Context:
Recently, the Lok Sabha Speaker accepted a no confidence motion moved by the Opposition against the Government.
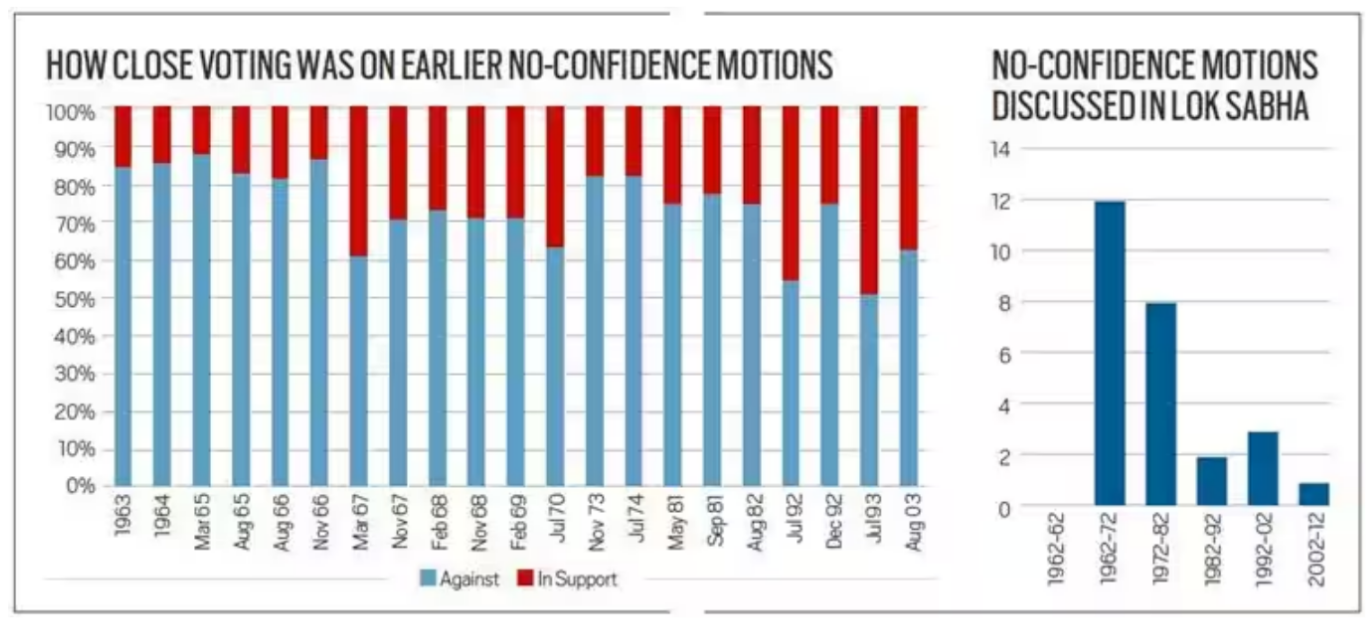 Image Credits: Indian Express
Image Credits: Indian Express
About No Confidence Motion:
- A no-confidence motion is a formal process in which a legislature expresses lack of confidence in government.
- Constitutional mandate: As per, Article 75 of the Constitution, the council of ministers shall be collectively responsible to the Lok Sabha.
- Interpretation: It means that the ministry stays in office so long as it enjoys the confidence of the majority of the members of the Lok Sabha.
- In other words, the Lok Sabha can remove the ministry from office by passing a no-confidence motion.
- Conditions:
- The motion needs the support of 50 members to be admitted.
- It can only be moved in the Lok Sabha.
- The allotted date has to be within 10 days from the day the motion is accepted.
- A motion of no-confidence can only be submitted six months after Parliament has rejected the previous one.
- Impact:
- When the Lok Sabha passes a no-confidence motion against the council of ministers, all the ministers have to resign including those ministers who are from the Rajya Sabha.
- Facts: The first motion of no confidence was moved by Acharya J B Kripalani in 1963 against the government headed by Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru.
Instances of No-Confidence Motion:
| Year |
Government of Day |
| 1990 |
- National Front Government
|
| 1997 |
|
| 1999 |
- National Democratic Alliance
|
Significance:
- Tool of Discussion: No confidence motion has historically been used as a strategic tool to force a discussion on a certain topic or issue.
- Accountability: It allows Members of Parliament (MPs) to hold the ruling government accountable for its actions and policies.
News Source: Times of India
![]() 27 Jul 2023
27 Jul 2023
 Image Credits: Indian Express
Image Credits: Indian Express