Context:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently released the Landslide Atlas of India, a detailed guide identifying landslide hotspots in the country.
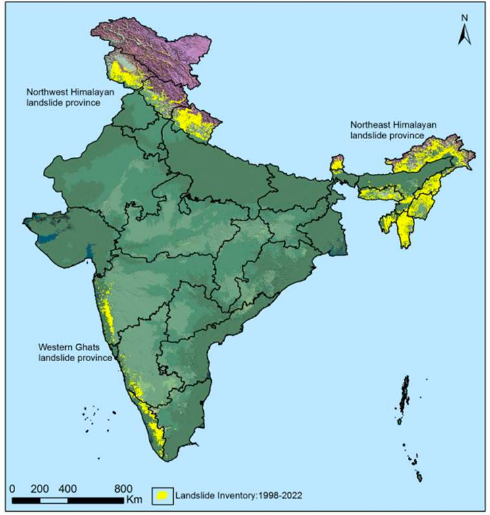
Image Source: The Indian Express
About Landslides:
- Landslides are natural disasters that occur mainly in mountainous terrains where there are conducive conditions of soil, rock, geology, and slope.
- Causes:
- Natural causes that trigger landslides include heavy rainfall, earthquakes, snow melting, and undercutting of slopes due to flooding.
- Anthropogenic activities such as excavation, cutting of hills and trees, excessive infrastructure development, and overgrazing by cattle can also cause landslides.
- Factors:
- Lithology, geological structures like faults, hill slopes, drainage, geomorphology, land use and land cover, soil texture and depth, and weathering of rocks.
- In India, rainfall-induced landslide events are more common.
How are landslides classified and mapped?
- Landslides are classified based on the type of materials involved, type of movement, type of flow, and lateral spread.
- ISRO’s National Remote Sensing Centre has created a database of landslide-prone regions in India based on events from 1998 to 2022 in the Himalayas and Western Ghats.
- Aerial and high-resolution satellite images captured using Indian Remote Sensing (IRS-1D) PAN + LISS-III, satellites ResourceSat-1 and 2, etc., were used to study landslides over the past 25 years.
- Landslides are classified into seasonal (2014, 2017 monsoon seasons), event-based, and route-based (2000 – 2017) in the pan-India landslide database.
How prone is India to landslides?
- India’s susceptibility to landslides: India is one of the top five landslide-prone countries globally, with high vulnerability in the Himalayas and Western Ghats.
- Major cause of landslides in India: Rainfall variability is the biggest cause of landslides in India.
- Percentage of India’s land area prone to landslides: 12.6% of India’s geographical land area (0.42 million sq km) is prone to landslides excluding snow-covered areas.
- Distribution of landslides in India: 66.5% of landslides occur in the North-western Himalayas, 18.8% in the North-eastern Himalayas, and 14.7% in the Western Ghats.
Landslide Atlas Findings:
- States with highest number of landslides: Uttarakhand, Kerala, Jammu and Kashmir, Mizoram, Tripura, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- State-wise trends:
- Mizoram reported the highest number of landslide events (12,385) in the past 25 years, with 8,926 in 2017 alone.
- Uttarakhand experienced the second highest number of landslides (11,219) since 1998, with events occurring post-2000.
- Kerala has been consistently reporting massive landslides since 2018 floods, with 5,191 events in 2018 and 29 in 2021.
- District-wise trends:
- Arunachal Pradesh has the maximum number of districts (16) with high landslide exposure.
- Rudraprayag in Uttarakhand is the top vulnerable district with the highest landslide density, total population and number of houses exposed to landslides.
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 11 Mar 2023
11 Mar 2023
