Context:
The Finance Ministry has called for actions to support Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows, which decreased last year and may continue to be low in the near future.
| Probable Question:
Q. What are the challenges and benefits associated with Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India, and what government initiatives have been implemented to promote FDI in the country? |
About Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- FDI is when a company or individual invests in business ventures located in another country.
- FDI involves purchasing a direct ownership stake in a foreign business, and it can be done through methods like establishing a subsidiary, acquiring an existing foreign company, or forming a joint venture partnership.
- It differs from Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) where investors only buy stocks and bonds without gaining control over the business.
Routes of FDI:
- Automatic Route: Under this route, foreign entities can invest in non-critical sectors without prior approval from the government or the RBI.
- In India, FDI up to 100% is allowed in non-critical sectors through the automatic route.
- Investments from Pakistan and Bangladesh, and sensitive sectors such as defence, media, telecommunication, satellites, private security agencies, civil aviation, and mining require government approval or security clearance from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Government Route: Foreign entities must obtain approval from the government for investments under this route.
- The Foreign Investment Facilitation Portal (FIFP) acts as a single window clearance system for applications that require government approval.
- It is managed by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Government measures to boost Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- Relaxing FDI norms: The government has eased FDI regulations across various sectors such as defence, PSU oil refineries, telecom, power exchanges, and stock exchanges, among others. This allows for greater participation of foreign investors in these sectors.
- ‘Make in India’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ campaigns: These initiatives, along with efforts to integrate India into global supply chains, have helped attract FDI inflows by promoting domestic manufacturing and self-reliance.
- Launch of investment-attracting schemes: The government has introduced schemes like the National Technical Textile Mission, Production Linked Incentive Scheme, and Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana, which aim to attract investments in specific sectors and provide incentives to investors.
- Revised FDI rules for e-commerce: The FDI rules have been revised to allow 100% FDI in the marketplace-based model of e-commerce, attracting more foreign investments.
- Simplified approval process for Real Estate Broking Services: Government approval for FDI up to 100% in Real Estate Broking Services has been eliminated, streamlining the investment process.
Advantages of FDI:
- Economic Growth: FDI leads to job creation and overall improvement in the functioning of the economy, particularly in developing nations.
- Development of Human Capital: FDI encourages investment in developing the necessary skills and knowledge among the workforce.
- Technological advancements: Foreign companies bring in improved technology and operational practices, benefiting the local economy.
- Increase in Exports: FDI often results in the production of goods specifically for global markets, leading to higher exports.
- Exchange Rate Stability: Regular foreign capital inflows through FDI help stabilize the exchange rates and build foreign exchange reserves.
- Competitive Market: FDI facilitates the entry of foreign entities, fostering a healthy competitive environment.
FDI Inflows in India:
- Gross FDI flows decreased by 16% (USD 71 billion in FY23) last year from the record high of $84.8 billion in 2021-22.
- Net inflows fell by a sharper 27.4%.
- Similar decline in net FDI inflows observed in emerging market economies (36% in 2022).
- According to the World Investment Report 2022, India has ranked 7th among the top 20 host economies for 2021.
- Country-wise FDI Equity Inflow FY-2021-22:
- Singapore (27.01%), USA (17.94%), Mauritius (15.98%), Netherland (7.86%) and Switzerland (7.31%) emerge as top 5 countries for FDI equity inflows
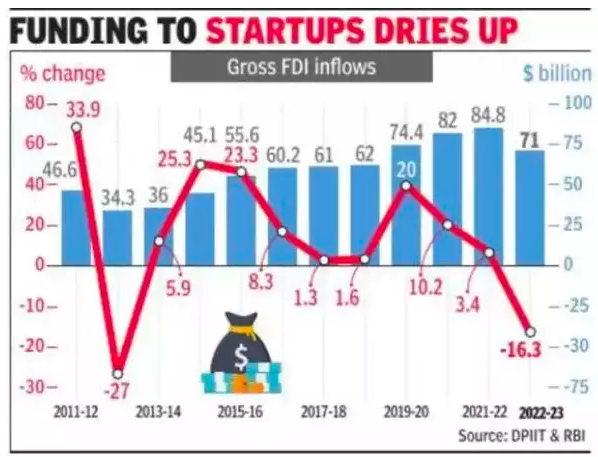
Image Source: The Times of India
Reasons for Dip in FDI inflow:
- Inflationary pressures and tighter monetary policies have contributed to the dip in FDI inflows.
- Political distance has become more influential than geographical distance, impacting FDI flows.
- External factors like
- Geopolitical stress,
- Volatility in global financial systems,
- Sharp price correction in global stock market corrections,
- A high magnitude of El-Nino impact, and
- Frail global demand poses challenges to India’s growth outlook.
- Fragmentation of FDI flows due to “friend shoring” and investments in geopolitically aligned countries.
- “Friend shoring” means that countries are investing more in other countries that have similar geopolitical interests.
- Competition from Other Emerging Markets: India faces competition from other emerging markets, such as China, Vietnam, and Indonesia, in attracting FDI.
Way Forward:
- FDI Concentration in Few States: FDI in India is concentrated in a few states, primarily Andhra Pradesh, Delhi, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu. These states receive around 60-70% of the total FDI inflows into the country.
- To promote more balanced FDI distribution, it is important to focus on bringing other states into the realm of FDI inflows.
- Improve Infrastructure: Addressing last-mile infrastructure issues is crucial to attract foreign investors. Developing transportation networks, power supply, logistics, and digital infrastructure can enhance the investment climate.
- Enhance Labor Availability: Ensuring a skilled and abundant workforce is essential. Investments in education, vocational training, and skill development programs can enhance the availability of skilled workers and attract more FDI.
- Facilitate Large Capacity Creation: Creating an environment conducive to setting up larger factories and production facilities can attract FDI. Streamlining regulations, providing land availability, and offering incentives for capacity expansion can be effective measures.
- Policy Reforms: Continuously monitoring FDI data and implementing favorable policies is important. Regularly reviewing and modifying regulations to create an investor-friendly environment and reducing bureaucratic hurdles can boost FDI inflows.
- Strengthen Geopolitical Alignment: Strengthening relationships with countries that are geopolitically aligned to India can attract FDI through “friend shoring.”
- Promote Stable and Predictable Economic Environment: Maintaining a stable macroeconomic environment, including inflation control and consistent monetary policies, can instill confidence in foreign investors. This will encourage long-term investments in India.
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 10 Jul 2023
10 Jul 2023
