![]() 3 Feb 2025
3 Feb 2025

India has recently sent a shipment of medical supplies to the Kurdistan Region in Iraq.
Kurds
|
|---|
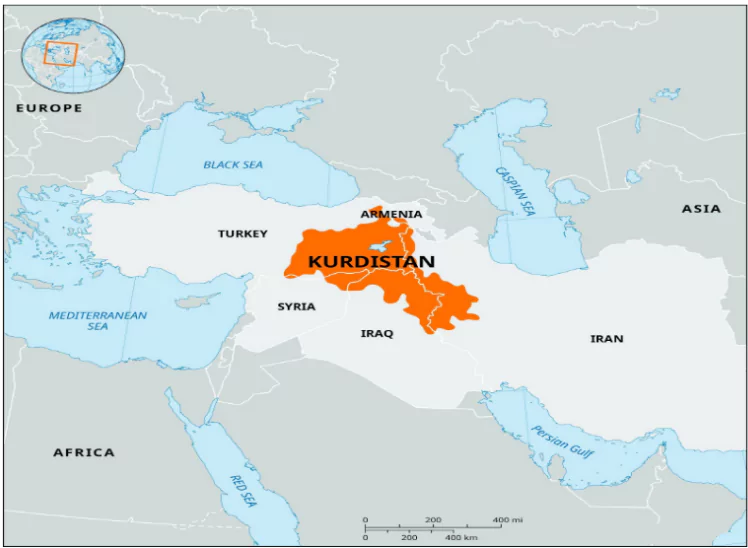 India and the Kurdistan Region: Consulate and Diplomatic Relations:
India and the Kurdistan Region: Consulate and Diplomatic Relations:Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!

<div class="new-fform">
</div>