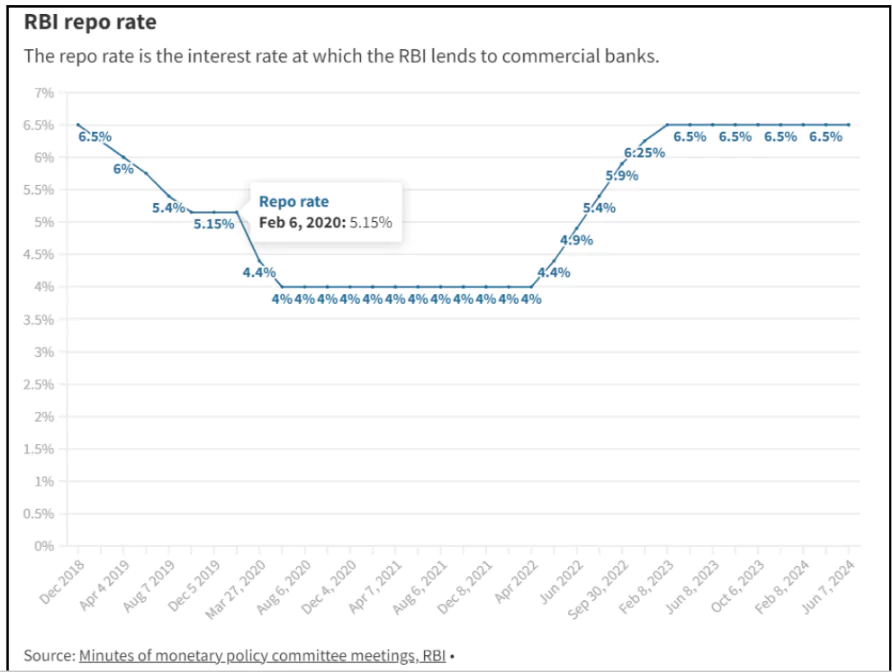
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank Of India (RBI) has decided to keep the repo rate unchanged at 6.5.
- This marks the eighth consecutive time the rate has been maintained.
Reasons for RBI Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged
- Inflation Concerns:
- Despite some moderation, food inflation remains high due to price pressures on vegetables, pulses, cereals, and spices.
 Potential future disruptions from adverse weather events add uncertainty to the food inflation trajectory.
Potential future disruptions from adverse weather events add uncertainty to the food inflation trajectory.- Volatility in crude oil prices, financial markets, and non-energy commodity prices could lead to higher inflation.
- The RBI prioritizes achieving the medium-term inflation target of 4% while supporting economic growth.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Balancing Growth and Inflation
- The MPC revised the GDP Growth forecast to 7.2% for 2024-2025, indicating a positive economic outlook.
- Reasons for rise in GDP growth forecast
- Positive Domestic Indicators
- High-frequency domestic activity indicators show resilience in 2024-25, suggesting strong internal economic momentum.
- Strong Agricultural Outlook
- The expectation of an above-normal southwest monsoon bodes well for agriculture, a key driver of rural demand.
- This will likely boost economic activity.
- Policy Stance: In response to the above-expected event, the committee remains focused on withdrawing accommodation to manage inflation.
- Inflation Target: It aims to achieve a medium-term CPI inflation target of 4%, within a band of +/- 2%.
- The outcome of changing the repo rate: Maintaining a neutral stance could risk reigniting inflation while lowering rates could hinder growth momentum.
Status of Inflation Over a Period ( 2024)
- Recent Trends
- Decrease in inflation: Inflation has shown a slight moderation since February 2024, dropping from 5.1% to 4.8% in April 2024.
- However, this decrease is narrow, and food inflation remains high due to price pressures on vegetables, pulses, cereals, and spices.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Current Major Risks of Inflation
- Persistent Food Inflation
- Food inflation remains high despite a slight moderation in inflation, driven by rising prices of vegetables, pulses, cereals, and spices.
- Adverse weather events are expected to continue to disrupt food production and put pressure on food prices in the future.
- Other Upward Pressures
-
- Volatility in crude oil prices and financial markets could lead to higher inflation.
- Rising prices of non-energy commodities also pose an upside risk to inflation.
About Repo rate
Repo rate stands for “Repurchasing option rate.”
- It is the interest rate at which the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lends money to commercial banks and lending institutions.
- Impact of Rate Changes:
- Increased Repo Rate: This makes borrowing costlier for banks, who pass on the higher costs to customers, making loans more expensive.
- Decreased Repo Rate: Lowers borrowing costs for banks, increases the availability of funds, and boosts consumer demand.
- Role of the Repo Rate
- Monetary Tool: Used to control inflation or stimulate demand.
- Influence: It affects interest rates on all types of loans, including personal, car, housing, and working capital loans.
- How the Repo Rate Works
- Mechanism: Commercial banks borrow money from the RBI by selling their securities and agreeing to repurchase them at a later date at the repo rate.
- Economic Impact: Influences overall interest rates in the economy, affecting borrowing costs, inflation, and economic growth.
- Policy Regulation: Adjustments to the repo rate help regulate Monetary Policy.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)
This committee decides the interest rate.
- Composition: There are six members on this committee.
- Three members are appointed by the government and three by the RBI.
- Meetings: Discuss the country’s macroeconomic situation and determine the repo rate.
- Considerations of factors: To set interest rates, factors like inflation, economic growth, exchange rates, and fiscal deficit are evaluated.
- Objective: This committee aims to maintain price stability while supporting economic growth.
|
![]() 8 Jun 2024
8 Jun 2024

 Potential future disruptions from adverse weather events add uncertainty to the food inflation trajectory.
Potential future disruptions from adverse weather events add uncertainty to the food inflation trajectory.