal Right: The Parliament has passed the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023, giving two types of operating rights to be granted to private sector through auction by competitive bidding, viz. production lease and composite licence
- Geological Survey India has delineate the resources of the following minerals in the offshore areas:
- 79 million tons of heavy mineral placers in the inner-shelf and mid-shelf off Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra.
- Phosphorite in the Eastern and Western continental margins.
- Polymetallic Ferromanganese (Fe-Mn) nodules and crusts in Andaman Sea and Lakshadweep Sea.
|
![]() 23 Jul 2024
23 Jul 2024



