UNESCO’s TWAS Award
Context: The TWAS Award 2026 in Engineering and Computer Sciences by UNESCO has been awarded by Suman Chakraborty.
- Diagnostic Solutions: The award is presented to honour his body of work constituting affordable, simple-to-execute, and innovative diagnostic solutions covering various medical challenges such as anaemia, cancer, COVID-19, tuberculosis etc.
About Professor Chakraborty
- Professor Chakraborty is currently a J.C. Bose National Fellow and is the institute chair professor for Mechanical Engineering department at Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur (IIT-KGP).
- Notable Innovations:
-
- Oroscreen: It is a torch-like imaging device for the early detection of oral cancer
- Covirap: It is a rapid COVID-19 detection test kit. It has been granted a U.S. patent for its rapid nucleic acid testing technology using DNA RNA samples.
- PrepapQR: It is a home test for women to accurately test vaginal Ph with the help of a strip
- HemoQR: It is a simplified anaemia screening technology currently available commercially.
- Currently developing a flagship technology for rapid detection of tuberculosis.
UNESCO’s TWAS (The World Academy of Sciences) Award
- It was established in 1985 by TWAS to recognize excellence in scientific research in the global South.
- Awarded By: UNESCO
- It is a biennial award (every two years)
- Eligibility: The award is given to individual scientists from developing countries who have been working and living there for at least 10 years.
- Criteria: Outstanding contribution to scientific knowledge in nine fields of sciences or the application of science and technology to sustainable development is considered criteria.
- Fields: Agricultural Sciences, Biology, Chemistry, Earth, Astronomy and Space Sciences, Engineering Sciences, Mathematics, Medical Sciences, Physics, and Social Sciences.
T-72 Tank
Context: The Ministry of Defence has signed a $248 million contract with Russian defence firm Rosoboronexport (RoE).
Key Highlights of the Contract
- The deal involves procuring 1,000-horsepower (HP) engines for T-72 battle tanks.
- Technology Transfer to Boost ‘Make in India’
-
- The contract includes Transfer of Technology (ToT) to India.
- Chennai-based Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (Heavy Vehicle Factory) will handle integration and production.
- This initiative supports ‘Make in India’ in the defence sector.
About T-72 tank
- The T-72 is a Soviet-era main battle tank that went into production in 1973.
- It is the most widely used main battle tank in the world.
- It was developed using ideas from the T-64 tank and the earlier Object 167M design.
- Features:
- Mobility: upgraded with 1,000 HP engines which helps to improve speed and maneuverability.
- Fire power: equipped with 125mm smoothbore gun, 7.62mm coaxial machine gun, and a 12.7mm anti-aircraft gun.
- Operational range: can travel upto 500 km on road.
- It has a fuel capacity of around 1,200 liters.
- Benefits:
-
- Upgrading to 1,000 HP engines will improve:
- Mobility on the battlefield.
- Offensive capabilities of the Army.
Koch-Rajbongshis
Context: The Koch-Rajbongshis, one of the largest communities in western Assam and northern West Bengal, have been demanding Scheduled Tribe (ST) status for decades.
Who are the Koch-Rajbongshis?
- The Koch-Rajbongshis, also known as Rajbanshi or Rajbongshi, are a community spread across:
- India – Lower Assam, North Bengal, and eastern Bihar.
- Nepal – Terai region.
- Bangladesh – Rangpur division and parts of North Bangladesh.
- Bhutan.
- They have historically associated themselves with the Koch dynasty.
- The word “Rajbongshi” literally means “royal community”.
- They have a rich cultural heritage and their own language.
- Language: They speak Rajbongshi/Rajbanshi language.
- Other names of the language are Kamtapuri, Rajbangsi, Rajbansi, Rajbongshi, Goalpariya and Tajpuri.
- Religion: Originally, they practiced animism. later, followed Hinduism (Sanatana Dharma).
- A small section practiced Christianity.
- Rejections and Temporary ST Status
- The Registrar General of India (RGI) rejected the ST demand for these six communities eight times between 1981 and 2006.
- Six communities are: Adivasis, Ahoms, Chutias, Mataks, and Morans along with them.
- In 1996, the Centre granted ST status to the Koch-Rajbongshis for six months.
- This decision was revoked after protests when they occupied a majority of reserved seats in medical and engineering courses.
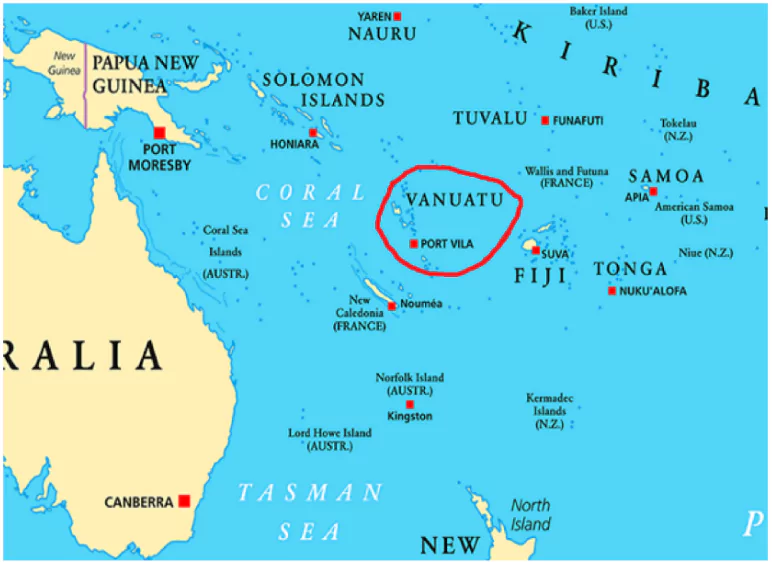
Vanuatu
Context: Vanuatu has decided to cancel the passport granted to former Indian Premier League (IPL) chairman Lalit Modi, who has been described as an economic offender by Indian investigating agencies.
- He has obtained Vanuatu citizenship through its Citizenship by Investment (CBI) program.
Vanuatu’s Citizenship by Investment (CBI) Program
- Allows wealthy individuals to purchase citizenship by making a financial investment.
- Offers visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to many countries, making it attractive for global fugitives and investors.
About Vanuatu
- Location: A South Pacific nation east of Australia and north of New Zealand.
- Composition: 83 volcanic islands, with 65 inhabited.
- Capital & Largest City: Port Vila, located on Efate Island (900 sq km).
Hantavirus
Context: Betsy Arakawa, wife of Oscar-winning actor Gene Hackman has died from a respiratory illness linked to hantavirus.
About Hantavirus
- Hantavirus is a group of viruses primarily transmitted to humans through contact with certain rodents, such as deer mice, white-footed mice, rice rats, and cotton rats.
- Hantavirus was first identified during the Korean War in the early 1950s.
- The virus was named Hantaan, in recognition of the Hantaan river, which flows through Korea.
- The virus can cause severe respiratory and hemorrhagic diseases in humans, with high mortality rates in some cases.
Transmission of Hantavirus
- Rodent Contact: Inhalation of aerosolized particles from rodent excreta is the primary mode of transmission.
- Human-to-Human Transmission: Some strains from Argentina and Chile, like the Andes virus (ANDV), have been reported to spread between people, though this is uncommon.
Hantavirus can cause two major illnesses
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
- Found mainly in the Americas
- Symptoms: Fever, muscle aches, fatigue, Severe respiratory distress and organ failure
- Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS)
- Found mainly in Asia and Europe
- Initial symptoms: High fever, headache, back pain, Low blood pressure, acute kidney failure.
Who is at risk from Hantavirus?
- Farmers, construction workers, and those cleaning unused spaces
- Campers and hikers who come into contact with rodent nests
- Homeowners dealing with rodent infestations
- Children under five, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Treatment: There is no specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for hantavirus infections.
- Management primarily focuses on early detection, supportive care, and symptomatic treatment to improve survival chances.
Pashu Aushadhi Kendras
Context: The government is planning to open “Pashu Aushadhi” stores across the country to provide affordable generic veterinary medicines to people engaged in animal husbandry and dairying.
- The Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying will soon release guidelines for the functioning of these stores
About Pashu Aushadhi Initiative
- It is a part of the revised Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP)
- LHDCP has an overall outlay of Rs 3,880 crore for the years 2024-25 and 2025-26.
- It aims to provide good quality and affordable generic veterinary medicine and incentive for sale of medicines available to people engaged in animal husbandry and dairying.
- Operated By: The Pashu Aushadhi stores will be run by cooperative societies and Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samriddhi Kendras (PMKSK)
- Ethnoveterinary Medicines: The Pashu Aushadhi Kendras will also sell ethnoveterinary medicines, based on traditional beliefs and indigenous knowledge and practices, to treat animal diseases.
- The National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) has compiled a list of ethnoveterinary formulations for the treatment of mastitis, FMD mouth lesions, FMD foot lesions/ wounds, fever, diarrhoea, bloating and indigestion, and worm.
- Need: India’s Livestock population stood at 535.78 million in 2019 as per the 20th Livestock Census with total bovine population (including cattle, buffalo, mithun and yak) of 302.79 million.
- Livestock Diseases: They are impacted adversely due to diseases like Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD), Brucellosis, Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR), Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF), Lumpy Skin Disease, etc.”
![]() 10 Mar 2025
10 Mar 2025

