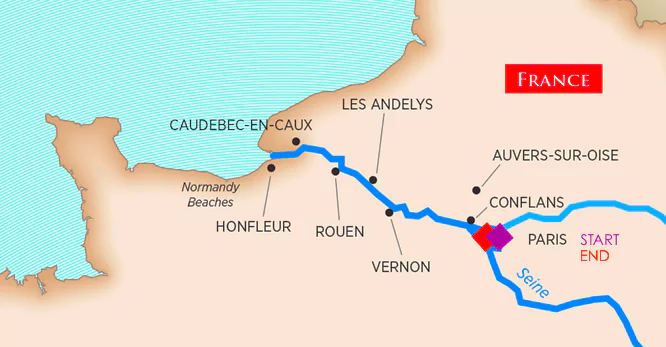
Seine River in Paris
|
- Paris mayor will swim in Seine River to prove cleanliness ahead of Olympics
Seine River:
- About: It is France’s second-longest river after the Loire.
- Course of the River: As it nears Paris, the Seine is joined on the right bank by one of its largest tributaries, the Marne.
- It empties into the English Channel, the arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates northern France from southern England.
- Features: Most of the river basin consists of permeable rocks, which help reduce the risk of river floods due to their absorptive capacity.
- As one of Europe’s great historic rivers, its drainage network handles the majority of French inland waterway traffic.
|
Tizu Zunki River

|
- The government has announced plans to boost Nagaland’s economy by using the Tizu and Zungki rivers (National Waterways 101).
Tizu Zunki River:
- Origins: The Tizu River serves as a crucial drainage system in eastern Nagaland. Beginning in the central part of Nagaland, it flows northeast through Kiphire and Phek districts before joining the Chindwin River in Myanmar.
- Course: The Chindwin River then merges with Myanmar’s largest river, the Irrawaddy.
- The Irrawaddy River flows southward and eventually empties into the Andaman Sea via the Irrawaddy Delta, passing through river ports such as Mandalay along the way.
- River system in Nagaland: Nagaland has four main rivers: Doyang, Dhansiri, Dhiku, and Tizu.
- The first three flow westward through the Assam plains to join the Brahmaputra River, while the Tizu River system flows east and southeast, eventually emptying into the Irrawaddy in Myanmar.
- Tributaries: Includes Zungki, Lanye, and Likimro rivers. Zungki River is the principal tributary of the Tizu River within Nagaland.
|
National Company Law Tribunal
|
- NCLT admits BCCI’s plea seeking insolvency proceedings against Byju’s
National Company Law Tribunal:
- About: It is a quasi-judicial body established to resolve civil corporate disputes arising under the Companies Act, 2013. This authority was established on June 1, 2016, under the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Origins: It was established following the recommendation of the Balakrishna Eradi Committee on laws concerning insolvency and the winding up of companies.
- Composition:It consists of a President and such number of other Judicial and Technical Members as may be prescribed.
- The President of the Tribunal shall be appointed by the Central Government after consultation with the Chief Justice of India.
- Powers of NCLT: It is not bound by the rules of the Code of Civil Procedure but follows principles of natural justice, within the provisions of this Act and any relevant Central Government rules.
- It can enforce its orders similarly to a court. It reviews its own orders.
- It regulates its own procedures.
- It acts as the adjudicating authority for the insolvency resolution process of companies and limited liability partnerships under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016.
|
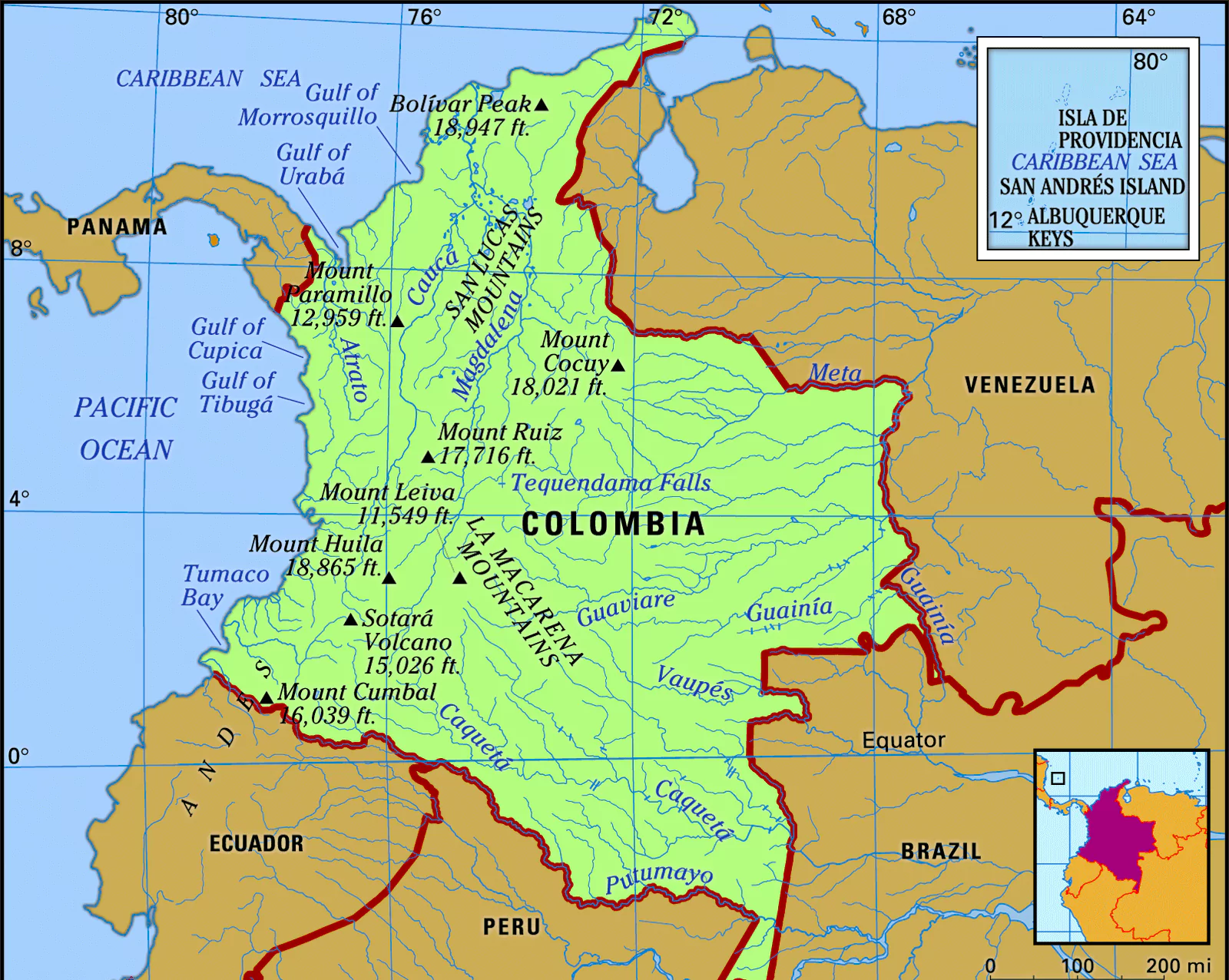
Colombia: Places in News
|
- Colombia, the epicentre of the global cocaine industry, is experiencing substantial transformations influenced by local and international factors.
Colombia:
- Location: Colombia, officially known as the Republic of Colombia, is situated in South America.
- Geographical Position: Colombia is situated in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth.
- Bordered by:
-
- Brazil to the southeast.
- Panama to the northwest.
- Venezuela to the east.
- The Pacific Ocean to the west.
- The Caribbean Sea to the north.
- Peru and Ecuador to the south.
- Ring of Fire: Colombia is part of the Ring of Fire.
- Landscape: Colombia features diverse terrain including desert, highlands, grasslands, and the Amazon rainforest.
- Approximately 25% of its land lies within the Andes Mountains.
- Official Language: Spanish serves as the official language.
- Unique Feature: Colombia is the sole South American country with coastlines touching both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
|
Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA)
|
- The Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA), is set to obtain diplomatic status, pending India’s signing of a headquarters agreement.
Global Biofuels Alliance (GBA):
- About: The Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) was inaugurated during the 2023 G20 summit in New Delhi.
- The Alliance aims to guarantee the availability, affordability, and sustainable production of biofuels.
- Aim: To promote international cooperation and enhance the adoption of sustainable biofuels.
- Member Nations: Founded by India, the United States, and Brazil, the alliance comprises nine countries: India, the US, Brazil, Argentina, Bangladesh, Italy, Mauritius, South Africa, and the UAE.
- Organizational Members: The alliance includes participation from the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, World Economic Forum, International Energy Agency, International Energy Forum, International Renewable Energy Agency, and International Civil Aviation Organization.
- Functions: Advancing biofuel technology b) Advocating for sustainable biofuel use to mitigate concerns about indirect land use change (ILUC)
- Establishing rigorous standards and certifications.
- The alliance will function as a hub of knowledge to foster international collaboration and ensure the reliable and cost-effective availability of biofuels.
|
15-minute neighbourhoods
|
- The potential of 15-minute neighbourhoods to address Bengaluru’s urban challenges, including congestion, water crises, and erratic weather.
15-minute neighbourhoods:
- About: The 15-minute neighbourhood concept in urban planning ensures that essential services and amenities—like groceries, schools, healthcare, and recreational facilities—are within a 15-minute walk or bike ride from residents’ homes.
- Aim: This model seeks to decrease dependence on cars, enhance environmental sustainability, and improve community well-being by encouraging walkability and local accessibility.
|
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
|
- The MV Sea Change, the world’s inaugural commercial passenger ferry fueled entirely by zero-emission hydrogen fuel cells, was launched in San Francisco.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells (HFC):
- About: It generates electricity through an electrochemical reaction that combines oxygen and hydrogen.
- Benefits: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles emit no tailpipe pollutants, including particulates, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
Methods of producing hydrogen fuel include:
- Steam Methane Reforming (SMR): Hydrogen is generated by reacting natural gas with high-temperature steam.
- This method is predominant, but it emits carbon dioxide due to its reliance on fossil fuels.
- Electrolysis: Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using an electrical current, producing pure hydrogen.
- When coupled with renewable electricity, this method produces ‘green’ hydrogen sustainably.
- Thermochemical Processes: High-temperature heat is used to extract hydrogen from water and hydrocarbons through multiple chemical reactions, often leveraging heat from nuclear plants or solar concentrators.
|
Chandipura Virus (CHPV)
|
- Recently, the Gujarat government has reported six deaths of children suspected to be due to Chandipura virus (CHPV) infection, with a total of 12 suspected cases identified.
Chandipura Virus (CHPV):
- About: CHPV is classified under the Rhabdoviridae family, which also includes viruses responsible for rabies.
- Vectors: The virus is transmitted by various species of sandflies (Phlebotomine sandflies, such as Phlebotomus papatasi), as well as mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti).
- Transmission: The virus resides in the salivary glands of insects and is transmitted through their bites to humans and other vertebrates.
- Impact: The infection can progress to affect the central nervous system, leading to encephalitis (inflammation of brain tissue).
- Contributing Factors to Outbreaks:
- Geographic and Seasonal Factors: Outbreaks typically occur in rural, tribal, and peripheral areas where sandflies are prevalent. These outbreaks coincide with the monsoon season.
- Environmental Factors: Sandflies are attracted to kutcha houses painted with cow dung, which can contribute to outbreaks.
|
![]() 18 Jul 2024
18 Jul 2024