Context: At the ongoing COP28 UN climate conference in the United Arab Emirates, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has released its latest update to the IUCN Red List which includes the first global freshwater fish assessment.
An Overview of New IUCN Red List
- The update highlights the impact of illegal logging and trade on mahogany.
- Red list: The IUCN Red List comprises 157,190 species out of which 44,016 are threatened with extinction.
- Four subterranean fishes from Kerala found in water bodies under the surface are facing the risk of extinction.
 Endangered Category: Kryptoglanis Shajii, Horaglanis Abdulkalami, Pangio Bhujia
Endangered Category: Kryptoglanis Shajii, Horaglanis Abdulkalami, Pangio Bhujia- Vulnerable category: Aenigmachanna Gollum (snakehead Gollum)
Decoding the IUCN Red List: A Vital Biodiversity Indicator
- Red List: Established in 1964, the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List of Threatened Species has evolved to become the world’s most comprehensive information source on the global extinction risk status of animal, fungus and plant species.
- Critical Indicator:The IUCN Red List is a critical indicator of the health of the world’s biodiversity.
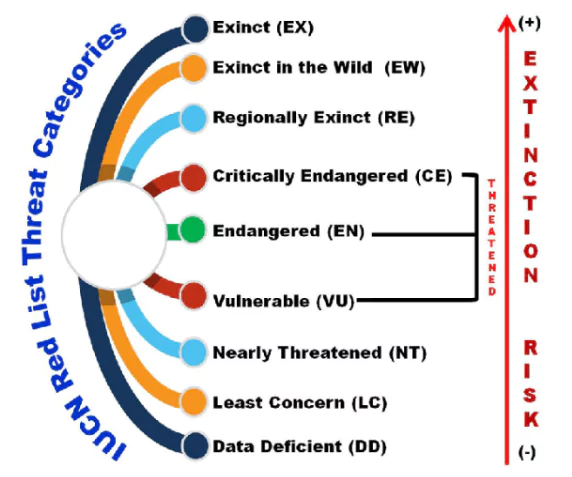
- For categories under Red List: Refer image
IUCN Report on Climate, Pollution, and Conservation
- Risk of extinction: 25% (3,086 out of 14,898 examined species) of the world’s freshwater fish species are at risk of extinction.
International Union for Conservation of Nature(IUCN)
- IUCN brings together governments and civil society organizations, united under the common goal of protecting nature and conserving life on Earth.
- It was established in 1948.
- Headquarters: Switzerland.
- It uses a set of quantitative criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of species.
|
- Impact of climate change:Climate change affects at least 17% of vulnerable freshwater fish species through altered seasons, increasing sea levels that force saltwater to travel up rivers, and declining water levels.
- Case study: The large-toothed Lake Turkana robber (Brycinus ferox) of Kenya has moved from Least Concern to Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List due to overfishing and climate-change events.
- Case study: Green turtles are more at risk from climate change due to rising sea levels and high temperatures reduce the likelihood that their eggs will hatch and drown the young.
- Threats from pollution: Pollution impacts 57% of freshwater fish species at risk of extinction.
- Case study: Atlantic salmon has moved from Least Concern to Near Threatened mainly because of water pollution and sedimentation, primarily from logging and agriculture leading to higher mortality of young salmon.
- Constructing dams and water extraction: It impacts 45% of the freshwater species.
- Overfishing: Overfishing threatens about 25% of the freshwater species
- Invasive species, pests and diseases: These impact about 33% of the freshwater species.
- Conservation Status Updates:
- Scimitar-horned oryx (Oryx dammah) : The species has moved from Extinct in the Wild to the Endangered category.
- Saiga antelope (Saiga tatarica) :The species conservation status has improved from Critically Endangered to Near Threatened.
- Large-toothed Lake Turkana robber (Brycinus ferox): The species has moved from Least Concern to Vulnerable
- Atlantic salmon: The species has moved from Least Concern to Near Threatened
News Source: IUCN
![]() 14 Dec 2023
14 Dec 2023
 Endangered Category: Kryptoglanis Shajii, Horaglanis Abdulkalami, Pangio Bhujia
Endangered Category: Kryptoglanis Shajii, Horaglanis Abdulkalami, Pangio Bhujia