![]() 3 Apr 2024
3 Apr 2024
According to a monthly survey released, India’s manufacturing sector had a strong performance in March, supported by strong sales and production.
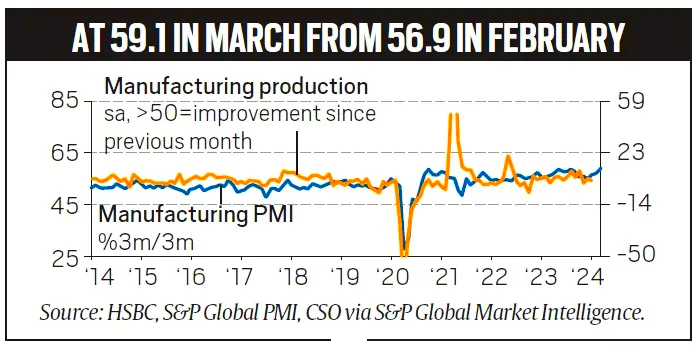 This coincided with the second-most significant increase in input inventories in the survey’s history.
This coincided with the second-most significant increase in input inventories in the survey’s history.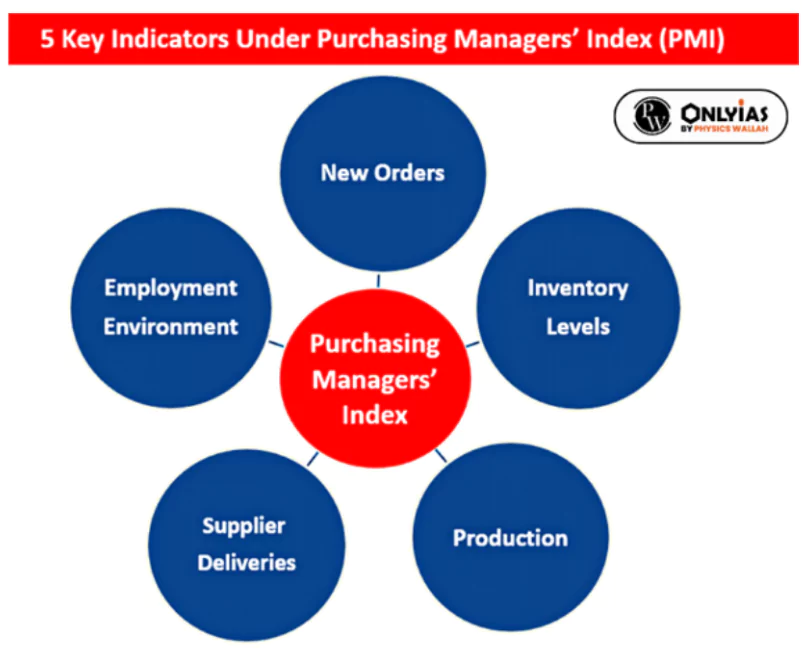 For manufacturing PMI, the questionnaire is sent to manufacturing companies. The questions are related to 5 key variables.
For manufacturing PMI, the questionnaire is sent to manufacturing companies. The questions are related to 5 key variables.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

<div class="new-fform">
</div>