Context
The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) has passed a resolution to protect the rights of intersex individuals.
- The resolution was spearheaded by Finland, South Africa, Chile, and Australia.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
UN Human Rights Council Adopts Landmark Resolution For Intersex Rights
- The resolution is titled “Combating Discrimination, Violence, and Harmful Practices against Intersex Persons.
- Key Objectives: To combat discrimination, violence, and harmful practices against intersex individuals and to address the underlying causes of such mistreatment.
- Example of Good practices adopted by nations:
- Several nations such as Australia, Malta, and Spain have made legislation to protect the interest of intersex individuals from discrimination.
- Similarly, Kenya and Portugal have taken various measures to protect the rights of intersex children in areas of healthcare, education, and social protection.
- Several nations like Mexico and South Africa have amended and included intersex within anti-discrimination statutes to ensure equality in legal frameworks.

About Intersex Individuals
- Intersex is when someone is born with reproductive or sexual parts that don’t fit typical definitions of male or female.
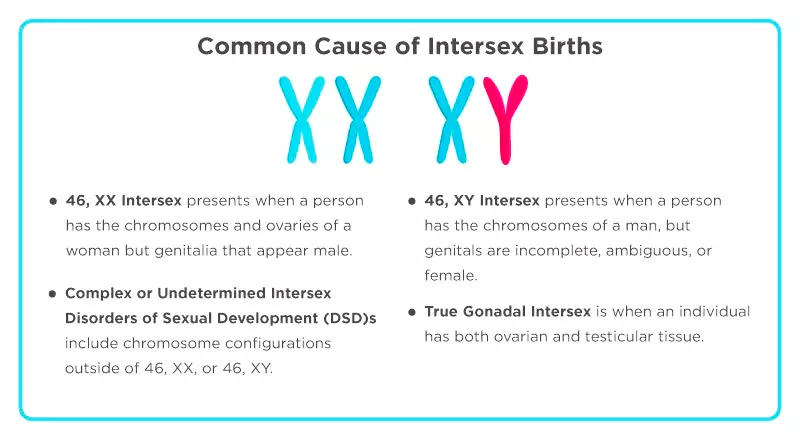
- Intersex can be divided into four categories:
- 46, XX intersex
- 46, XY intersex
- True gonadal intersex
- Complex or undetermined intersex
 Currently, 1.7% of newborns are intersex.
Currently, 1.7% of newborns are intersex.- Example:
- Penis with Female Hormone Levels
- Absence of Penis but Male Traits
- Outwardly Female, Male-Typical Anatomy Inside: Some individuals may have a female appearance externally but predominantly male-typical internal anatomy.
- Blend of Male and Female Genital Characteristics.
- Mosaic Genetics: In some cases, individuals may have mosaic genetics, where certain cells contain XX chromosomes (typically female) while others contain XY chromosomes (typically male).
Intersex Rights Movement in India
- It started in 2021
- Objective: legal protection mechanism for intersex children against unnecessary ‘normalising’ surgeries.
- DCPCR Recommendation: DCPCR first recommended to ban medically unnecessary surgeries on intersex infants in Delhi.
- Tamil Nadu: In 2019, It became the first state to mandate legal protection for intersex children.
- Delhi Medical Council also supported the DCPCR Recommendation of banning surgeries.
- Way forward: There is a need to act on DCPCR’s recommendation by the Delhi government.
Intersex Asia:
- It is the pan-Asian intersex human rights organization.
- It aims to protect the rights of intersex people in Asia.
|
Causes of Intersex Traits
- Intersex traits are estimated to occur in 1% to 2% of the population, making it more common than having red hair or being an identical twin.
- Underlying Factors:
- Genetic conditions that disrupt hormone levels during fetal development.
- Exposure to hormones from medications or other sources during early stages of development.
- Random variations in chromosomes occurring at conception.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Challenges faced by Intersex People
-
Prejudice and Discrimination:
- These people face discrimination in the society due to non-alignment of their body with societal norms of sex and gender.
- Violence, and even infanticide: In various nations, people having visible intersex traits, such as ambiguous genitalia, face abandonment and violence.
- Intersex infanticide is prevalent in the southern and eastern Africa, South Asia, Brazil, and China.
-
Unnecessary medical intervention:
- These people have to go through medical treatment due to People’ belief that intersex people need to be “fixed.”
- In this process, many young children get traumatized due to the experiences in medical procedures.
-
Legal Identity:
- These people face problems in getting identity as society segregates intersex babies and people based on gender.
- Many a time, organizations prohibit them to issue identification which prevent them from doing jobs, opening bank accounts and getting higher education.
Impact of Resolution on the life of Intersex Persons
- Increased awareness and recognition: The resolution brings greater visibility to the issue of intersex people and their human rights. This can help to combat stigma and discrimination.
- Protection from harmful practices: The resolution calls on states to address violence and harmful practices against intersex people, such as medically unnecessary surgeries on infants.
- This can help to protect intersex people from physical and psychological harm.
- Improved access to healthcare: The resolution emphasizes the right of intersex people to the highest attainable standard of health.
- This could lead to better access to healthcare services that are sensitive to the needs of intersex people.
- Empowerment and self-determination: The resolution calls on states to respect the autonomy and bodily integrity of intersex people.
- This can empower intersex people to make their own decisions about their bodies and their lives.
- Foundation for further progress: This resolution is a significant step forward, but it’s just the beginning.
- It can pave the way for further legal and policy changes that protect the rights of intersex people around the world.
Also Read: Supreme Court Verdict On Same Sex Marriage In India
![]() 8 Apr 2024
8 Apr 2024

 Currently, 1.7% of newborns are intersex.
Currently, 1.7% of newborns are intersex.